
Unit 7: (Theories of Development)
The Brandt Line: A visual depiction of a North-South development divide by GDP per capita (1980s)
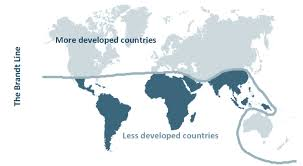
Inconsistent: Australia is included, even though it is in the South
Rostow’s Stages of Economic Growth:
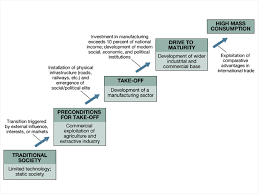
Stage 1: Traditional Society
Subsistence agriculture based economy
bartering
Stage 2: Preconditions to take off
more commercial agriculture
starts to build infrastructure
Stage 3: Take Off
Industrialized
Secondary Sector grows
Technology advances
Stage 4: Drive to Maturity
Development of commercial base
tertiary sector grows
global trade
Stage 5: High Mass Consumption
Highest level of development & infrastructure
USA & West EU
Issues:
Does not account for globalization or interdependence
Does not account for imperialism or colonialism
Argued all countries will progress through the 5 stages of development to become mass consumption societies (1960)
Wallerstein’s World Systems Theory:
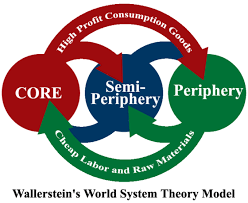
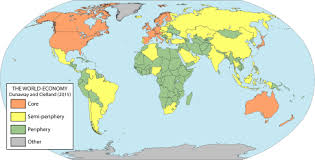
World is an interdependent economic system based on the unequal division of labor & resources exchanged between the core, periphery, and semi-periphery
Core countries:
Industrialized first
MDCs
Imperialists, Exploiters
Periphery:
LDC: many primary sector jobs
exploited for cheaper labor & resources
Semi-Periphery:
Acts as core in their region but periphery to core states
BRICS: Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa
Issues:
Little opportunity for periphery countries to advance into core
Does not account for self-sufficiency/economic growth
Dependency Theory:
Highly connected to World Systems Theory
Argues poverty in periphery is due to colonialism & imperialism
colonized countries become economically dependent on core
Neocolonialism
MDCs take natural resources and use lower labor costs in periphery to profit
Commodity Dependence: when more than 60% of a state’s exports are commodities
raw materials, agricultural products, energy, natural resources
More common in periphery & semi-periphery states
reliant on unstable global market prices
Unit 7: (Theories of Development)
The Brandt Line: A visual depiction of a North-South development divide by GDP per capita (1980s)

Inconsistent: Australia is included, even though it is in the South
Rostow’s Stages of Economic Growth:

Stage 1: Traditional Society
Subsistence agriculture based economy
bartering
Stage 2: Preconditions to take off
more commercial agriculture
starts to build infrastructure
Stage 3: Take Off
Industrialized
Secondary Sector grows
Technology advances
Stage 4: Drive to Maturity
Development of commercial base
tertiary sector grows
global trade
Stage 5: High Mass Consumption
Highest level of development & infrastructure
USA & West EU
Issues:
Does not account for globalization or interdependence
Does not account for imperialism or colonialism
Argued all countries will progress through the 5 stages of development to become mass consumption societies (1960)
Wallerstein’s World Systems Theory:


World is an interdependent economic system based on the unequal division of labor & resources exchanged between the core, periphery, and semi-periphery
Core countries:
Industrialized first
MDCs
Imperialists, Exploiters
Periphery:
LDC: many primary sector jobs
exploited for cheaper labor & resources
Semi-Periphery:
Acts as core in their region but periphery to core states
BRICS: Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa
Issues:
Little opportunity for periphery countries to advance into core
Does not account for self-sufficiency/economic growth
Dependency Theory:
Highly connected to World Systems Theory
Argues poverty in periphery is due to colonialism & imperialism
colonized countries become economically dependent on core
Neocolonialism
MDCs take natural resources and use lower labor costs in periphery to profit
Commodity Dependence: when more than 60% of a state’s exports are commodities
raw materials, agricultural products, energy, natural resources
More common in periphery & semi-periphery states
reliant on unstable global market prices
 Knowt
Knowt