L3: Troubleshooting Common Hardware Problems - CompTIA A+ 220-1101 - 5.2
Power-On Self-Test (POST)
Definition: POST is a diagnostic testing sequence that occurs immediately on power-up to check key components of the PC.
Components Checked:
CPU status
Video functionality
Keyboard operation
Memory (RAM) installation
Error Indication:
If issues are detected, the system emits beep codes or displays error messages.
Different beep patterns correspond to different errors, highlighting hardware issues.
Important to refer to the motherboard's documentation for beep code meanings.
BIOS and System Errors
BIOS Role: The Basic Input/Output System is responsible for tracking system date and time.
Battery Dependency: A battery on the motherboard keeps time; failure results in recurring manual resets.
Boot Order Issues:
Incorrect boot drive may lead to startup failures.
Check BIOS boot order settings to prioritize correct drives.
USB drives may sometimes attempt to boot first; unplugging can resolve the issue.
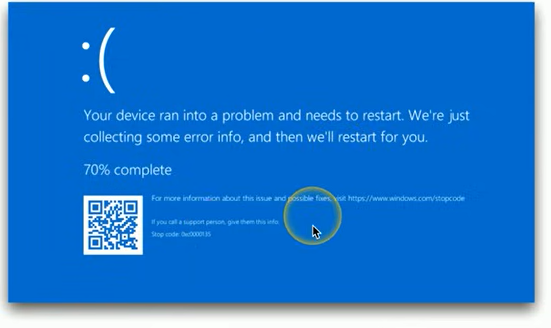
Windows Stop Error (Blue Screen of Death):
Indicates a critical failure; requires system restart to recover.
Can view details in Windows Event Viewer post-restart for troubleshooting insights.
Visit the Microsoft website for stop code references and further support.
Typical causes include faulty hardware, incompatible drivers, or system application errors.
Recovery methods: Last Known Good Configuration, Safe Mode boot, system restore.
System Performance Issues
Slow Performance: Possible causes include:
Background processes like Windows Update.
Low disk space affecting system operations.
Laptop power settings may throttle CPU to save battery.
Monitoring Tools: Use Task Manager to view CPU usage; identify resource-heavy applications or processes.
Heat Management: High temperatures can cause throttling; ensure proper fan and ventilation function.
Dust Accumulation: Clean PC components to improve airflow and cooling efficiency.
Troubleshooting Tips
Black Screen Issues:
Verify monitor power connections and input source settings.
Check for any output via alternate inputs like HDMI, DisplayPort, etc.
Replace the monitor temporarily to identify possible hardware failure.
Power Issues:
If the system fails to power on, inspect power cables and connections.
Use multimeter to check power supply functionality.
Validate whether power is reaching motherboard and components through checks.

Unusual Noises:
Grinding noises indicate possible hardware failure; remove or secure components as needed.
Clicking sounds may signal drive or fan issues; inspect for obstructions.
System Freezes
Unresponsive System:
Check for activity lights; ensure the mouse locks or status indicators are operational.
Recent changes (hardware/drivers) may be the cause.
If completely stuck, perform hardware diagnostics.
Repeated Restarts
Troubleshooting Cycles: Track where reboot occurs (BIOS, OS startup).
Configuration Recovery: Use the F8 key for Last Known Good Configuration, especially after driver updates.
Safe Mode: Booting in Safe Mode loads minimal drivers, useful for isolating issues.
Additional Diagnostics
Capsule Failure: Monitor the health of capacitors on the motherboard; bulging or leaking caps require replacement.
Event Viewer and Reliability Monitor: Analyze logs for errors that might indicate hardware or software failures.
BIOS Battery Issues: Discharged batteries may reset time/date; replacement accessible and vital for stable operation.
Resetting BIOS: For a full BIOS reset, short the jumper rather than just removing the battery.
 Knowt
Knowt