Unit 6 Bio
Intro
Autotrophs- Organisms that make their own food by getting carbon from the environment
Heterotrophs- Get carbon from other organisms
Photosynthesis- Metabolic pathway that uses sunlight, CO2, H2O to get sugar and O2
Light Waves (electromagnetic radiation)
Wavelength- The distance between 2 waves
Photon- light wave groups
Shorter = more energy
Pigment- molecule that Absorbs specific wavelengths w/ electrons
Accessory Pigment- secondary pi
reflected light gives color
Chlorophyll A- most common pigment in plants
best with Blue and Red light
Light Dependent Reactions-
Thylakoid membrane
Photosystems- Large protein complex that converts light into chemical energy
Type 1 and Type 2
Noncyclic Pathway
Input: Light and Water
Produces: NAPDH and ATP
Waste Product: Oxygen
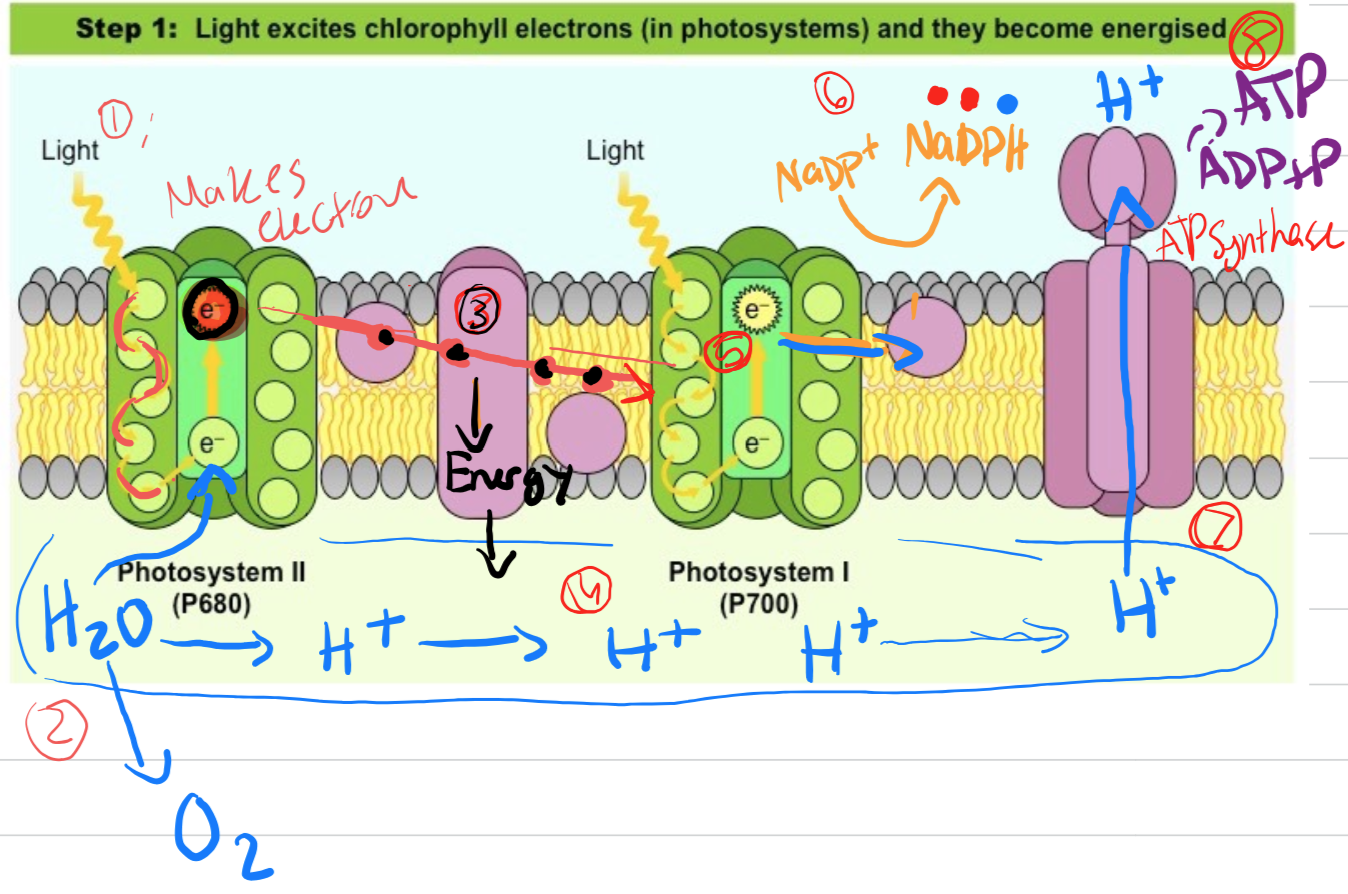
Photosystem 2 absorbs photon. Making a chlorophyll pair emit an electron
(light to chemical energy).
Water splits into replacement electrons and Hydrogen ions w/ Oxygen as waste (Photolysis)
Released energy from the electron transfer chain power the Hydrogen ion gradient
The electrons get accepted into photosystem 1 and repeats step 1
The electrons move into a second chain
At the end the electrons and hydrogen bond with NADP+
NADP+ + electrons + H+ = NADPH
NADPH- A powerful electron donor
The H+ leaves the compartment through ATP Synthase (a transport protein)
The H+ phosphorylates ADP so ATP forms in stroma - Electron Transfer Phosphorylation
Cyclic Pathway (only photosystem 1)
Electrons do not go to NADP+
Instead, it goes back to photosystem 1
Does not produce o2 b/c no water splitting
Used to make extra ATP
Light Independent Reactions-
Stroma
Calvin-Benson Cycle
Input: Carbon Dioxide, Phosphate (ATP), hydrogen + electrons (NADPH)
Product: Sucrose, NADP+ / ADP (goes back to light-dependent cycle)
Goal: Build Carbon backbones of sugar molecules from CO2
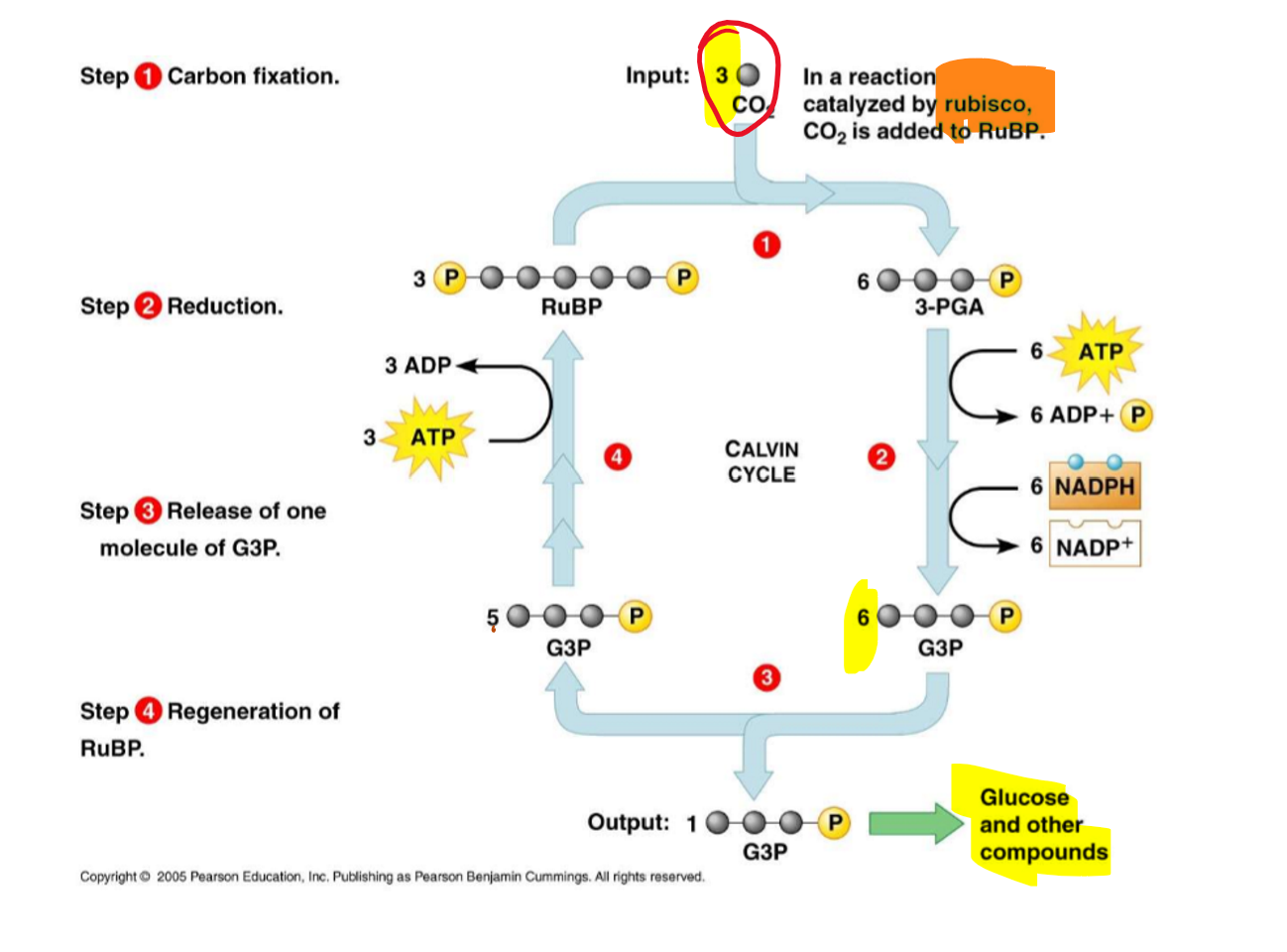
Stage 1: Carbon Fixation
Rubisco (a protein/enzyme) bonds CO2 (3 × 6C) to RUBP (3 × 5C)
RUBP gets +1 Carbon from CO2 = PGA
PGA is unstable and SPLITS in half (6 rows x 3 Carbon)
Stage 2: Reduction (adding energy) Note: PGAL = G3P = simple sugar
Each PGA gets a Phosphate group and Hydrogen + Electrons = PGAL
6 PGA turns into 6 PGAL
-1 PGAL to make ½ sugar = 5 PGAL
Stage 3: Regeneration
5 PGAL combine back into RuBP using ATP
Photorespiration
Stomata- Holes in a plants surface that let gases in and out
When stomata is closed O2 rises and CO2 decreases
Photorespiration- When O2 is more than CO2, O2 attaches to RuBP
The intermediate is shipped from the chloroplast to the peroxisome to Mitocondria and back
Then the molecule can enter the CB cycle
Waste products:
CO2 is lost and cannot be reused
Hydrogen Peroxide in peroxisome is necessary for signaling growth and defense responses
Ammonia that needs to be detoxified in mitoconrdia
C3 Plants
Only fix carbon in CB cycle
Does both stages of photosynthesis all day
O2 and CO2 compete for rubisos active site