Endocrine Part 1
Pars Distalis(Anterior of pituitary gland)
A tissue made of irregular parenchymal cells near fenestrated capillaries.
Staining identifies chromophils, which are divided into acidophils and basophils, responsible for synthesizing, storing, and releasing hormones. Their activity is regulated by stimulatory and inhibitory hormones from neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus. Cells that do not stain are termed chromophobes.
Image summary
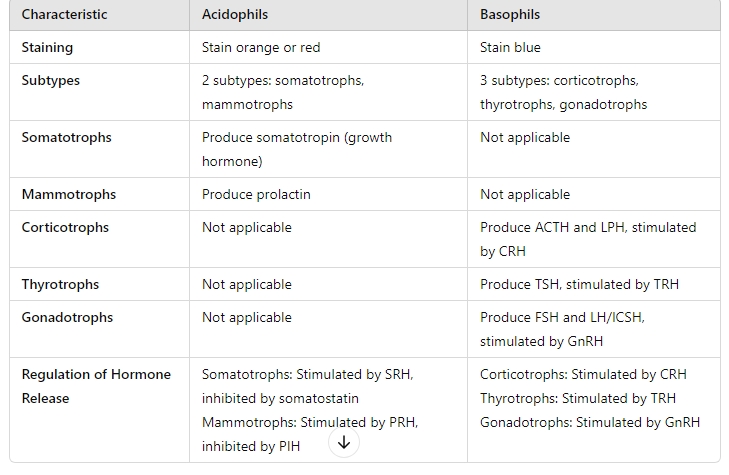
Acidophils vs Basophils
Somatotrophs: Produce growth hormone (somatotropin), stimulated by somatotropin-releasing hormone (SRH) and inhibited by somatostatin.
Mammotrophs: Produce prolactin, stored in secretory granules, stimulated by prolactin-releasing hormone (PRH) and inhibited by prolactin-inhibiting hormone (PIH).
Corticotrophs:
Produce: Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and lipotropic hormone (LPH).
Stimulated by: Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH).
Thyrotrophs:
Produce: Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
Stimulated by: Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH).
Gonadotrophs:
Produce: Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH, also known as interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) in men).
Stimulated by: Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
Folliculostellate cells
Located in the pars distalis of the pituitary gland. These cells, positioned between chromophils and chromophobes, have long processes that create gap junctions with other folliculostellate cells.
They produce various peptides believed to regulate hormone production in the pars distalis through a paracrine mechanism.
Pars Intermedia
Location: Between pars distalis and pars nervosa(posterior pituitary).
Characteristics: Contains colloid-filled cysts (Rathke cysts) lined by cuboidal cells.
Cell Types: Contains Basophilic cells that secrete proopiomelanocortin (POMC).
Hormone Production: POMC is cleaved to produce melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH).
Functions of MSH:
Modulates inflammatory responses.
May influence body fat storage.
Pars Tuberalis
A structure surrounding the cranial part of the infundibulum (hypophyseal stalk).
It consists of cuboidal basophilic cells organized in cords within a rich capillary network.
While these cells may secrete FSH and LH, this has not been definitively confirmed.