Unit 1+2 - Introduction to Chemistry
Day 1 - The Scientific Method
The scientific method - An organized approach to solve problems
Steps in the Scientific Method:
Observe
Use your five senses
Define the problem
Hypothesis
“educated guess”
Reasonable explanations for what was observed
Experiments
Tests each hypothesis to prove/disprove them
Analysis
Compares the results from the experiment to the original hypothesis
Conclusion (theory)
A hypothesis supported by experimental evidence
Law - Used to describe a natural phenomenon which has been tested over a long time under different conditions
Day 2 - Classification of Matter
Chemistry - The study of matter and the changes it undergoes
Matter - Anything that has mass and volume (everything)
Mass - The amount of matter in an object (how much “stuff”)
Energy - Anything that can do work or produce heat
Weight - The force of gravity acting on an object’s mass
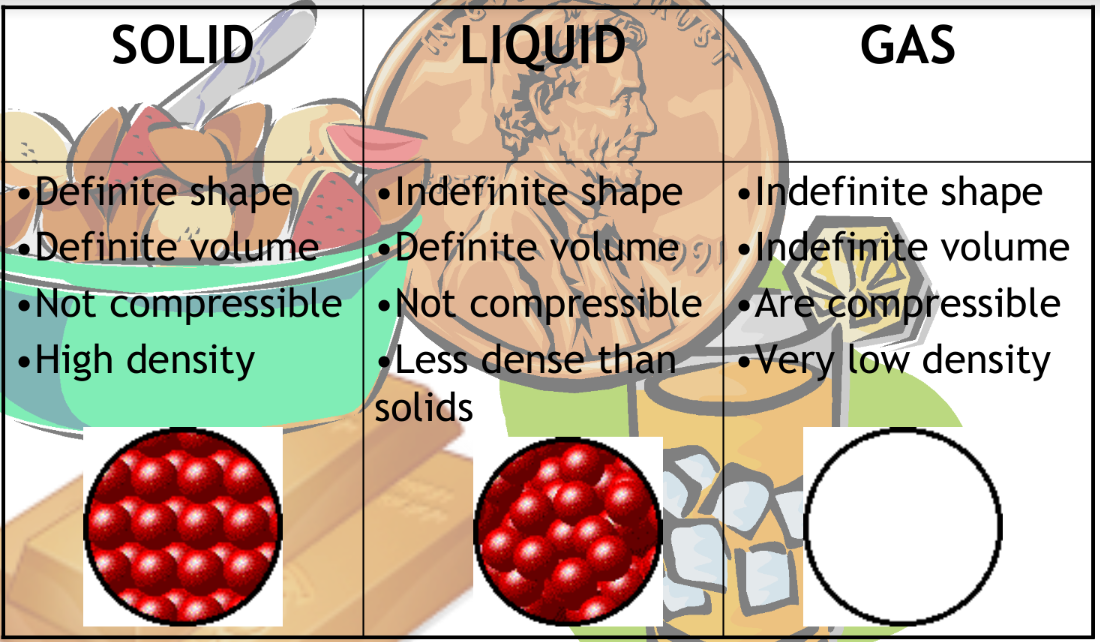
Matters are classified into pure substances and mixtures.
Pure substances - Have uniform and definite composition
Elements - Found on the periodic table (approx. 118)
Described by symbols: H, He, etc.
Compounds - Formed when elements chemically combine: H20, CO2, NO2
Mixtures - Two or more pore substances physically mixed together.
In compounds, elements are bonded to each other
In mixtures, the substances are blended
No definite composition - cannot assign a fixed ratio (ex: H2O)
Two types of mixtures:
Heterogeneous mixtures - Does not have a uniform composition
Parts of the mixtures can be physically seen and “picked out” of the mixtures
Ex. Cereal, pizza, salad
Homogeneous mixtures - Has a uniform composition
Parts of the mixture cannot be “picked out”
Ex. Sugar, water, milk
Day 3 - Chemical/Physical Changes and Properties
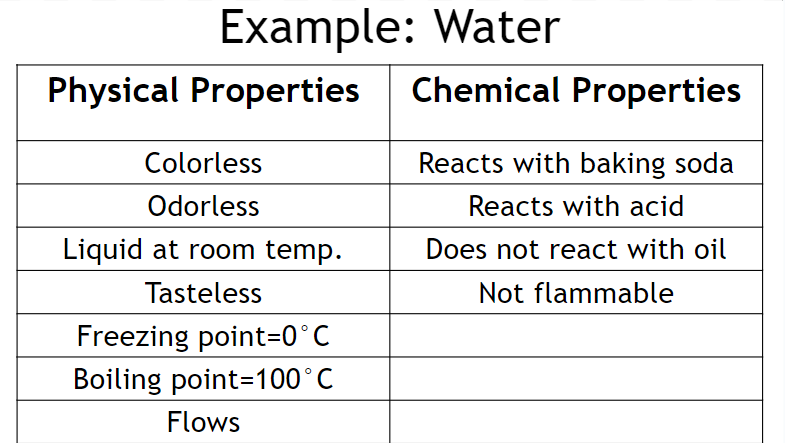
Pure substances have a unique set of chemical and physical properties
Physical properties - Properties that can be measured/observed w/o changing the identity/composition of a substance
The chemical make-up does not change when these properties are observed
Ex. color, odor, texture, taste, freezing point, melting point, density, mass, hardness
Chemical properties - Properties that indicate how a substance reacts with other substances
These properties are only observed when the substance undergoes a chemical change
Ex. Flammable, combustible, burnable, “reacts with…”
Physical Changes - Changes in appearance without changing the composition (Ex. cutting, breaking)
Changes in state such as: melting, freezing, boiling, subliming (going from a solid to gas)
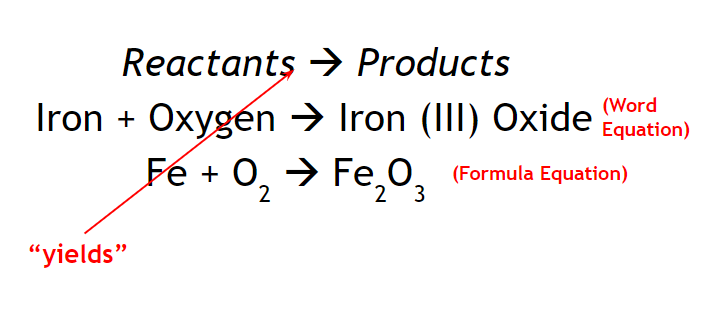
Chemical Changes (Reactions) - One or more substances react to form new substances with different chemical and physical properties
The beginning substance is different than the ending substance
Ex. Rusting, burning, corrosion, digestion, respiration, decaying
All chemical reactions can be described by a chemical equations
Law of Conservation of Mass - In any chemical or physical change, matter cannot be created/destroyed
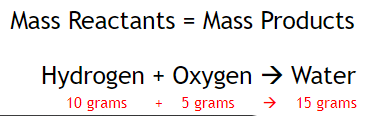
Day 4 - Types of Measurements and Observations
Measurement - A type of observation
Qualitative measurements - Descriptive
Ex. hot, cold, heavy, light, big, blue
Quantitative measurement - Observations with measuring instruments and includes a number and a unit
Ex. ruler, balance, thermometer, 13.5 c, 25 KG
Accuracy - How close a measurement is to the true/accepted value
Ex. Weighting 50g mass
50.00g - accurate
32.18g - not accurate
49.99g - accurate
Precision - How close multiple measurements are to each other
Ex. weighting a 50g mass
Accurate, precise: Not Accurate, precise:
50.00g 32.18g
50.00g 32.18g
50.00g 32.18g
ACurate = Correct
PRecision = Reproducibility
Day 5 - Introduction to Dimensional Analysis
https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1AgDm3T_yVV4a9ckTmKlRJEClY50nsCO2h9Nv-FJDN8c/edit#slide=id.p1
Day 6 - Dimensional Analysis Calculations with more that 2 steps
https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1qLW9ihonLWArZ1UIAjkvCnaUmW0fCvO8a6r1tymVjuU/edit#slide=id.p1