Unit 8.3 Database Management Systems & SQL (DDL &DML)
Aims
Know what is meant by the term Database Management Systems (DBMS) and the tools that are commonly included.
Know what is meant by the term Structured Query Language (SQL) and why it is used.
Be able to use Data Definition Language (DDL) to create and modify database objects.
Be able to use Data Manipulation Language (DML) to add, retrieve and update data in a database.
Database Management Systems (DBMS)
Software that provides user with an Interface for managing database.
Allows user to interact with databases with tools to create/retrieve/update/delete and other admin tasks.
Benefits of DBMS
Terms | Explanation |
Integrity | Database structure can change but the applications using data can stay the same. |
Efficiency | Avoids data duplication & inconsistency, less storage space taken up as data is shared. |
Consistency | Data is the same regardless of who or when its being viewed |
Automatic Backups | Can be configured to automatically backup to local and remote storage while preserving integrity. |
Security | In one central secure place. |
Access Rights for Users/Groups | Users can be given varying access levels including what data they can access/read/write/execute/delete/append access. |
Customization | Applications can be stored to suit users needs. |
Data Modelling | Can do Customisation and Access rights. DBMS often consists of forms & reports. Most importantly separating applications from data. When application is used only data needed is called upon as not all data is needed every time so database with DBMS can be viewed by many with different responsibilities |
Structured Query Language (SQL)
Industry standard programming language that allows manages and interacts with databases.
Two subsets - Data Definition Language (DDL) and Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DDL creates & modifies database objects whereas DML adds/retrieves/updates data in database.
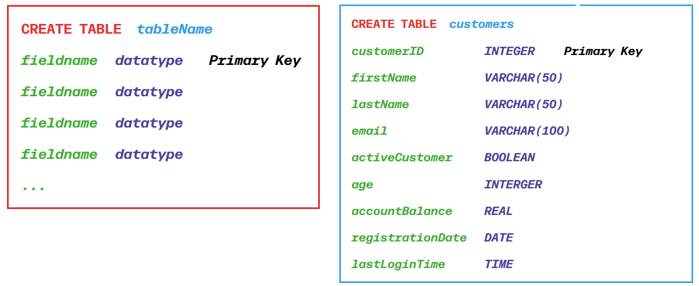
Data Types
Different data types assigned to fields in SQL, DDL & DML
Type | Explanation |
CHARACTER(n) | Stores specific character number, needs to be stated when table set up. |
VARCHAR(n) | Stores variable character number, needs to be stated when table set up. |
BOOLEAN | Stores Boolean values, True or False. |
INTEGER | Stores whole numbers (integers) without decimal places. |
REAL | Stores numbers with decimal places. |
DATE | Stores date value without time component |
TIME | Stores time value without data component |
Must use speech marks around string values that are textual data e.g. “Robert” but not to be used around numbers or Boolean.
Brackets are used when calling a function with arguments (data) e.g. using SUM(LENGTH)
Also when providing multiple values e.g. INSERT INTO Customers (FirstName, LastName)
Also grouping conditions together e.g. SELECT * FROM employees WHERE (Salary>10000 AND departmentID=2) OR (salary<30000 AND departmentID=3)
Data Definition Language (DDL)
Creates and modifies Database objects
Memorize ones with red box as they are syntax’s for exam!!! blue boxes are examples
Creating a Database

Creating a Table
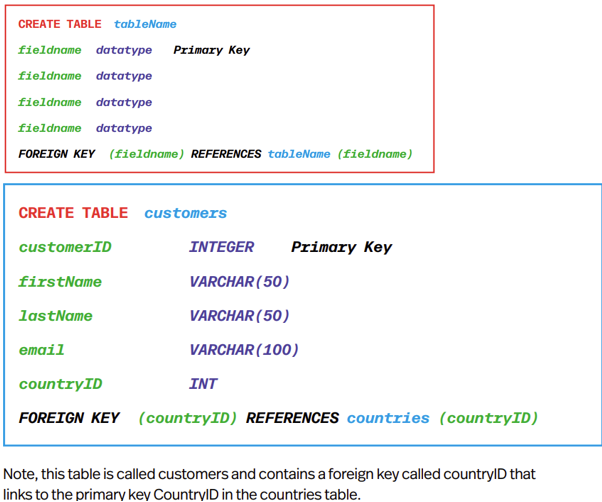
Defining a Foreign Key
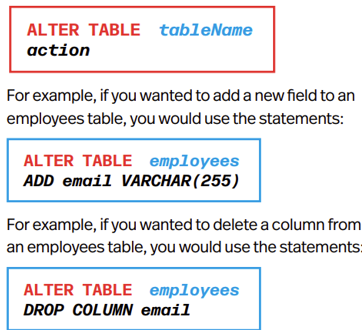
Changing a Table Definition
Modify structure of database object use ALTER
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Adds, retrieves and updates etc. data in a database
Memorize Red boxes for Syntax!! blue boxes are examples.
Selecting Data from a Single Table
SELECT retrieves data but you need to specify which fields
FROM specifies table name you want the data from
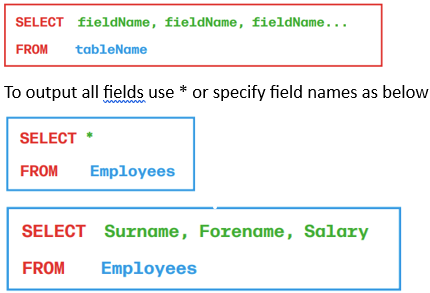
Selecting Data with a Condition
WHERE finds date that meets a specified condition.

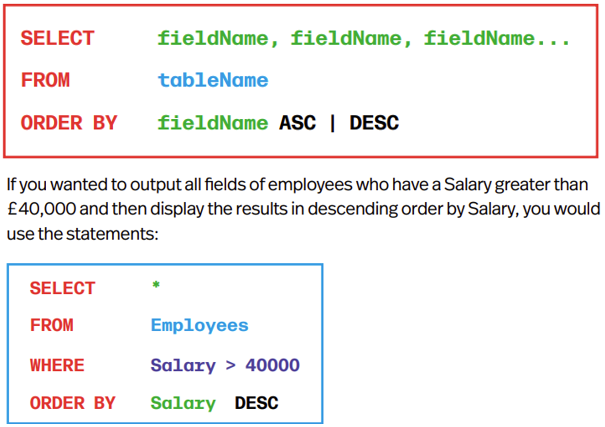
Ordering Data
ORDER BY sorts results from 1+ fields - ASCENDING (ASC) or DESCENDING (DESC)
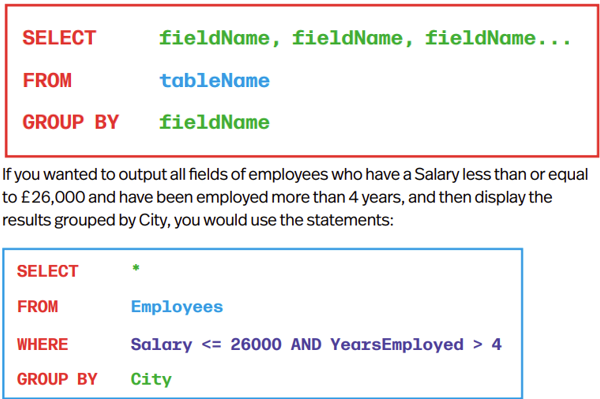
Grouping Data
GROUP BY groups rows that have the same values together
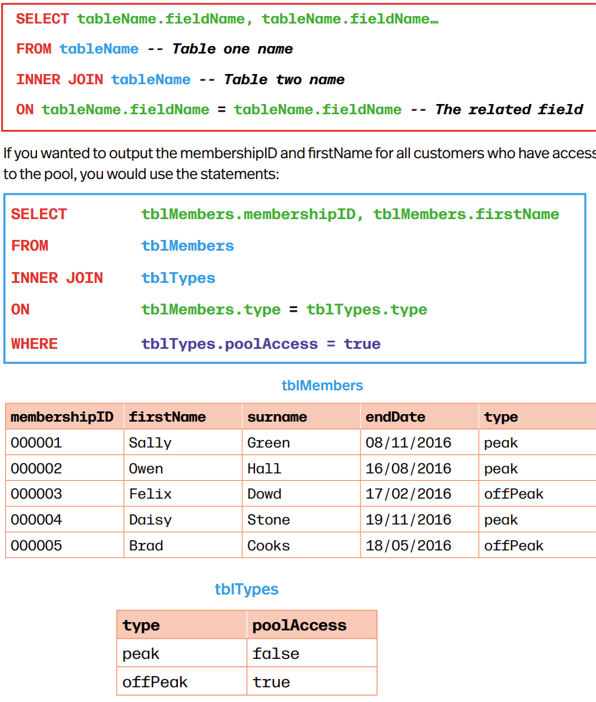
Selecting Data from Multiple Tables
INNER JOIN combines rows from 2+ tables that have related column such as Foreign Key, if selecting data from multiple tables you must state table name for each field.
Below only shows SQL Comment and isn’t needed in SQL Code
On section is where two common fields are mentioned (The PK&FK relationship)
Performing Calculations
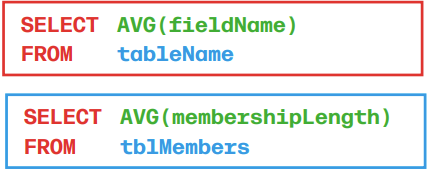
AVG finds average
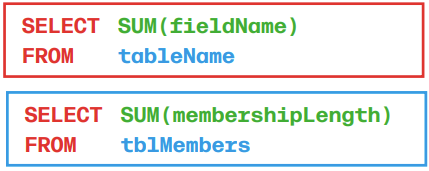
SUM finds sum of values in a column
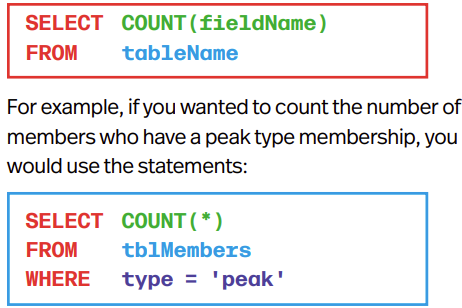
COUNT will count number of rows in a table
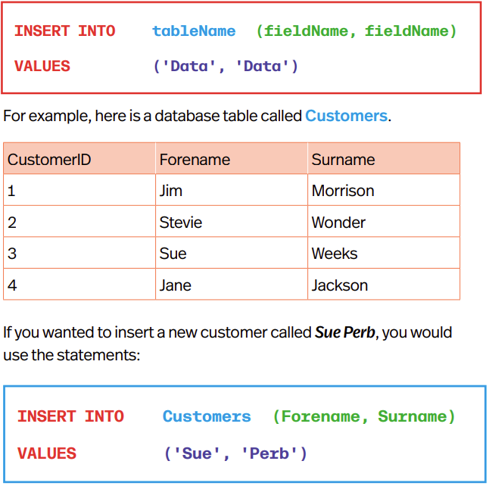
Inserting Data into a Table
INSERT INTO inserts new information into table - All punctuation is important!! if information is a string use ‘’ if integer no ‘ needed
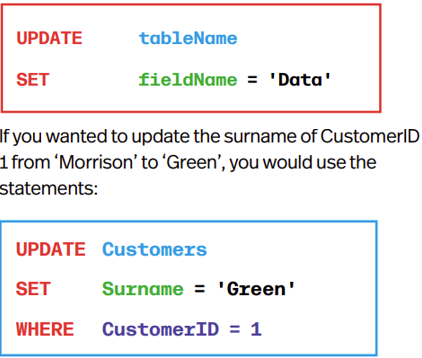
Updating Tables
UPDATE will update data in the table
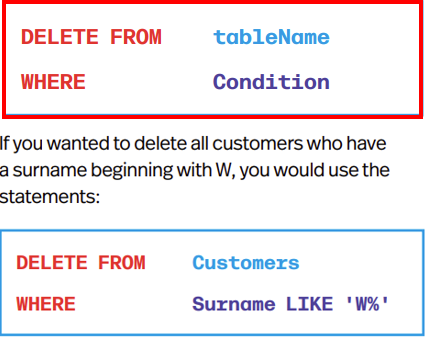
Deleting Data from Tables
DELETE FROM will delete data from tables
Others
LIKE is a SQL clause - find information that begins with a certain character dont forget format LIKE ‘?%’
AND is a SQL clause, use it to set up multiple conditions
OR is a SQL clause, use it set different conditions i.e. retrieve information if field name begins with letter A or B
% wildcard - represents one or more string characters, e.g. LIKE ‘A%’ would ask system to find data in any field beginning with A.