Note
5.0(1)
Explore Top Notes Note
Note Studied by 3 people
Studied by 3 people Note
Note Studied by 16 people
Studied by 16 people Note
Note Studied by 22 people
Studied by 22 people Note
Note Studied by 6 people
Studied by 6 people Note
Note Studied by 375 people
Studied by 375 people Note
Note Studied by 46 people
Studied by 46 people
AP Psch pg 163-184
5.0(1)
2.2: Data Transformations and Z-Scores
5.0(1)
Chapter 2: Electricity
5.0(2)
FLQ - October Crisis, Fall 1970
4.5(2)
World History- Ancient Greece
5.0(1)
Chapter 8: Biological Bases: Consciousness
5.0(2)
Cognitive Approach - Cognitive Processes
==Multi-Store Model of Memory==
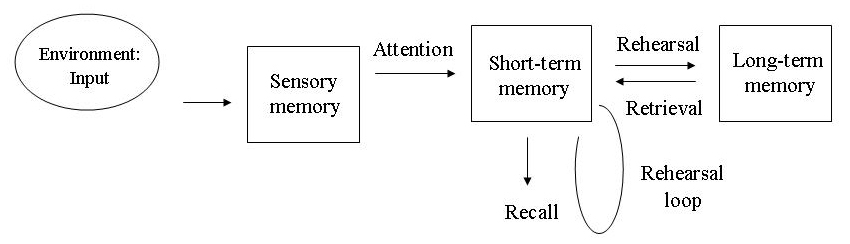
- Sensory memory – iconic memory
- Stores visual sensory information
- Capacity: unlimited
- Duration: 1/3 of a second
- Short Term Memory
- Capacity: 5-9 pieces
- Duration: 20 seconds
- Chunking can help increase the capacity
- Move stuff from short term memory to long term memory through rehearsal
- Maintenance rehearsal involves repeating information again and again
- Elaborative rehearsal involves elaborating on the information in a meaningful way
- Takes more effort, but it is more effective as it ensures that information is encoded into long term memory
- Long Term Memory
- Whenever we remember something we are retrieving it from what is stored in long term memory
- Capacity: unlimited
- Duration: unlimited
- Procedural memory: “knowing how”, memory of how to do things (skills)
- Declarative memory: “knowing that”, memory of information about the world (semantic memory) and personal experiences (episodic memory)
- Episodic memory: stores events (episodes) involving personal experiences. Stores information about context (when and where), state (physical and psychological condition)
- Semantic memory: LTM declarative memory that stores info about the world. E.g. facts (sun is a star), definitions, rules, concepts, everyday knowledge (a bus is a form of transport) and specialized knowledge (chess piece moves)
==Working Memory Model==
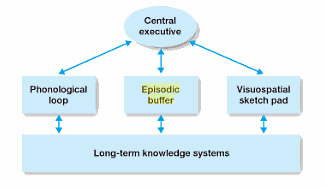
- Central Executive
- Replaces the sensory memory buffer
- Responsible for monitoring an coordinating the operation of ‘slave systems’
- The central executive directs attention to tasks
- Allocates information based on modality
- Phonological loop
- Limited capacity (like STM in MSM of memory)
- Deals with auditory info and language - both written and verbal
- Baddley (1986) further divided it into the:
- Phonological store; holds words for a brief period - can be thought as the inner ear
- Articulatory process; holds words seen/heard and silently repeated like an inner voice
- Episodic Buffer
- Temporarily holds several sources of auditory, long-term and visual information active at the same time, while consideration of what is needed in present situation takes place
- Visuospatial Sketchpad
- Limited capacity (like STM in MSM of memory)
- Visual component of short-term memory/inner eye
- Temporary store for spatial and visual information about what things look like; form and colour
- The inner scribe; processes spatial and movement information.
==Dual Processing Model==
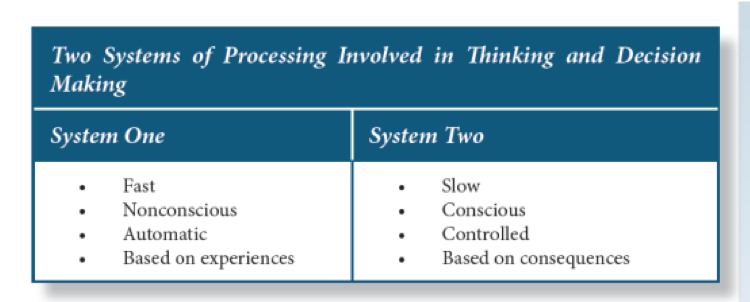
- System 1 Thinking
- the one that is reliant on past information and schema, makes quick and effortless decisions based on limited information.
- Tend to use mental short-cuts called heuristics
- 90% of time we access system 1
- System 1 thinking and take shortcuts - quick thinking, intuitive
- System 2 Thinking
- System 2 thinking - much more effortful and requires more conscious reasoning
- 5% of the time we access system 2 where we slow down.
- System 2 thinking - rational thinking
Note
5.0(1)
Explore Top Notes Note
Note Studied by 3 people
Studied by 3 people Note
Note Studied by 16 people
Studied by 16 people Note
Note Studied by 22 people
Studied by 22 people Note
Note Studied by 6 people
Studied by 6 people Note
Note Studied by 375 people
Studied by 375 people Note
Note Studied by 46 people
Studied by 46 people
AP Psch pg 163-184
5.0(1)
2.2: Data Transformations and Z-Scores
5.0(1)
Chapter 2: Electricity
5.0(2)
FLQ - October Crisis, Fall 1970
4.5(2)
World History- Ancient Greece
5.0(1)
Chapter 8: Biological Bases: Consciousness
5.0(2)