ICT FINAL
I reccoment studying the flashcards since they r edited way better than the notes
Network Terms and Definitions
1. Network: Connected computers sharing info.
2. Internet: Global network of connected computers.
Network Devices
Hub: A hardware device that connects multiple devices in a LAN by sending data packets to all connected devices, leading to potential security issues and increased traffic.
Switch: Similar to a hub but smarter; it sends data packets only to the intended device using MAC addresses, enhancing security and reducing unnecessary traffic.
Network Interface Card (NIC): A device enabling a computer to connect to a network by converting data into electrical signals; each NIC has a unique MAC address.
Wireless Network Interface Card (WNIC): A NIC for wireless connectivity using an antenna.
Bridge: Connects separate LAN segments to function as a unified network, improving internal connectivity.
Router: Directs data packets between networks using IP addresses, essential for connecting a LAN to the internet.
Access Point: Allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network using Wi-Fi.
Modem: Converts digital signals to analog for transmission over telephone lines and vice versa, enabling internet connectivity.
Firewall: A security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules.
Communication Technologies
Bluetooth: A short-range wireless technology (up to 30 meters) for connecting devices using radio waves around 2.45 GHz.
Wi-Fi: A wireless technology for larger networks, offering faster speeds and better range (up to 100 meters), using 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
Cloud Computing
1. Cloud Storage: Storing data on remote servers managed by hosting companies, offering accessibility, data redundancy, and remote backup.
Addressing
MAC Address: A unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communication on the physical network segment.
IP Address: A unique label assigned to devices on the internet, available in IPv4 and IPv6 formats.
Types of IP Addresses
1. Private IP: Used in local networks.
2. Public IP: Used on the internet.
3. Static IP: Doesn't change.
4. Dynamic IP: Changes often.
LAN (Local Area Network)
Advantages:
1. Share resources (printers, files).
2. Easy communication between devices.
3. Central control for security.
Disadvantages:
1. Virus can spread easily.
2. Slower access to outside networks.
3. If the main server fails, the network can stop working.
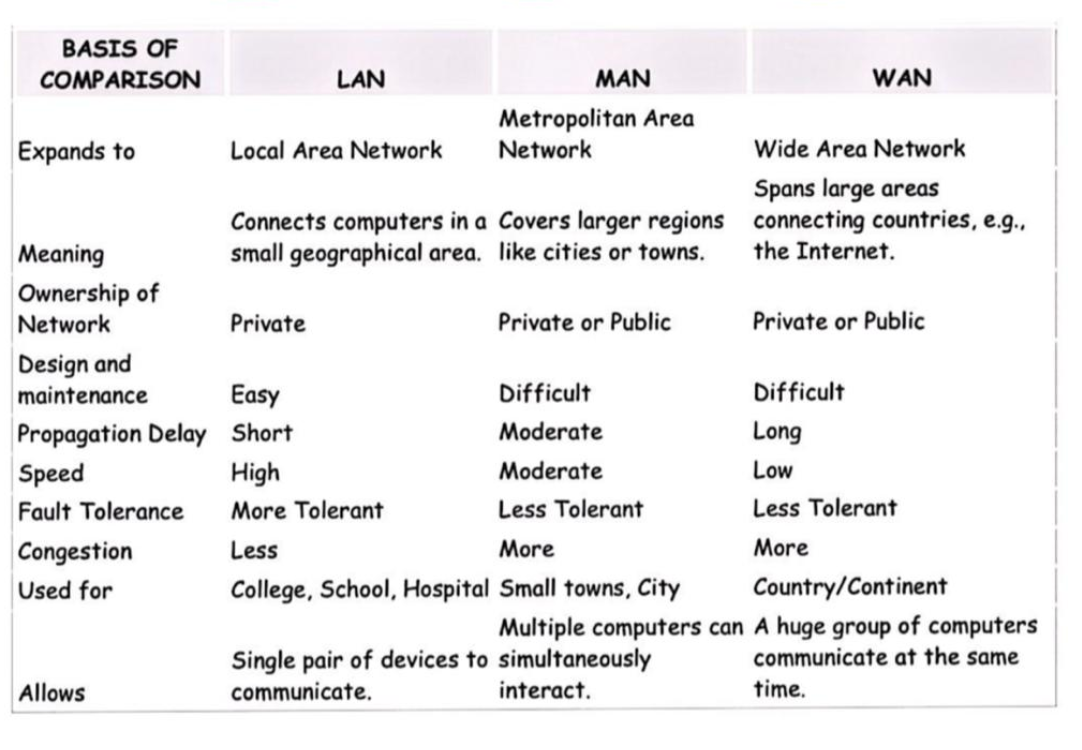
LAN (Local Area Network)
- Expands to: Local Area Network
- Spans large areas: Connects computers in a small geographical area.
- Meaning: A network that connects computers within a limited area like a residence, school, laboratory, or office building.
- Ownership of Network: Private
- Design and Maintenance: Easy
- Propagation Delay: Short
- Speed: High
- Fault Tolerance: More Tolerant
- Congestion: Less
- Used for: College, schools, hospitals
- Allows: single devices can simultaneously communicate at the same time.
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- Expands to: Metropolitan Area Network
- Spans large areas: Covers larger regions like cities or towns.
- Meaning: A network that connects users with computer resources in a geographic area or region larger than that covered by a LAN but smaller than the area covered by a WAN.
- Ownership of Network: Private or Public
- Design and Maintenance: Difficult
- Propagation Delay: Moderate
- Speed: Moderate
- Fault Tolerance: Less Tolerant
- Congestion: More
- Used for: towns, cities
- Allows: A huge group of computers interact.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
- Expands to: Wide Area Network
- Spans large areas: Connecting countries, e.g., the Internet.
- Meaning: A network that extends over a large geographical area, often a country or continent, and is used to connect LANs and other types of networks.
- Ownership of Network: Private or Public
- Design and Maintenance: Difficult
- Propagation Delay: Long
- Speed: Low
- Fault Tolerance: Less Tolerant
- Congestion: More
- Used for: Country/Continent
- Allows: many groups of devices to communicate.