P2: Bone Pathology
Bone Density
Low Density
- rickets (rachitis)
- osteoporosis
- tumours
Increased Density
inflammation
productive tumour
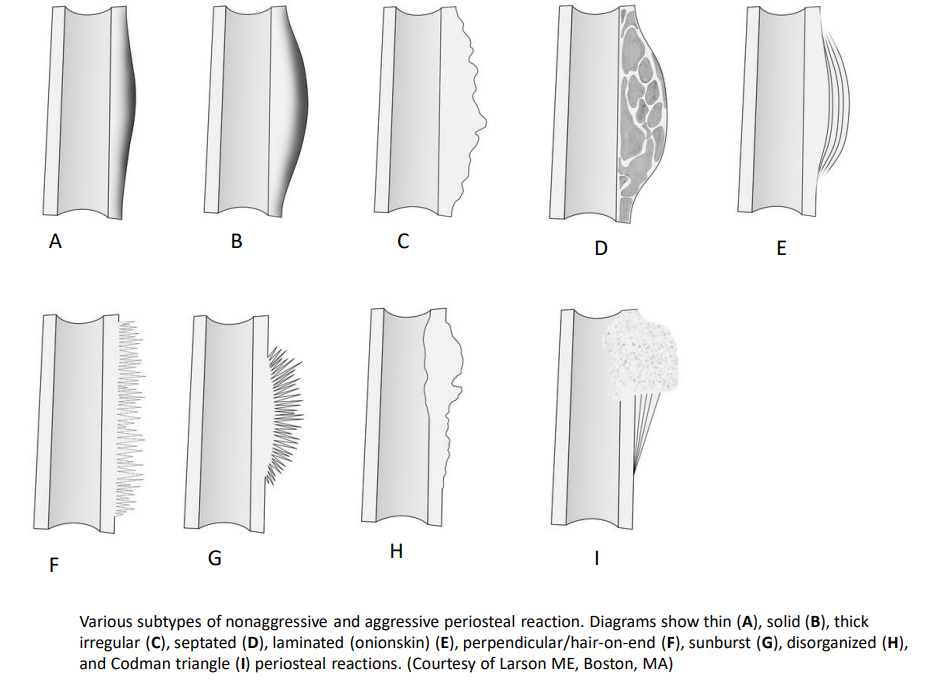
A
B
C - typical for inflammation
D
E
F
G - more aggressive - tumour (osteosarcoma)
H
I - more aggressive - tumour (osteosarcoma)
osteoma - benign
osteosarcoma - malignant + metastatic action (spreading to other tissues/locations in the body)
treatment is different with and without metastatic action
(ligamentum patellare - runs over patella to tibial tuberosity )
(cranial and caudal cruciate ligaments - fix tibia and femur)
Hypertrophic Osteodystrophy (HOD)
sometimes referred to as metaphyseal osteopathology
typically first presents between 2-7 months
characterised by decreased blood flow to metaphysis leading to failure of ossification (bone formation) and necrosis and inflammation of cancellous bone (spongiosis)
usually bilateral in the limb bones, especially distal radius, ulna, and tibia
- diagnosis is based on history, symptoms, physical exam showing pain and swelling at the growth plates, and with x-rays
- x-rays will show a thin radiolucent (dark) line at the metaphysis (growth plate) at the end of the ulna, radius, or tibia
- bony inflammation and bone remodelling may also be seen at these sites, fever and high white blood cell count
- treatment is generally supportive. Since this is a very painful condition, anti-inflammatories and painkiller such as carprofen are given
- bone disease that occurs in fast-growing large and giant breed dogs
- Characteristics:
- rare pathology
- disease process, secondary in nature, which commonly occurs due to neoplastic or infectious masses in the thoracic cavity
- hypertrophic osteopathy can also cause periosteal new bone. The joints are not affected
- secondary disease
- periosteal reaction especially metacarpal and metatarsal bones
- swelling, pain
- mostly older dogs
- primary - lungs - chronic infectious disease, parasites, tumours, bacterial endocarditis
- RTG - the chest and limbs affected : irregular proliferation of periosteal new bone the fingers and small bones (joints show no pathological changes)
Nutritional Secondary Hyperparathyroidism - Ca-P Imbalance
- puppies fed meat, increasing P, decreasing Ca = increased PTH
- or hormonal
- x-ray: long bone thin cortex, the medullary cavity is abnormally wide
- decreased bone density, pain, deformation, fracture
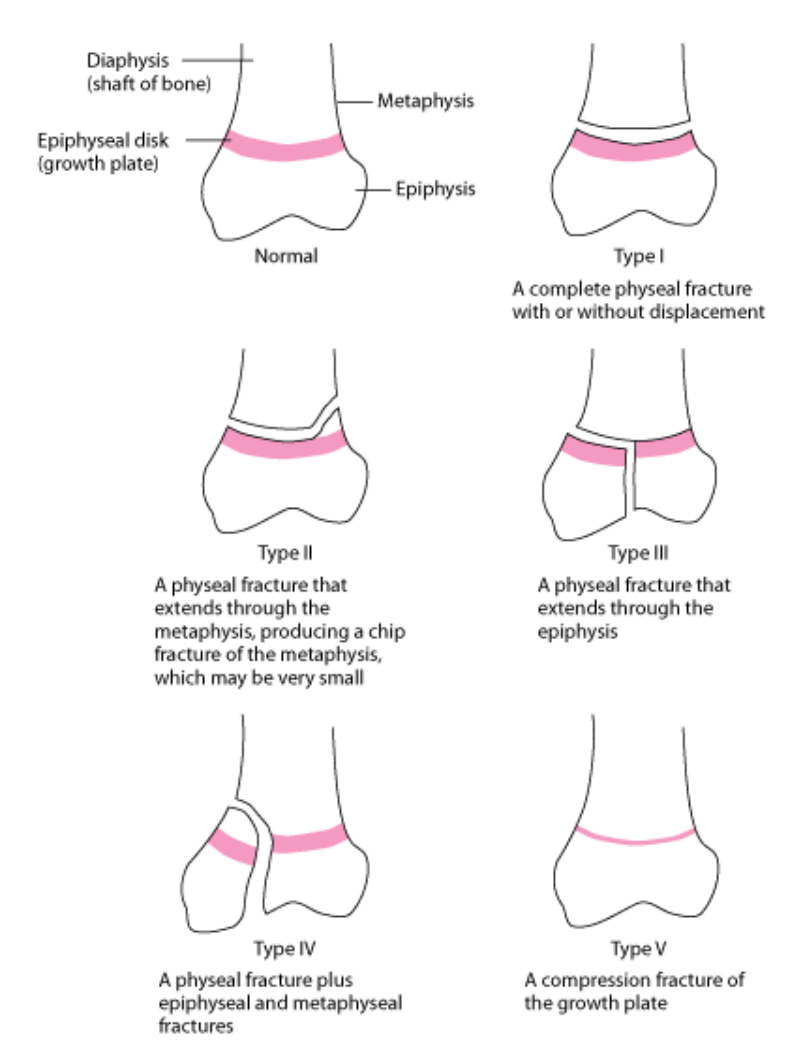
Early Closure of Growth Plates on Dog
cause: trauma in physis
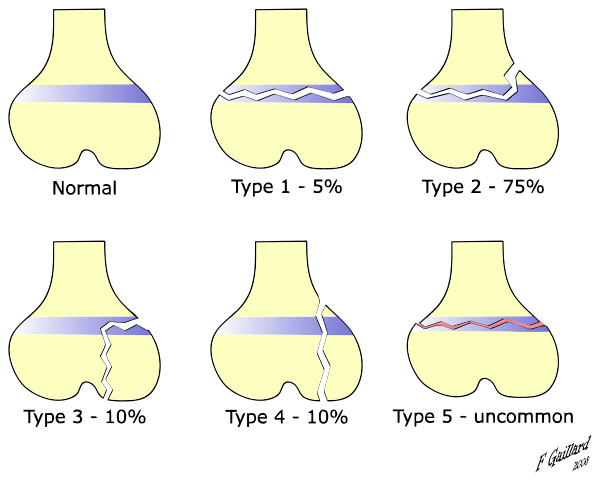
salter-harris classification
Type I – transverse fracture through the growth plate (also referred to as the "physis"): 6% incidence
[[6]](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salter–Harrisfracture#citenote-6)
Type II – A fracture through the growth plate and the metaphysis, sparing the epiphysis: 75% incidence, takes approximately 12-90 weeks or more in the spine to heal.
[[7]](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salter–Harrisfracture#citenote-7)
[[8]](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salter–Harrisfracture#citenote-8)
Type III – A fracture through growth plate and epiphysis, sparing the metaphysis: 8% incidence
[[9]](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salter–Harrisfracture#citenote-9)
Type IV – A fracture through all three elements of the bone, the growth plate, metaphysis, and epiphysis: 10% incidence
[[10]](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salter–Harrisfracture#citenote-10)
Type V – A compression fracture of the growth plate (resulting in a decrease in the perceived space between the epiphysis and metaphysis on x-ray): 1% incidence
localisation: physia distal ulna, radius
limb distal to the growth plate deformity - lateral-valgus deformity
subluxation of the elbow joint
x-ray: ossification of the growth plate of the ulna
premature ossification of the growth plate of the radius: incongruity in the elbow joint → dysplasia → arthrosis
treatment: surgical - cut smaller bone
Panosteitis
- inflammatory disease of long bones of large breeds aged 5-12 months
- affects the the medullary cavity and endoost-osteroblastic activity → increased radiopacity
- palpation: pain
- due to food balance and high activity
- treatment: balance food and activity, anti-inflammatories
Osteomyelitis
- open fractures (bacteria, fungi), the response to the osteosynthesis material
- acute: pain, swelling, fever, x-ray image is indefinite
- chronic: muscle atrophy, cutaneous fistula, lameness, changes to all structures of the bone: Volkmann, Havers
- x-ray: periosteal reaction, increased radiopacity marrow - avascular bone segments
Tumours
- benign or malignant
- primary
- secondary - prostate, mammary gland, lung, bowel cancer, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels
| Type of Sarcoma | Tissue/ Cell Type |
|---|---|
| multiple myeloma | blood or bone marrow |
| chondrosarcoma (various types) | cartilage (chondrogenic) |
| osteosarcoma | bone (osteogenic) |
| fibrosarcoma | connective tissue (fibrogenic) |
The next step after x-ray suspected diagnosis is histological sample
Osteosarcoma
- mixed?
- productive formation
- lytic formation
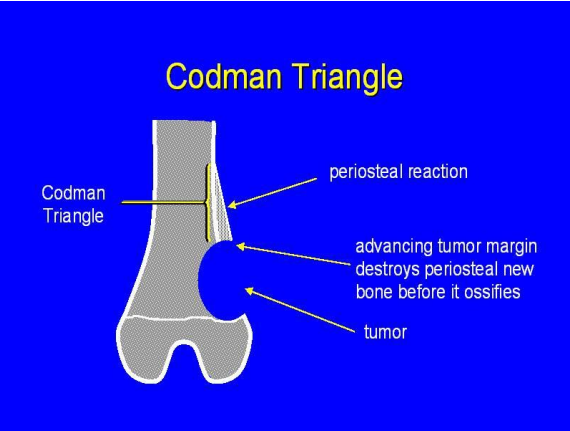
Codman Triangle
a type of periosteal reaction seen with aggressive bone lesions where bone lesions grow so aggressively that they lift the periosteum off the bone and do not allow it to lay down new bone
Treatment
- amputation
- treatment
- radiotherapy
- chemotherapy
Oncotic Patient
- Palliative care - elimination of pair
- Euthanasia
Fractures
Classified by Bone
- humerus
- radius
- femur
- tibia
Classified by Location
- proximal epiphysis
- diaphysis
- distal epiphysis
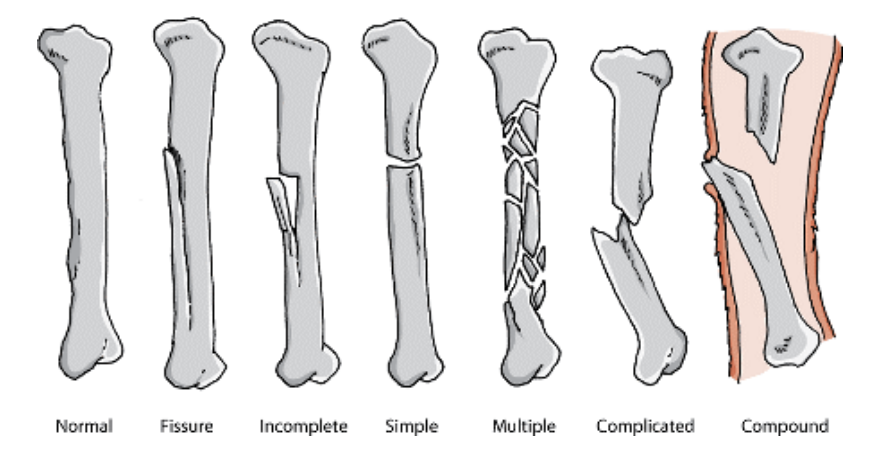
Types of Fracture
- Linear Fracture
- fracture parallel to the bone’s long axis
- Transverse Fracture
- fracture at right angle to the bone’s long axis
- Oblique Fracture
- fracture diagonal to the bone’s long axis
- Spiral Fracture
- fracture where at least one part of the bone has been twisted
- Incomplete Fracture
- a fracture in which the bone fragments are still partially joined. In such cases, there is a crack in the osseous tissue that does not completely traverse the width of the bone
- Complete Fracture
- a fracture in which bone fragments separate completely
- Comminuted Fracture
- a fracture in which the bone has broken into several pieces
 Salter-Harris Fractures in Young Animals
Salter-Harris Fractures in Young Animals