Jan 17 (sexual orientation) +
What is Sexual Orientation?
Sexual Orientation In Relation to ones own sex (3 types)
Must know their sex as well as who they are attracted to
Heterosexual
attraction to people whose sex is opposite to oneself
Homosexual
attraction to people whose sex is the same as oneself
Bisexual
attraction to both sexes
Heterosexual
heterosexual males
heterosexual females
Homosexual
homosexual males
homosexual females
Whatever is producing heterosexuality is the same in males and females, same for homosexuality (vice versa). However, homosexual and heterosexual systems wholly differ from each other.
the systems or dynamics that define and differentiate heterosexual and homosexual orientations are distinct.
Terms for Sexual Orientation independent of one’s own sex (3 types)
Gynephilic
sexual attraction adult females
Androphilic
sexual attraction to adult males
Ambiphilic
sexual attraction to adults of both sexes (bisexual)
For these terms of sexual orientation, ones own sex doesn’t matter. The focus is the sex of the target (who they are attracted to)
Gynephilia and Androphilia Groupings: What groupings of Homosexual or Heterosexual males or females have more in common?
Similarity implies same/similar development processes
Gynephilia = similar that both are attracted to adult females
Gynephilic male (heterosexual males)
Gynephilic female (homosexual females)
Androphilia = similar that both are attracted to adult males
Androphilic male (homosexual males)
Androphilic female (heterosexual females)
What is a very general definition of what is sexual orientation
Relative sexual attraction to adult males, to adult females, or to both when given a choice. (what you are attracted to)
This suggests that sexual orientation is about the preference or attraction one has towards adult males, females, or both when there is a choice involved.
Issue of Choice: individuals might adjust their behavior based on the available choices or circumstance
Commonly Employed Indices of Sexual Orientation (IBFA)
Sexual (Orientation) Identity: (I)
Definition: Refers to how individuals identify their own sexual orientation (e.g., heterosexual, homosexual, bisexual).
Notes: Identities can vary between different cultures, highlighting the influence of societal factors
social context has a huge impact, wether any identity develops at all
Sexual Behavior: (B)
Definition: Involves the actions and choices individuals make regarding their sexual interactions.
Notes: Choices are crucial; for instance, men in environments with limited options may engage in same-sex behavior due to a lack of choice, not necessarily a change in inherent orientation.
Sexual Feelings (F)
Definition: Involves attractions and fantasies individuals experience (find peak sexual attraction)
Notes: Easier to collect data as it only requires asking individuals about their feelings. This index is less affected by social context, making it a valuable measure. (seen as the best indice)
subjective measure
Sexual (Physiological) Arousal: (A)
Definition: Measures physical responses, such as genital arousal (vaginal or penile blood flow) and pupil dilation when exposed to neutral or sexual stimuli.
Notes: Provides a more objective measure but is influenced by physiological reactions. It reflects the body's response to stimuli.
Viewing Time Patterns:
Definition: Examines the time individuals spend viewing sexual stimuli compared to neutral stimuli.
Notes: Seen as a more precise indicator than sexual feelings (since its less subjective), preferred in scientific settings. However, it involves a more complex assessment (harder to employ than sexual feelings) This index is more cognitive and behavioural in nature.
Assumptions and Implications for the Indices of Sexual Orientation
The different indices of sexual orientation are not necessarily concordant
may not align or agree with each other
So these indices are different phenomenons
Sexual orientation is a social construct when conceptualized as something that encompasses all four of these indices (IBFA)
Sexual (Orientation) Identity
Sexual Behavior
Sexual Feelings
Sexual (Physiological) Arousal
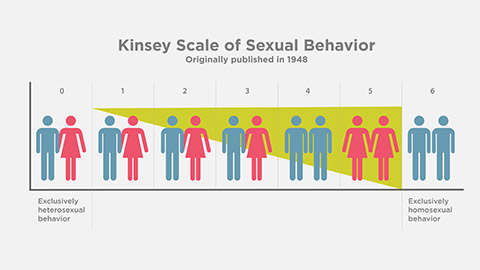
Sexual Feelings as an Index of Sexual Orientation: THE KINSEY SCALE
Definition: A scale developed by Alfred Kinsey to measure sexual orientation on a continuum from 0 to 6.
Ratings:
"0": Exclusively heterosexual behavior or attraction.
"6": Exclusively homosexual behavior or attraction.
"2, 3, 4": Bisexual, with varying degrees of attraction to both sexes (not many 3s)
Ratings 1–5: Indicate varying levels of attraction or sexual activity with either sex.
Self-Report Nature:
Nature: Sexual feelings are subjective and self-reported, assessment relies on individuals' personal introspection and disclosure
Subjective Data:
Sexual feelings, being subjective, involve individuals providing insights into their own attractions.
Some pitfalls involved in assessing sexual feelings
its SELF SUBJECTIVE and as we know our own self reports are not always reliable
People can intentionally misreport their sexual behaviour and feelings (lie)
People can also unintentionally misreport their sexual behaviour and feelings (confabulate)
Confabulation = involves producing an explanation, but not one that that accounts for the real factors underlying one’s behavior or psychology
give motive but it isnt plausible
believe it’s true but it actually isnt
It is a Double edged sword:
compromises understanding of reality (not actually fact)
but also makes us feel better about ourselves (helps with self image)
Sexual Aversion/Disgust
Sexual orientation is usually thought about in terms of attraction
The flip side of attraction is aversion or disgust
Sexual attraction and sexual aversion may operate independently
Attraction = orient you toward one sexual stimuli
Aversion = orient you away from a sexual stimuli, usually done with disgust
Sternberg’s Triangular Theory of Love: What makes up the 3 corners?
Proposes 3 parts of love
Total of 7 types of love when these 3 combined in different ways
Intimacy: Refers to close, connected, and bonded feelings in love relationships. It involves warmth and includes aspects like mutual understanding, emotional support, and valuing the loved one.
Passion: Relates to drives that lead to romance, physical attraction, and sexual consummation. It can encompass various needs such as self-esteem, affiliation, dominance, submission, and self-actualization (proximity and lust)
Decision/Commitment: Consists of both short-term (the decision to love someone) and long-term (the commitment to maintain that love) aspects. These components may not always align, and commitment doesn't necessarily imply an initial decision to love. (conscious cognitive decision to maintain relationship)
The forms of love closely linked to sexual orientation
Infatuation (Passion)
Romantic love (Passion + Intimacy)
Fatuous love (Passion + Commitment)
Consummate love (Passion + Intimacy + Commitment)
All must show Passion: drives that lead to physical attraction, and sexual consummation.
The forms of love that do NOT involve sexual feelings
Liking (Intimacy)
Empty love (Commitment)
Companionate love (Intimacy + Commitment)
Characterized by comfort, security and care. NOT really sexual (no passion)
Other Dimensions of Sexual Orientation: Different Age Attraction
Teleiophilia = sexual attraction to adults
Hebephilia = sexual attraction pubescent individuals (11-14)
Pedophilia = sexual attraction to pre-pubescent children (11 and under) [majority of offenders are male]
Orientation versus behavior
Orientation:
Definition: Orientation refers to an individual's enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and sexual attractions towards others, a deep-seated aspect of one's identity.
Behavior:
Definition: Behavior refers to the actions or conduct of an individual. The actual engagement in specific activities or actions.
Pedophilia as an Orientation:
Explanation: Pedophilia, as an orientation, implies having a persistent and exclusive attraction to prepubescent children, but they are NOT acting on these attractions.
Pedophile as a Behavioral Term:
Explanation: The term "pedophile" is often used to describe someone who acts on their pedophilic attractions, engaging in illegal or harmful behavior involving children.
Dimension of Sexual Orientation: The 2 different Focused targets
Location:
External
focusing on allosexual targets
focus on others
Internal
focusing on oneself
bond with self
become the sexual thing one focuses on
Other Dimensions of Sexual Orientation: Sexual attraction to Humans VS Animals
Species:
Anthrophilia = sexual attraction to humans
Zoophilia = sexual attraction to animal
Other dimensions of Sexual Orientation: Different attractions to intense sexual activities
Masochism = sexual arousal to being subjected to pain, suffering and humiliation
Sadism = sexual arousal to inflicting pain, suffering and humiliation
Biastophilia = sexual arousal to sexual activity with non- consenting partners (not interested in violence per say)