The Brain
Old brain: lack of conscious thought:
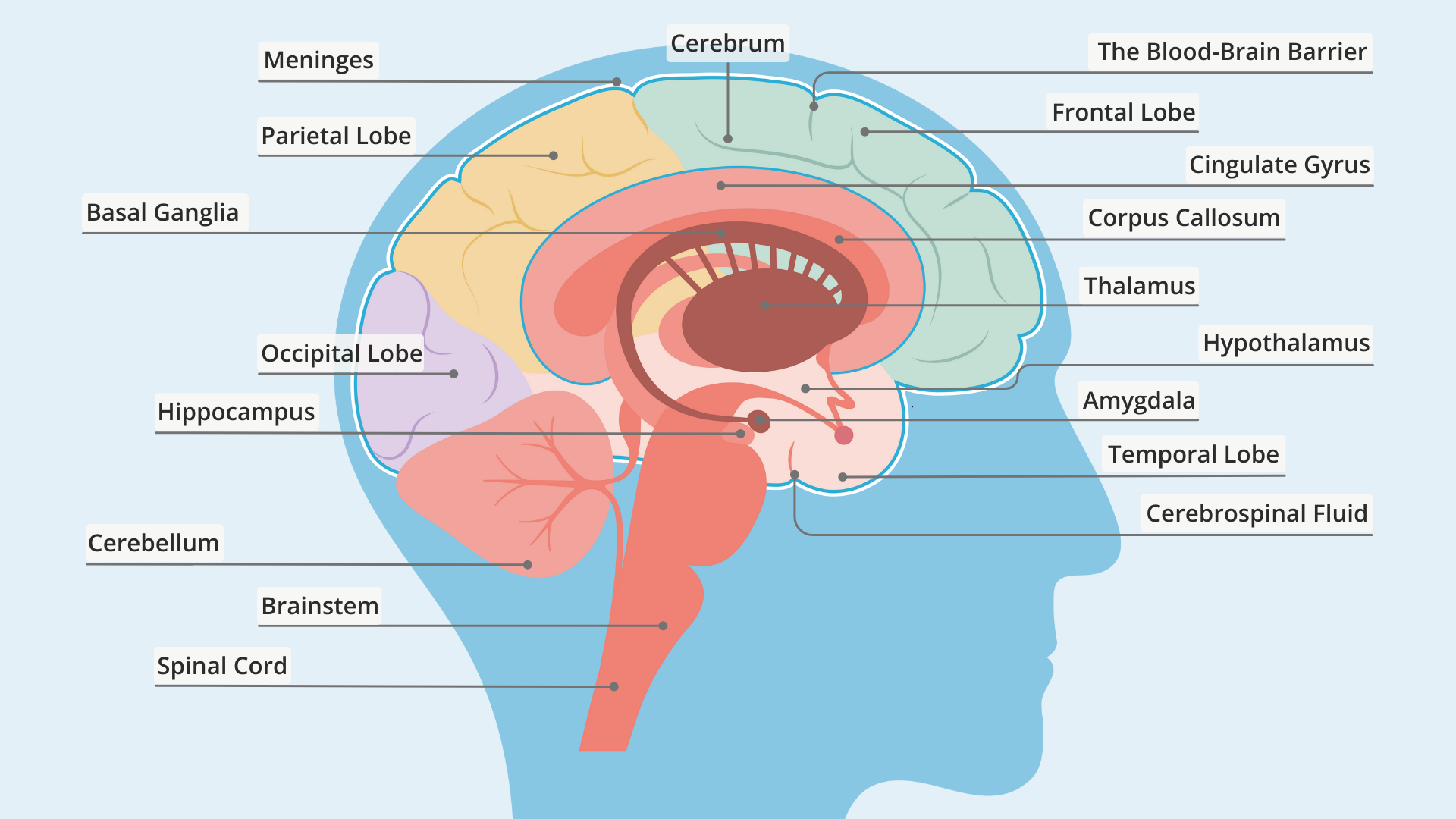
brainstem: responsible for automatic survival functions
medulla: controls heartbeat and breathing
pons: coordinate movement
reticular acting system (RAS): maintains consciousness and alertness
functions in sleep and arousal from sleep
thalamus: receives and delivers all sensory messages (except smell)
delivery system
cerebellum: helps coordinate voluntary movement and balance
The Limbic system:
hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus deal with basic drives, emotions, and memories
hippocampus: memory processing
amygdala: aggression (fight) and fear (flight)
hypothalamus: hunger, thirst, body temperature, and pleasure
regulates pituitary gland (hormones)
The cerebral cortex: the body’s ultimate control and information processing
frontal lobes:
prefrontal cortex: judgement, planning, processing new memories
motor cortex: speaking, muscle movement
parietal lobe: somatosensory cortex
occipital lobe: receive visual information
temporal lobe: receives auditory information
Hemispheres:
left: language, math, logic
controls right side
right: art, creativity, emotions
controls left side
corpus callosum: bundle of nerve fibers that connect the hemispheres
Roger Sperry discovered the purpose of it and researched its function in split brain patients
whatever falls on the left side of your eyes goes on the right hemisphere and vice versa
Functional plasticity:
shifting functions from damaged to undamaged parts of the brain
ex. learning how to walk again
Structural plasticity:
ability to change the physical structure of the brain
ex. learning new things
Cortical localization:
there are specific locations where certain brain functions happen
Broca’s area
speech production
left frontal lobe
Wernicke’s area
speech comprehension
left temporal lobe
Aphasia
difficulty with processing and comprehending spoken and written word