accounting
Ch. 2
Classified balance sheet- groups together similar assets and similar liabilities, using standard classifications and sections
Classifications of Classified Balance Sheet
Assests
Current Assets
company-owned assets that can be converted to cash within one year or the operating cycle, whichever is longer.
basically, using cash to gain more cash
Operating cycle is the average time it takes to go from cash to cash. This is the time to purchase inventory, sell it on account and then collect cash from customers.
For most businesses, the cycle is less than a year so a one-year cutoff is used.
Current assets are listed in the order in which convert to cash.
Long term investments
Investments in stocks and bonds of other companies that are held for more than one year.
Long-term notes receivable
Investments in long-term assets such as land not currently being used in operating activities.
debt investment- Debt investment is when you lend money to someone, like a company or a government, and in return, they promise to pay you back with interest.
It’s like giving a loan and earning money from the interest they pay you.
Common types of debt investments include bonds and loans
stock investment- Stock investment is when you buy a small piece of ownership in a company, called a "share" or "stock." By owning stock, you become a part-owner of the company
Property, plant and equipment (PPE)
Assets with long useful lives that are currently used in operating the business
Examples: Land, buildings, equipment, vehicles, and furniture
A process known as depreciation is used to allocate the cost of these assets to a number of years
depreciation- a way of spreading out the cost of a big purchase over time.
When a business buys something like equipment, machinery, or a vehicle, that item loses value as it gets older and wears out. Instead of taking the whole cost as an expense right away, businesses use depreciation to gradually reduce the value of the item on their books each year
The accumulated depreciation account shows the total of depreciation that a company has taken so far on its assets
Intangible assets
Assets that do not have a physical substance yet are often valuable
assets that give you rights
Examples: goodwill, copyrights, patents, franchises, trademarks
List 5 common current assets in order of liquidity
Cash
Investment (short term)
Receivables- notes receivable, accounts receivable
Inventories
Prepaid Expenses- prepaid insurance, prepaid rent, supplies
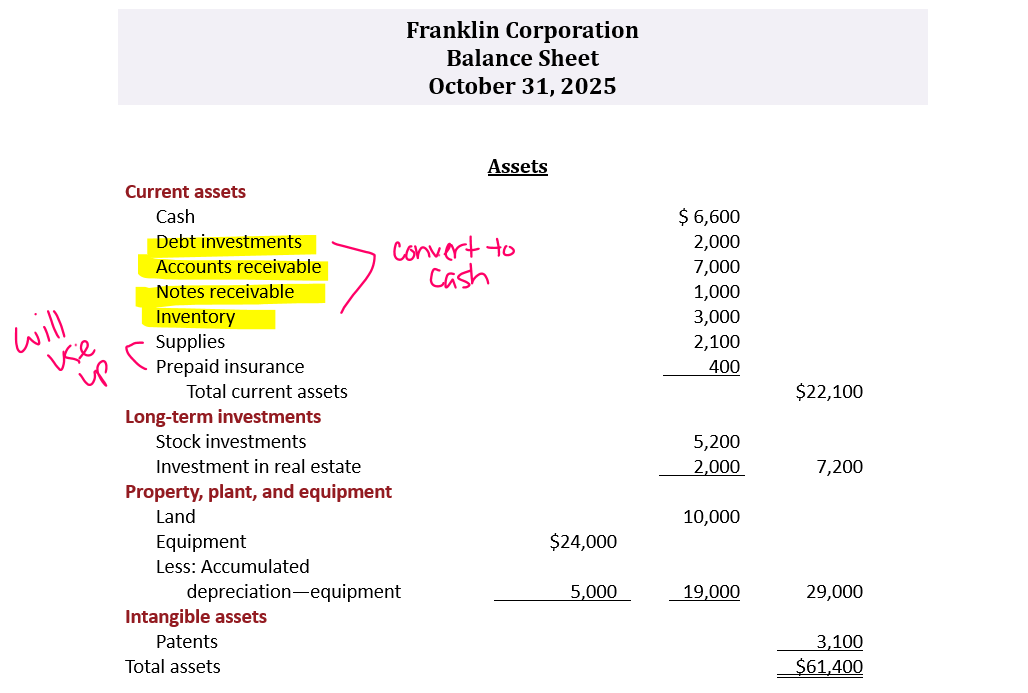
Liabilities & Stockholders’ Equity
Current liabilities
Current liabilities are obligations that the company is to pay within the coming year or operating cycle, whichever is longer. For most companies, this is one year.
Usual order is notes payable, accounts payable, and then others in order of magnitude
Examples: accounts payable, short-term notes payable, salaries payable, interest payable, income taxes payable, unearned revenue
unearned revenue- Unearned revenue in business is money a company receives before it has provided the product or service. It's like getting paid in advance.
ex. giftcards
be careful with notes payable. they can be short term or long-term liability.
Usual order is notes payable, accounts payable, and then others in order of magnitude
Long term liabilities
Obligations that a company expects to pay after one year
Examples: long term notes payable, bonds payable, mortgages payable, lease liabilities, pension liabilities
Stockholders’ equity
Stockholders’ Equity consist of two parts:
1.Common stock- investments of assets into the business by stockholders
2. Retained Earnings- income retained for use in the business
Ratio Analysis
Ratio- expresses the mathematical relationship between one quantity and another
Types of Ratios
Profitability- Measure the income or operating success of a company for a given period of time
EPS (earns per share)- measures the income earned on each share of common stock
Eps= (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) / Weighted Average Common Shares Outstanding
increase in EPS is favorable
Liquidity- a measure that helps determine how easily a company can pay off its short-term debts using its available assets.
working capital ratio- a measure used in business to see if a company has enough short-term assets (like cash, inventory, and receivables) to cover its short-term liabilities (like bills and loans due soon).
Working Capital Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
Solvency- Measure the ability of the company to survive over a long period of time
debt to assets- it tells you what portion of the company’s assets are paid for with borrowed money.
Debt to Assets Ratio= Total Assets / Total Debt
Current ratio= current assets/ current liabilities
Government organizations?
(GAAP) Generally Accepted Accounting Principles - A set of rules and practices, having substantial authoritative support that the accounting profession recognizes as a general guide for financial reporting purposes.
(SEC) Securities and Exchange Commission- is an agency of the federal government that oversees the US financial markets and accounting standard setting bodies
(FASB) Financial Accounting Standards Board- is the primary accounting standard setting body in the US. A private organization.
Verifiability- Information that can be proved that it is free from error
Timeliness- Information that is available to decision makers before it loses capacity to influence decision makers
Comparability- Results when different companies use the same accounting principles
Consistency- Results when a company uses the same principles and methods from year to year
Understandability- Information has this quality if it is presented in a clear and concise fashion
(PCAOB) Public Company Accounting Oversight Board- determines the US auditing standards and reviews the performance of auditing firms.
(IASB) International Accounting Standards Board- issues standards called IFRS which have been adopted by countries overseas, mostly Europe.
Vocab
cost principle- an accounting rule that says assets should be recorded on the balance sheet at their original cost, not their current market value.
fair value principle- a way of estimating the value of an asset or liability based on what it would sell for in the market today
cost constraint- a company has a certain budget or limit on how much it can afford to spend on things like production, marketing, salaries, or other expenses
Full disclosure principle-
Periodicity assumption-
Going concern assumption-
Historical cost principle-
Monetary unit assumption
Economic entity assumption
Ch. 3
The accounting information system is a system of collecting processing transaction, data, and communicating financial information to decision makers
An accounting information system relies on a process called the accounting

The Account & Debits and Credits
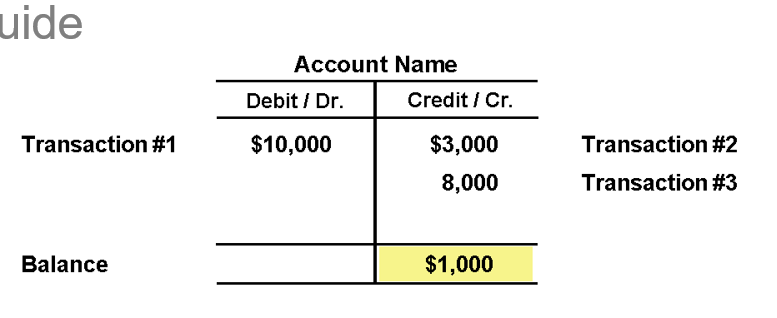
An account is a record of debits and credits in a specific asset, liability, equity, revenue, or expense item
An account has three parts:
1. the title of the account
2. a left side called the debits side
3. a right side called the credits side
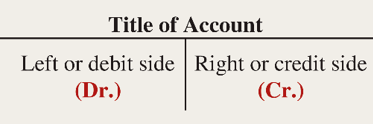
Debt balance
If debits are more than credits the account will have a debit balance such as in this example
Credit Balance
if credit is more than debits the account will have a credit balance such as in this example
credit- that the business owes money
after eating let’s read comics
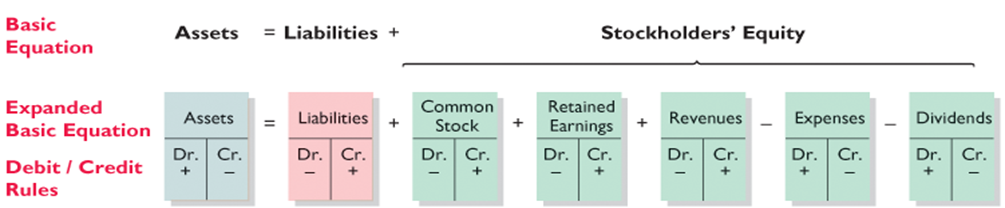
types of accounts that increase with a debit
assets
expenses
dividends
types of accounts that increase with credit
liabilities
revenues
retained earnings
common stock
After Eating Dinner Lets Read Comics (after eating dinner lets read comics)
Questions to ask:
What accounts are affected?
Is it increasing or decreasing?
Apply the AED=DEC rule
Journal Entries
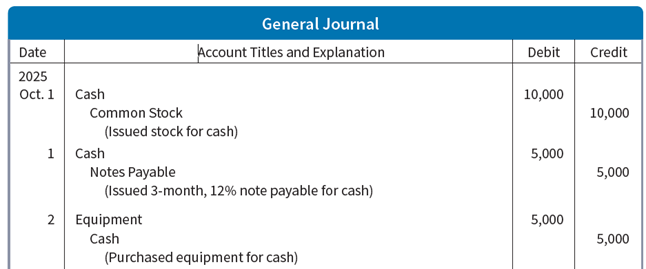
The ledger provides the balances of the accounts as weel keeps track of changes in these balances.
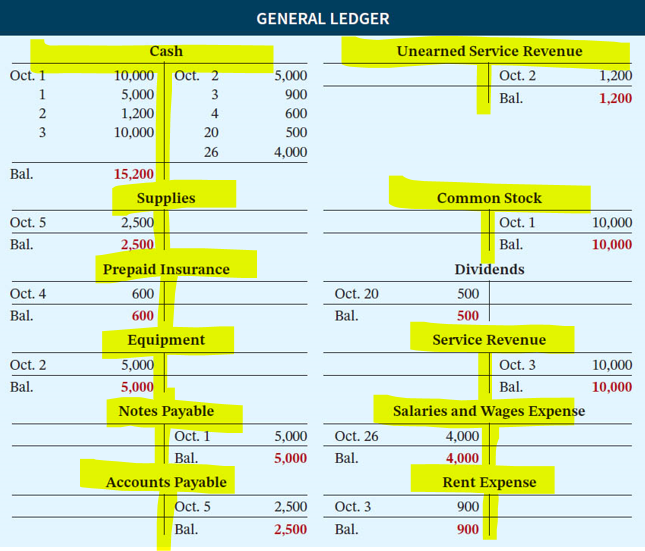
Prder of trail balance:
assets
liab
equity
revue
expenes
Ch. 4
Timing Issues
The periodicity assumption requires accountants to divide the economic life of business into artificial time periods.
Accounting time periods are usually a month, quarter or a year.
The Revenue Recognition Principle is an accounting rule that says businesses should only record revenue (money earned) when it is actually earned, not when they receive the cash.
If a company sells a product or service, they can count it as revenue only when they deliver the product or finish the service.
This principle ensures that financial reports show a more accurate picture of a company’s actual earnings during a specific time period.
Ex. October 15- Starr Company provided $500 services on account to a client.
assets- 500 debits
service revenue 500
The Expense Recognition Principle is an accounting rule that expenses should be recognized in the same period as the revenue they help to generate.
In other words, expenses are matched with related revenue. If an expense contributed to generating revenue in a particular period, it should be recorded in that period, even if the payment for the expense occurs earlier or later.
For example, if a company incus expenses in December to deliver services for which it will receive payment in january, the expenses should be recorded in December when the related revenue was earned.
Accrual vs. Cash Basis of Accounting
Accrual and Cash Basis are two common methods of accounting used to record income and expenses.
Accrual
Transaction recorded in the periods in which the events occur. (recording transactions)
To follow GAAP, companies have to do Accrual basis accounting
Revenues are recognized when the performance obligation is satisfied, even if cash was not received
accrued revenues- revenues for services performed but yet received in cash or recorded
Expenses are recognized when incurred even if cash was not paid
accrued expenses- expenses incurred but not yet paid in cash or recorded
Cash
revenues are recognized only when cash is received
expenses are recognized only when cash is paid
not allowed under generally accepted accounting principles
Adjusting Entries
Adjusting entries include one income statement account and one balance sheet
never cash?
Types of Adjusting entries

Deferrals- means to postpone or delay. Deferrals are revenues or expenses that are recognized at a date ___later______ than the point when cash was originally exchanged.
Accruals- Revenues for services performed but not yet recorded at the statement date
interest rate formula:
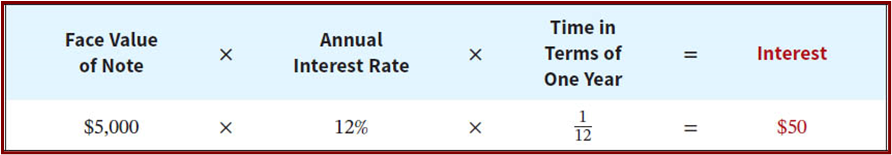
—— expense ——— payble
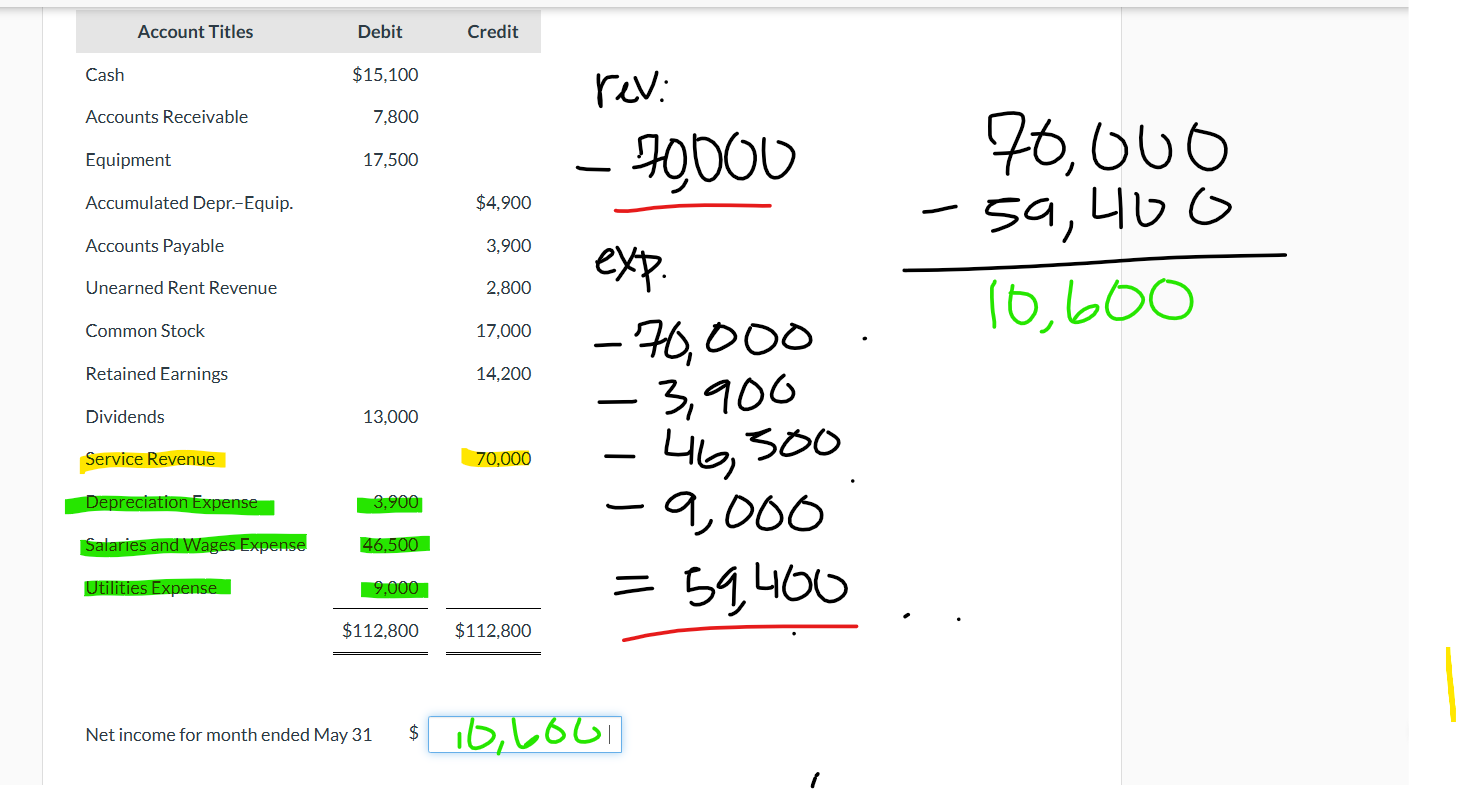
income summary
 Knowt
Knowt