nervous system <3
Neurons
structural and functional part → transmits via bioelectrical changes called nerve impulses
nerve impusles = action potiental
sent along nerve fibers (dendrites and axons)
*mature nuerons do not divide
made of: soma, cytoplasm, cell membrane, cellular organelles, chromatophilic substance such as nissl bodies, large nucleus + nucleolus
Two Types of Nerve Fibers (Dendrites vs Axons)
Dendrites: Receive incoming signals from other neurons and transmit them toward the soma.
Axons: Conduct electrical impulses away from the soma to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
Types of Nerve Cells
1.) schwann cells (glial)
Schwann Cells: Specialized glial cells that form the myelin sheath around axons in the peripheral nervous system, enhancing signal transmission efficiency.
2.) bipolar, unipolar, multipolar
bipolar = sensory, ex: retina and olfactory bulb
unipolar= sensory, ex: skin receptors, joints, ,muscles, internal organs
multipolar= motor , exL brain or spinal cord
sensory = afferent
interneuron= association
motor= efferent
3.) neuroglial cell types
1- oligiodendrocytes → hangs and makes mylen
2- astrocytes → supports and regulate nutrients, constricts and dilates blood vessels (astro, think of astro world and peoples lifes being constricted and not supported)
Defects
ischemia= oxygen deficiency from lack of blood flow
hypoxemia= abnormally low blood oxygen levells
prosopagnosia- facial blindness
multiple sclerosis- autoimmune dirsorder in cns and pns
alzheimer disease
huntington disease
Nerve Impulse
nerve impulse has electrical depolarization

na+ into , K out
Brain structures

cerebrospinal fluid- clear watery
3 Main Parts of the Brain!!! →
Cerebrum (higher function)
1.) corpus callosum- connection between halves
2.) convolutions aka the gyri (ridges)
3.) sulci - grooves that divide into 4 lobes (frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal)
4.) fissure- deep groove
5.) cerebral cortex- outer layer
What does the cerebrum do?
higher brain functions, interprets sensory, initiates voluntary movement, stores info (memory), reasoning, intelligience and personaility
Diencephalon
Thalamus- central relay station of sensory info
Hypothalamus- maintains homeostasis functions ex blood pressure
Cerebellum (coordination)
(2 lateral hemispheres connected by vermis)
grey matter on surf, reflex center, coordinates cimplex skeletal muscle and posture_
Brain Stem (connection of nerves to cerebrum)
midbrain- visual and auditory reflex
pons- relays sensory info from peripheral nerves to higher brain
medulla- controls vitals
reticular activiating system- resposinvle for awakebing the cortex, samage will become comotose
longitudinal sulcus- divides into left and right halves
optic chiasm- optic nerves cross
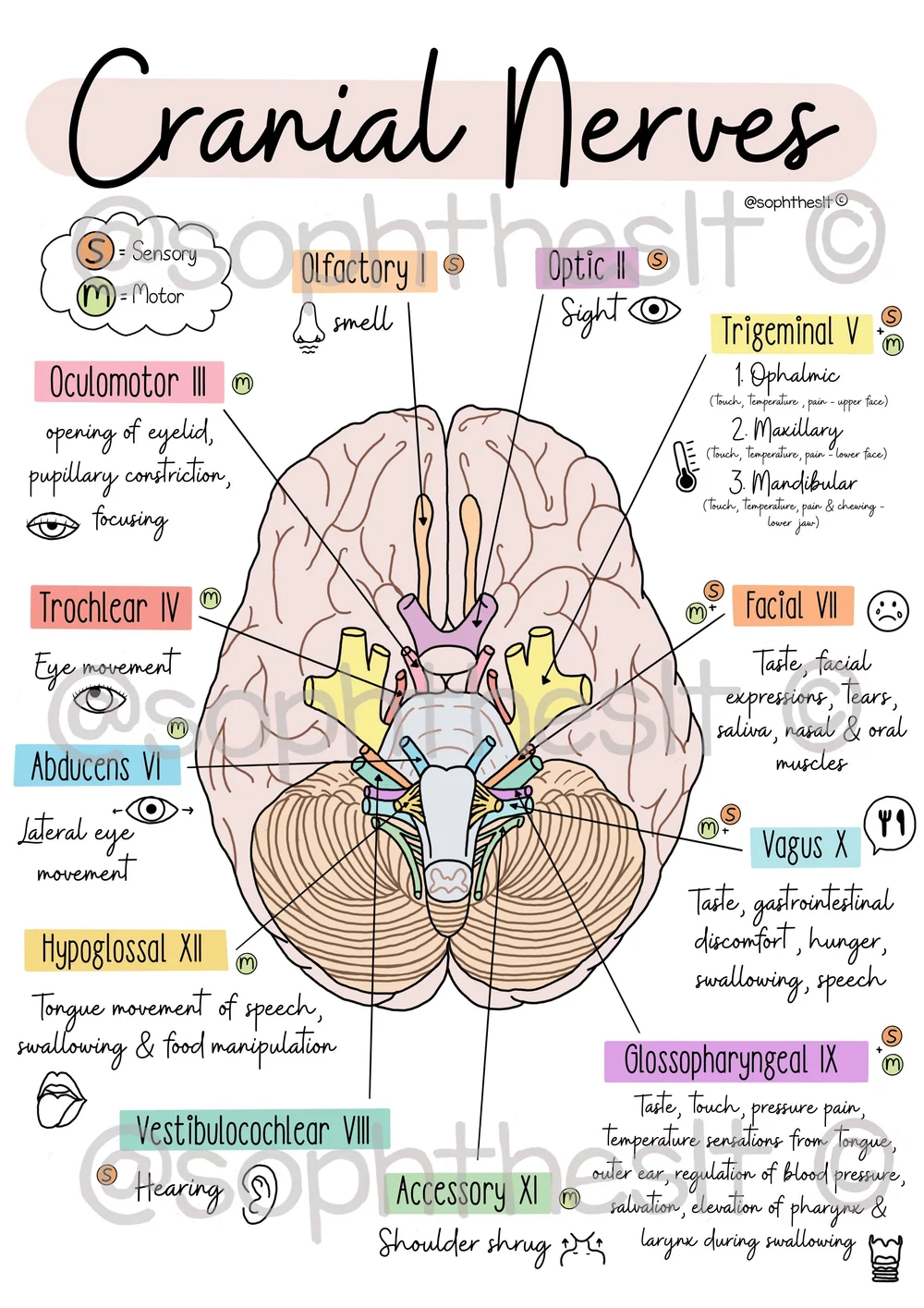
Cranial Nerves (PNS)
numbers describe order, name describes primary function
1- olfactory (sensory)- smell
2.) optic (sensory) - vision
3- oculomotor (motor) - eyelid movement
4- trochlear (motor) move eyes
5- trigeminal (mixed) - fACE sensort and movement
6- abducens (motor) - move eyes
7- facial (mixed)
8- vestibulochlear (sensory) - equilibrium, hearing,
9- glossopharyngeal (mixed)- sensory and motor for mouth
10- vagus (mixed) -speech swallow
11- accessory (motor)
12- hypoglassal (motor) tounge

\
reflex arcs
https://knowt.com/note/69bd13ea-77ea-4c65-b24f-d1f14d8310ce/nervous-system
1.) patellar tendon reflex
2.) bicep jerk
3.) tricep jerk
4.) achilles heel
5.) plantar reflex
receptor → cns → effecor (only uses two neurons)
(track to brain = ascending tract, tact to muscle = descending tracts)
