Vid Lecture 2
Social Theory
““- Ideas about how humans live and interact
highlights different aspects
use different theories and develop new ideas
Classical Theorists
Marx
not communism lol

conflict theorist
the heart of society is conflict
saw history as the history of class struggles between the oppressed and the oppressors
transition into capitalism was inevitable
ultimately, tension and conflict, which lead to revolution
focus on economic relations and materialistic concepts within society/history
it all boils down to economic relations
economics was the key

diferent from anarchism
big difference is that Marxism is rooted in economics and Anercism is rooted in government (government is the central crux)
Two Classes
The Bourgeoisie- the capitalist class who own the means of production
the oppressors, and have an interest in maintaining control
land, factory, tools, capital
increase in economic power = increase of political power
The Proletariat- the working class who sell their labor for wages
the oppressed, with the lack of consciousness of themselves as a class to revolt
concerned with working conditions
exploitation
child labor
long work hours
low wages
age and sex determine the expense of labor
The middle class cannot compete and isn’t sustainable.
oppression of workers built into capitalism
wealth generates more wealth
middle class supports Bourgeoisie in order to keep wealth
Margin of Exploitation
Labor is always worth less than what they pay.
source of profit
substance, ability to produce another generation
reproduction of oppression and inequality
Margin of Exploitation- the difference in what labor is worth and what is actually paid
workers became the “appendage of the machine
”
workers alienated from…
products from their work
other workers
human potential
self
False consciousness- we do not recognize ourselves as a class
believed workers had to unify and break through false consciousness in order to overthrow power
why he wrote the communist manifesto
Social Change
Marx anticipated the fall of capitalism at the hand of the proletariat coming together in a revolution (think France)
Only the proletariat can be revolutionary
secret “dangerous class” that was brought in to take the place of the strikers
you’re not working? we got people to take your place
requires class consciousness

Max Weber
Rationalization/Disenchantment
Moving away from traditions passed down to calculated rationality

Why did capitalism develop in Western societies? It’s because of an attitude or moral outlook. Our beliefs change our economy.
flips Marxism
Protestant Ethic
Calvinist Predestination- it is predetermined whether you are going to heaven or hell
the LIST
sign of one’s salvation might be found in one’s conduct
if you’re a religious person, you are bound to be the type to go to heaven
The world is filled with temptation
Asceticism- if fun = not good
Temptation and Profit
Suppose you were to do everything a good Christian and religious person is to do. In that case, you are to have more excess to fun things in life as a reward i.e. money
accumulation of wealth is not based on greed, but seen as morally riotous
you can’t keep your money, how can you spend your money? TEMPTATION is everywhere so you spend it on your business and hire a worker. You can’t pay your workers much money because that leads to temptation, so you accumulate more and more money, and you invest it more and more into your business.
Disenchantment
Weber believes this type of thinking kicked off capitalism. Even if you weren’t a Calvinist, you are likely to partake in similar acts because you have to compete with other businesses. It might be popular, but it was built into the country.
disenchanted
accumulation isn now for accumulation's sake
transition from value to rational
Weber and Class
Class- one’s relationship to production
Status- lifestyle, relationship to consumption
Party- voluntary organizations that people enter together to make voices heard collectively
like political parties
The Bureaucracy
Ideal Type- abstract statement of essential characteristics f any social phenomenon
not good or best
Bureaucracy is another more towards efficiency and “rationality”
ahead of his time for thinking of it
Alienation and Rationalization
Alienation is the result of increased rationalization.
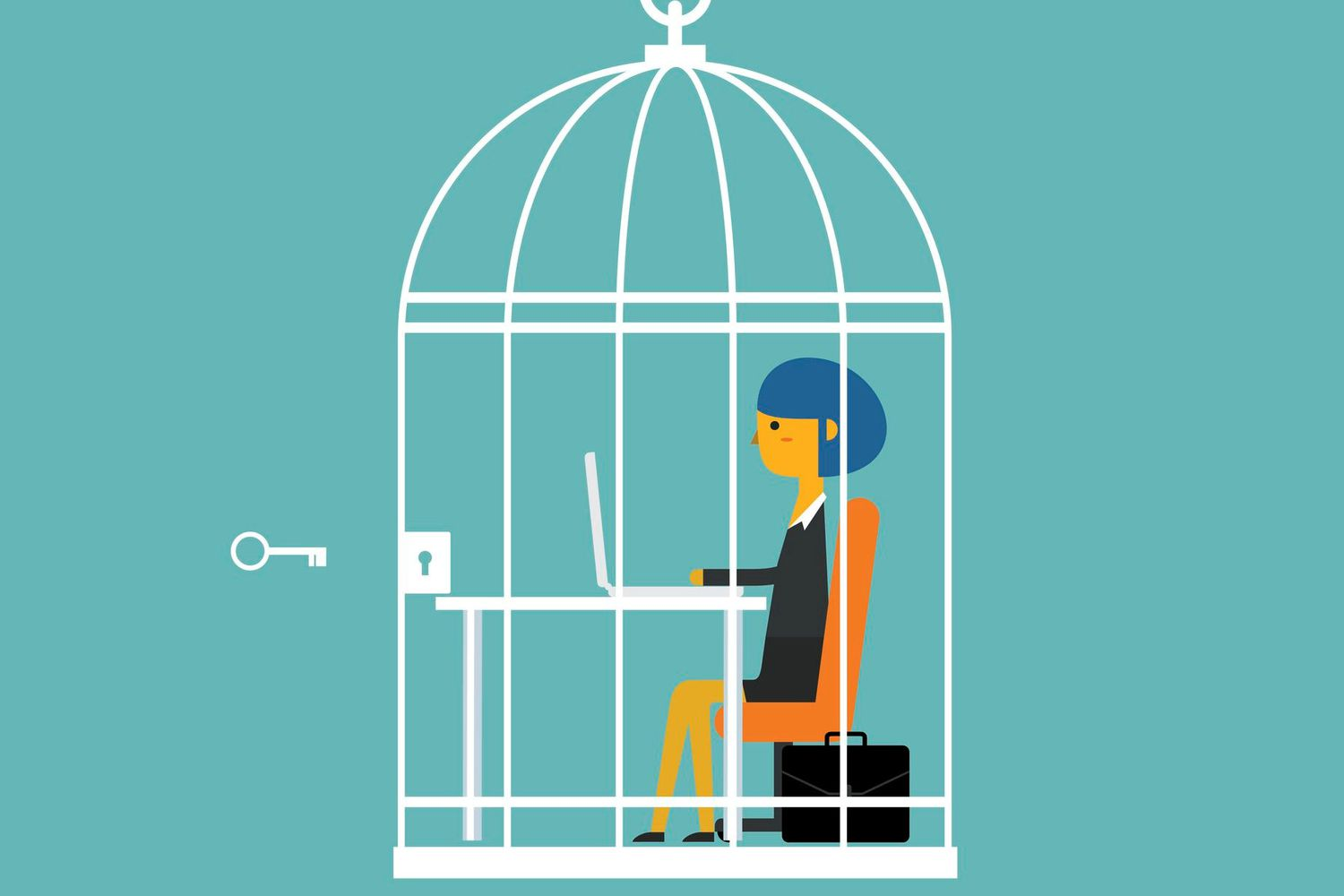
Iron Cage- the concept of how individuals become trapped in systems of rationality, leading to a loss of autonomy and individuality.
an utterly dehumanized and mechanized world
limit our freedom and autonomy
we are locking ourselves away from humanity

Emile Durkheim

He believed sociology could be studied with the same objectivity as other sciences.
Social Facts- established patterns of human behavior
Social Cohesion
Integration- how connected we feel to social life
Regulation- the amount our individual freedoms are constrained
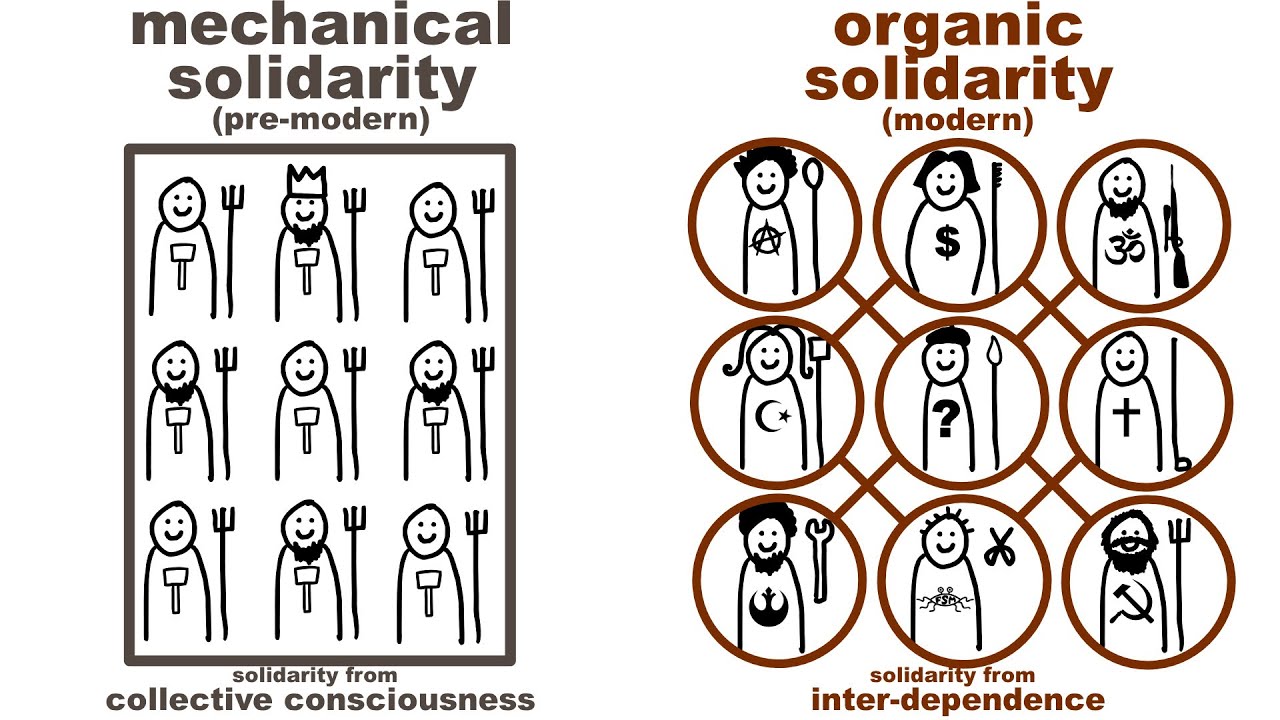
Integration and regulation hold society together. Previously, he believed there was a shift from mechanical to organic solidarity.
Mechanical Solidarity- little differentiation between people
individuality nonexistent
shared beliefs and norms
Organic Solidarity- increased differentiation of tasks, responsibilities with industrialization, and interdependence
individualistic society of different people and background
interdependence is what’s holding us together
Collective Consciousness- developed agreements about what behavior is expected
Durkheim and Crime
Deviance exists in all societies because all societies have to have behaviors that are allowed and behaviors not allowed
serves a function