Chapter 2: Company and Marketing Strategy: Partnering to Build Customer Engagement, Value, and Relationships
Key Terms to Know:
Strategic planning: The process of developing and maintaining a strategic fit between the organization’s goals and capabilities and its changing marketing opportunities.
Mission statement: A statement of the organization’s purpose— what it wants to accomplish in the larger environment.
Product/market expansion grid: A portfolio-planning tool for identifying company growth opportunities through market penetration, market development, product development, or diversification.
Marketing strategy: The marketing logic by which the company hopes to create customer value and achieve profitable customer relationships.
Market segmentation: Dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers who have different needs, characteristics, or behaviors and who might require separate marketing strategies or mixes.
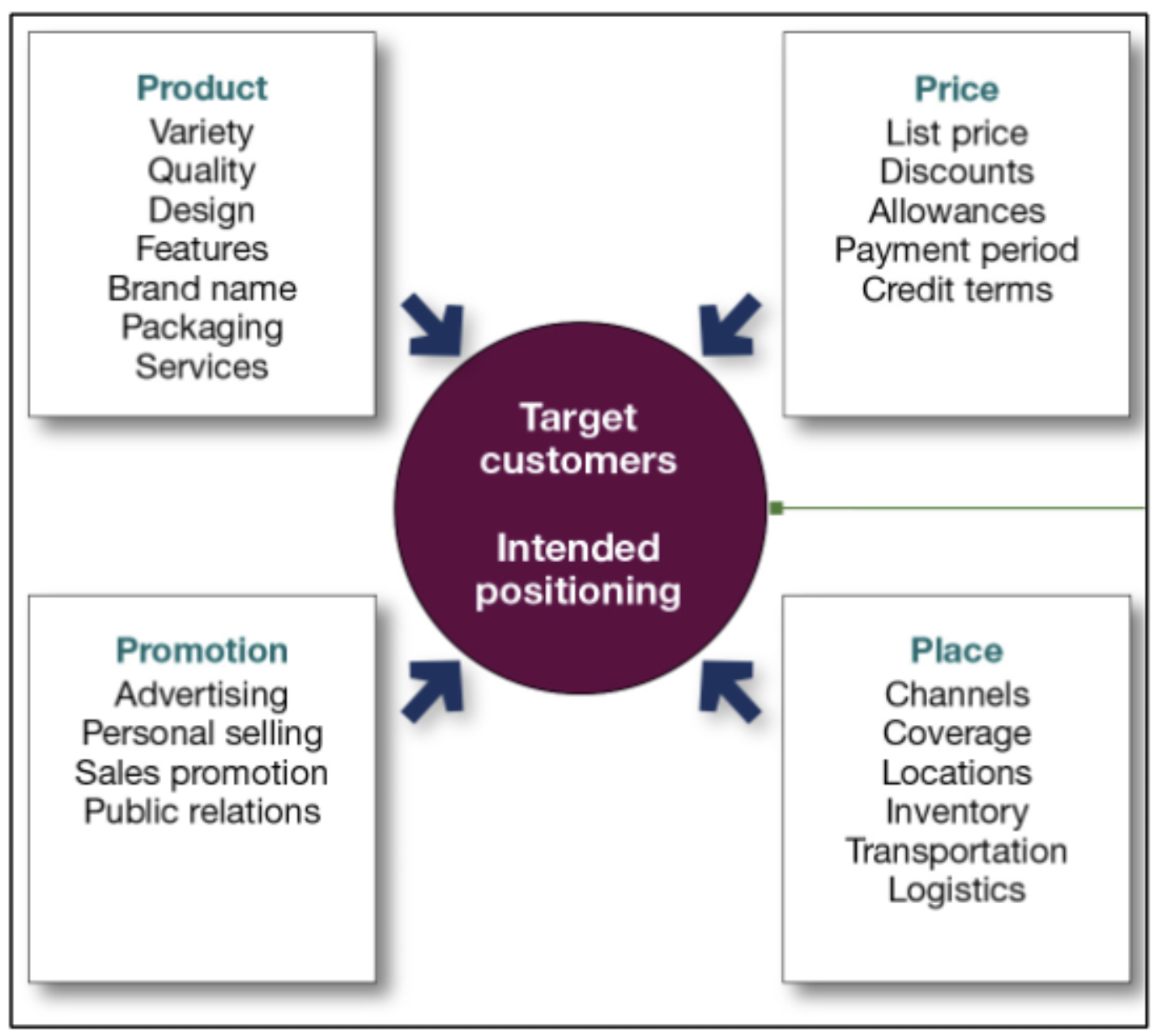
Marketing mix: The set of tactical marketing tools—product, price, place, and promotion—that the firm blends to produce the response it wants in the target market.
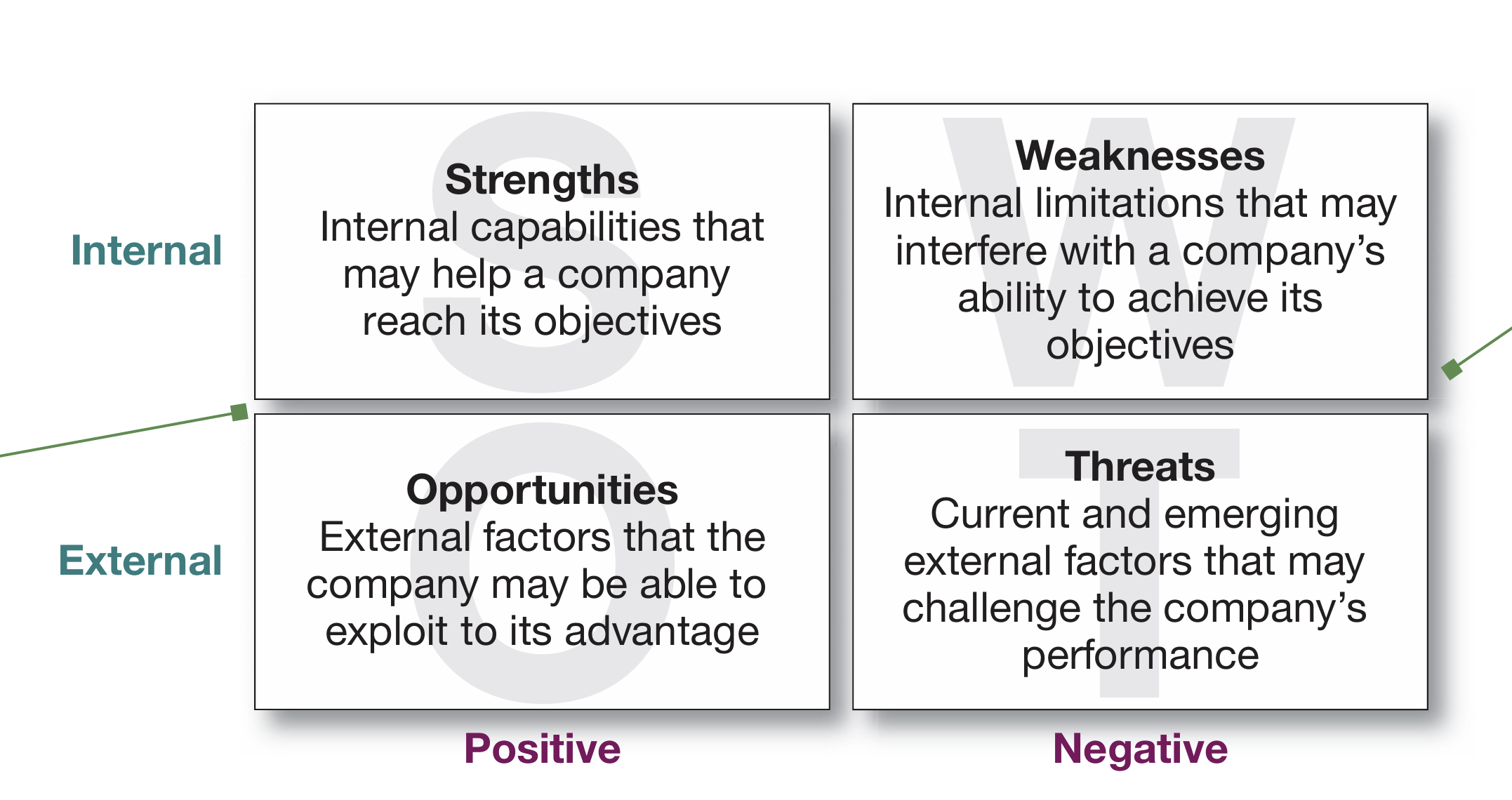
SWOT analysis: An overall evaluation of the company’s strengths (S), weaknesses (W), opportunities (O), and threats (T).
Marketing return on investment (marketing ROI): The net return from a marketing investment divided by the costs of the marketing investment.
2-1. Explain company-wide strategic planning and its four steps.
strategic planning: process of developing and maintaining a strategic fit between the organization’s goals and capabilities and its changing marketing opportunities.
4 Steps
Defining the company mission
Setting company objectives and goals
Designing the business portfolio
Planning marketing and other functional strategies
2-2. Discuss how to design business portfolios and develop growth strategies.
Business portfolio: The collection of businesses and products that make up the company.
Portfolio analysis: he process by which management evaluates the products and businesses that make up the company.
Growth-share matrix: A portfolio-planning method that evaluates a company’s SBUs in terms of market growth rate and relative market share.
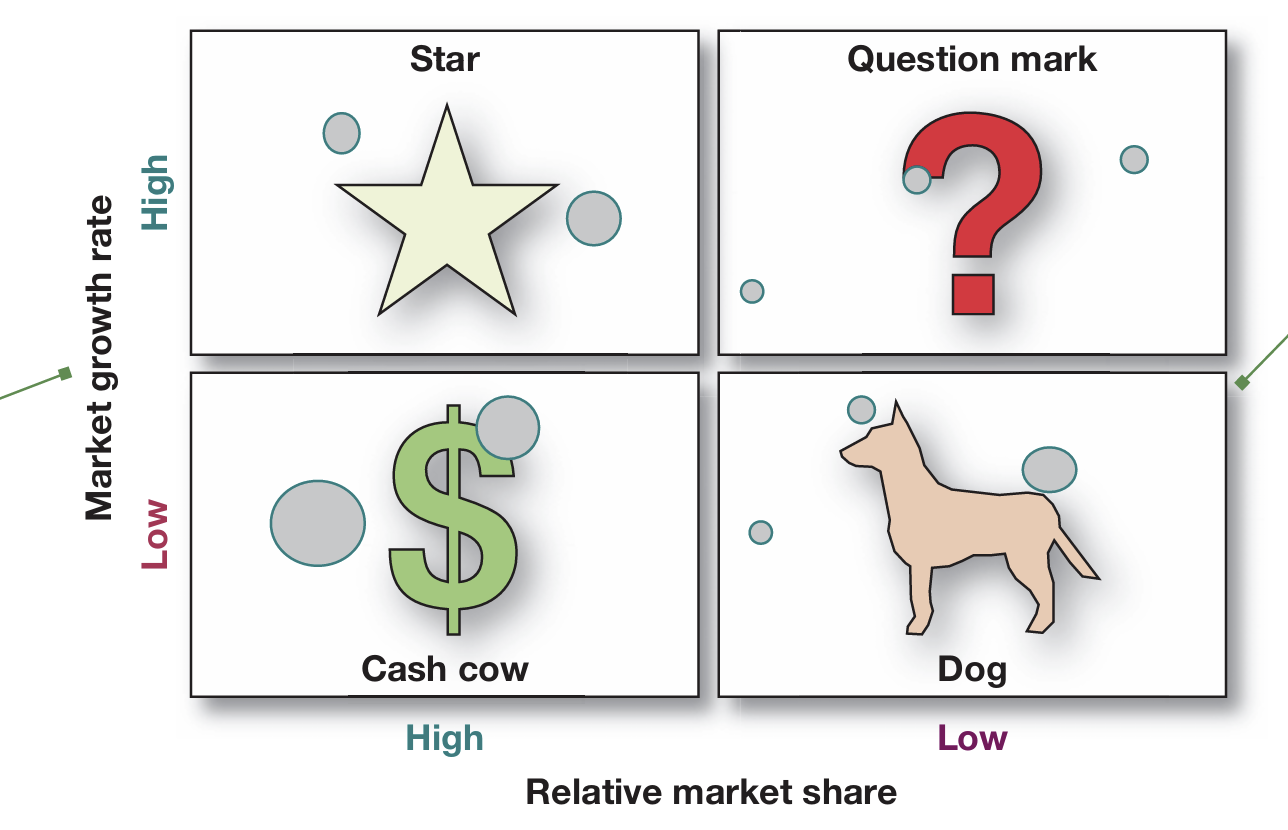
Stars. Stars are high-growth, high-share businesses or products. They often need heavy investments to finance their rapid growth. Eventually their growth will slow down, and they will turn into cash cows.
Cash cows. Cash cows are low-growth, high-share businesses or products. These established and successful SBUs need less investment to hold their market share. Thus, they produce a lot of the cash that the company uses to pay its bills and support other SBUs that need investment.
Question marks. Question marks are low-share business units in high-growth markets. They require a lot of cash to hold their share, let alone increase it. Management has to think hard about which question marks it should try to build into stars and which should be phased out.
Dogs. Dogs are low-growth, low-share businesses and products. They may generate enough cash to maintain themselves but do not promise to be large sources of cash.
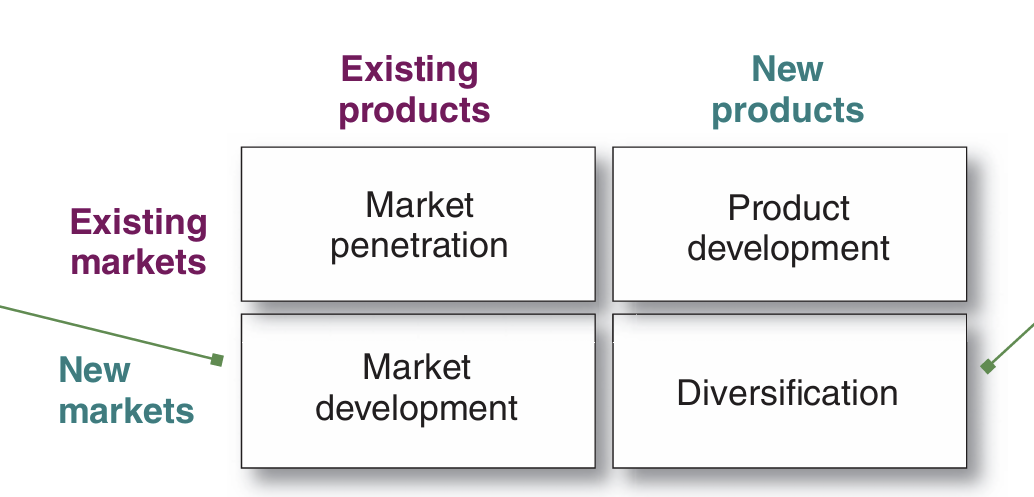
Product/market expansion grid A portfolio-planning tool for identifying company growth opportunities through market penetration, market development, product development, or diversification.
Market penetration Company growth by increasing sales of current products to current market segments without changing the product.
Market development Company growth by identifying and developing new market segments for current company products.
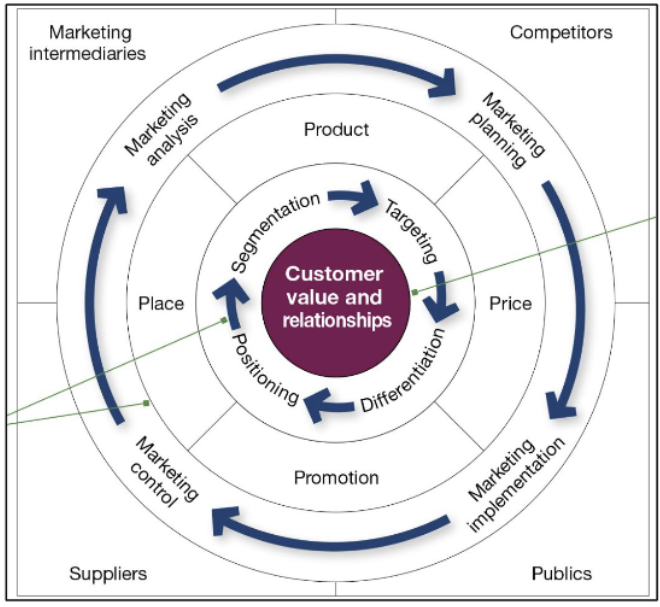
2-3. Explain marketing’s role in strategic planning and how marketing works with its partners to create and deliver customer value.
Planning Marketing
Partnering to build customer relationships
Partnering with other company departments
Partnering with suppliers, distributors, and customers
Value delivery network
2-4. Describe the elements of a customer value-driven marketing strategy and mix and the forces that influence them.
Marketing Strategy
Marketing Mix (The 4Ps)
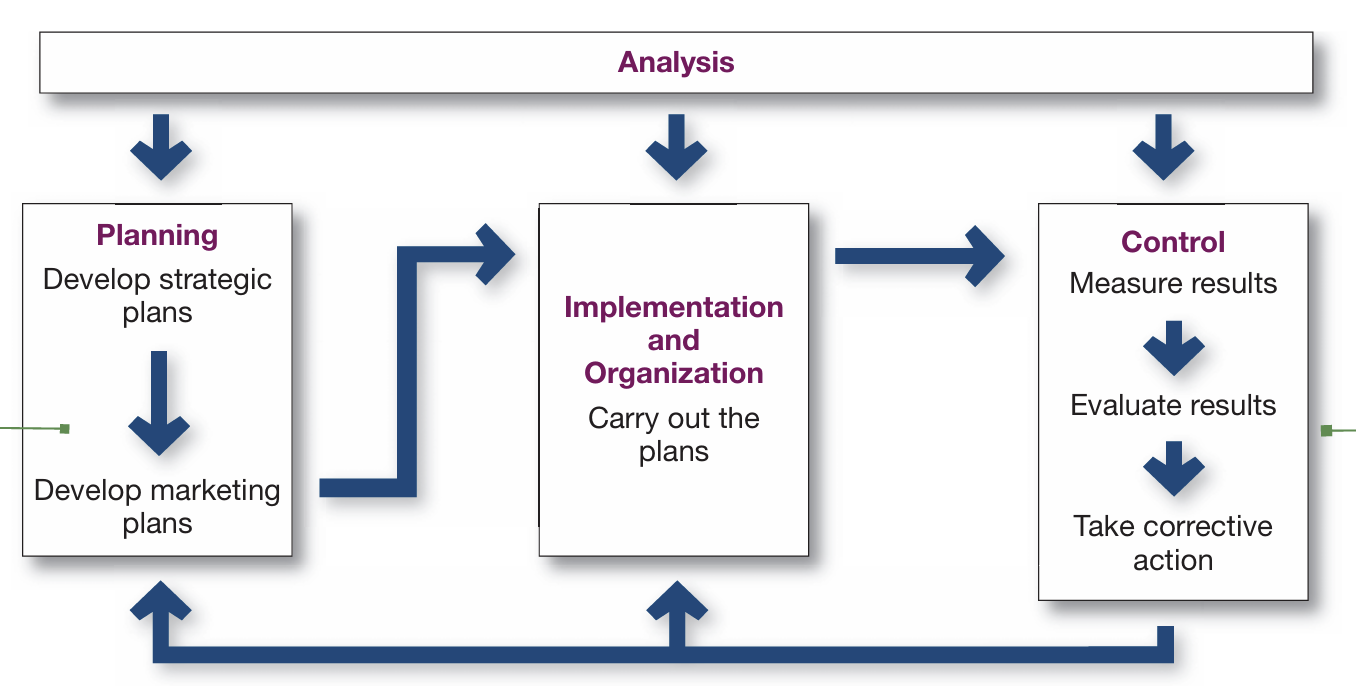
2-5. List the marketing management functions, including the elements of a marketing plan, and discuss the importance of measuring and managing marketing return on investment.
SWOT analysis: An overall evaluation of the company’s strengths (S), weaknesses (W), opportunities (O), and threats (T)
Strengths include internal capabilities, resources, and positive situational factors that may help the company serve its customers and achieve its objectives. Weaknesses include internal limitations and negative situational factors that may interfere with the company’s performance. Opportunities are favorable factors or trends in the external environment that the company may be able to exploit to its advantage. And threats are unfavorable external factors or trends that may present challenges to performance.