Mortgage Boot Camp – Primary & Secondary Markets, Loan Process, Federal Regulations
Markets & Key Players
Primary market: \text{Depositories} \ (banks, \ S\&Ls, \ credit\ unions),\ Mortgage\ Bankers\ (non!!!–depositories\ using\ warehouse\ lines),\ Mortgage\ Brokers\ (middlemen),\ Mortgage\ Loan\ Originators\ (MLOs)
MLO categories: \text{Registered}\ (depository/Farm\ Credit) vs \text{Licensed}\ (non!!!–depository/broker)
Secondary market = liquidity via securitization; main purchasers: \text{Fannie\ Mae},\ \text{Freddie\ Mac},\ \text{Ginnie\ Mae},\ \text{Private\ Label}
Loan Cycle “Critical (4)”
Application completed when ALIENS (Address, Loan amt, Income, Estimated value/purchase price, Name, SSN)
Only fee allowed prior to LE+ITP: credit report
Appraisal: creditor chooses, borrower pays; lower of appraised vs contract value used
Underwriting notice (Notice of Action Taken) due \le 30 days from ALIENS
Closing = consummation; coordinated by settlement agent
Fees & Cash Calculations
Collect other fees after LE+ITP
Seller concessions limited by program (≈ 2\%–6\%)
Discount points: 1 point = 1\% of loan; borrower may raise rate for credit (formerly YSP)
Cash-to-close formula: \text{Total Acquisition} - \text{Total Credits} = CTC
Refi types: No-cash-out vs Cash-out (must meet Net Tangible Benefit)
Occupancy & Credit Types
Occupancy: Primary, Secondary, Investment (all 1!–4 units)
Closed-end = lump-sum w/ set term; Open-end (HELOC) = revolving
Security & Lien Basics
Security instrument: Mortgage/Deed of Trust (gives foreclosure right)
Note = repayment terms; Deed = ownership
Lien priority = recording order; super-liens (taxes, IRS, HOA) jump ahead
Core Ratios & Formulas
LTV = \dfrac{1^{st}\ mtg}{Value}
CLTV = \dfrac{1^{st}+2^{nd}\ balances}{Value}
HCLTV = \dfrac{1^{st}+2^{nd}\ LIMIT}{Value}
Housing payment = PITI + MI + HOA
Front-end DTI = \dfrac{Housing}{GMI}; Back-end DTI = \dfrac{Housing+Debt}{GMI}
ARM Essentials
Components: Index (SOFR, COFI, CMT), Margin (fixed profit), Rate caps (initial, periodic, lifetime, payment)
Fully-indexed rate: Index + Margin
Hybrid ARMs: 3/1,\ 5/1,\ 7/1,\ 10/1 etc.
Loan Families
Conventional
• Conforming (FNMA/FHLMC limits) vs Non-conforming (jumbo, sub-prime, etc.)
• PMI required when LTV>80\%, cancels at 78\%FHA
• Min score 500 ((<580\Rightarrow10\%\ down; \ge580\Rightarrow3.5\%\ down) • MIP: UFMIP=1.75\%; Annual for life if >90\%\ LTV, else 11 yrs
• HECM reverse mortgage (≥62 yrs)VA
• 100\% financing; guaranty 25\% of loan; Funding Fee (waived for disabled, etc.)USDA
• Rural, income-limited; 0\% down; Guarantee fee financed; fixed-rate only
RESPA (Reg. X) “R.E.S.P.A.”
R Referrals: giving/receiving thing‐of‐value = 10k fine/ 1 yr jail
E Escrows: 2-month cushion, 50/30 rule; Initial & Annual statements
S Servicing Transfer Notice 15/15/60
P Purchase booklet “Your Home Loan Toolkit” within 3 biz days of ALIENS
A ABA disclosure at referral (ownership %, cost, free to shop)
TILA (Reg. Z) – CAR
C Cost of credit: disclose APR & Finance Charge; redisclose if APR>0.125\% change or +\$100 finance charges
A Advertising: trigger terms (#PDF) require full details
R Rescission: primary-dwelling refinance, 3 biz days, 2 copies; violation = 3-yr window
TRID Timing
Loan Estimate: within 3 biz days of app AND \ge 7 biz days before close
Closing Disclosure: borrower receives 3 biz days before consummation
Zero-tolerance fees (credit, origination, appraisal, affiliate, transfer tax)
Ability-to-Repay & Qualified Mortgage
ATR: must verify 8 factors via docs; no equity-based lending
QM limits: fees \le3\%, term \le30 yrs, points triggers; NO Balloon, Interest-only, Neg-Am
Privacy & Credit Laws
GLBA (Reg. P): Privacy notices, Opt-out, Safeguards
FCRA: permissible purpose to pull credit; adverse action disclosures
USA PATRIOT Act: CIP – collect ID, verify, retain, compare to OFAC
Discrimination Laws
ECOA: protects race, color, religion, national origin, sex, marital status, age, public-assist; Notice of Action within 30 days
HMDA: collects data (race, ethnicity, sex); mandatory reporting
High-Cost & Higher-Priced Loans
HOEPA (Section 32): triggers by APR, points/fees, or PPP; counseling; bans PPP, Neg-Am, Balloons (few exceptions)
HPML (Section 35): APR ≥ \text{APOR}+1.5\% (first lien); needs ATR, escrow \ge5 yrs; no PPP > 2 yrs, poss. 2nd appraisal
Essential Disclosure Timeline Cheat-Sheet
Application \rightarrow LE, CHARM, Toolkit, HUD counselor list, SSP list (all 3 biz days)
Before Closing: ABA (referral), Closing Disclosure (3 biz days PTC)
At Closing: Right to Cancel (where applicable), Initial Escrow Stmt
After Closing: Servicing transfer notice, Annual Escrow & Privacy, PMI annual
Detailed Notes:
Markets & Key Players
Primary market: This is where borrowers and lenders directly interact.
Key players include:
ext{Depositories} (banks, S&Ls, credit unions): Financial institutions that accept deposits and originate loans. They typically hold loans in their portfolio or sell them on the secondary market.(These banks use our deposits to fund the loans)
Mortgage Bankers (non–depositories using warehouse lines): Companies that originate and fund loans using funds from lines of credit (warehouse lines-meaning revolving) and then typically sell these loans on the secondary market.
Mortgage Brokers (middlemen): Individuals or firms who do not lend their own money but connect borrowers with various lenders. They earn a commission or fee for matching borrowers with suitable loan programs. (Brokers are Broke) (Get Paid mortgage broker fee)
Mortgage Loan Originators (MLOs): Individuals who take residential mortgage loan applications and offer or negotiate terms of a residential mortgage loan for compensation or gain. They must be licensed or registered. (Can be employed by all three listed above)
Who Approves or Denies your application for licensing?
The approval or denial of your application for licensing is typically handled by state regulatory agencies or a designated mortgage licensing board, which evaluate the application based on criteria such as background checks, credit history, and compliance with state laws. They assess the qualifications of applicants to ensure that they meet all necessary regulations and standards. In some cases, additional documentation or disclosures may be required to support the application process. It is important for MLOs to understand the specific requirements in their state, as these can vary significantly and may affect their ability to operate within the industry.
Components of Background Check:
F-Fingerprints
C-Civil background check
C-Criminal Background Check
C-Credit Check
NMLS is a holding tank for applications
forwards applications to each state
MLO categories:
\text{Registered} (depository/Farm Credit): MLOs who work for federally insured depositories (like banks, S&Ls, credit unions) or institutions regulated by the Farm Credit Administration. They are registered with NMLS but are not required to be state-licensed.
obtains a unique identifier and gets a background check
\text{Licensed} (non–depository/broker): MLOs who work for non-depository institutions (like mortgage bankers) or as mortgage brokers. They must be licensed by the state(s) in which they conduct business and pass the SAFE MLO exam.
employees of housing finance agencies or non-profits are exempt from licensure.
Secondary market = liquidity via securitization: This market allows primary lenders to sell their originated loans to investors, thereby replenishing funds and enabling them to make more loans (providing liquidity or a source of funds).
Main purchasers/entities involved:
\text{Fannie Mae} (Federal National Mortgage Association - FNMA): A government-sponsored enterprise (GSE) that buys conventional conforming loans from lenders, pools them, and sells mortgage-backed securities (MBS) to investors.
\text{Freddie Mac} (Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation - FHLMC): Another GSE similar to Fannie Mae, primarily focused on buying conventional conforming loans from smaller lenders and thrift institutions.
\text{Ginnie Mae} (Government National Mortgage Association - GNMA): A government corporation that guarantees MBS backed by FHA, VA, and USDA loans, making them more attractive to investors. Ginnie Mae does not buy loans directly.
\text{Private Label} : Non-governmental entities that pool and securitize loans, often non-conforming loans like jumbo loans or those with unique characteristics.
A processor performs clerical/support duties
they can: communicate with a borrower to collect information needed to process or underwrite a loan
they cannot: communicate with a borrower to take or complete an application
Why not? Because they are not licensed.
Fine of up to $25,000 per application
This is a violation of the SAFE Act.
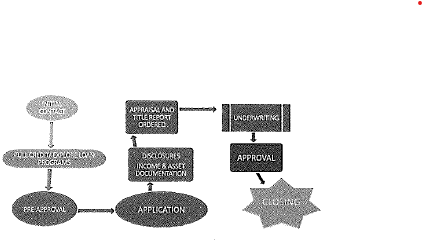
Loan Cycle “Critical (4)”
Application completed when \text{ALIENS} are received:
This stands for
(A) Address of the property
(L) Loan amount requested
(I) Income of the borrower
(E) Estimated value/purchase price of the property
(N) Name of the borrower(s)
(S) Social Security Number of the borrower(s).
Receipt of all six elements triggers the 3-business-day disclosure clock for the Loan Estimate.
Only fee allowed prior to \text{LE+ITP} :
The only fee a lender may charge a borrower before providing the Loan Estimate and receiving the borrower's Intent to Proceed (ITP) is a reasonable charge solely for obtaining a credit report.
Appraisal: The creditor (lender) chooses the appraiser to ensure objectivity, but the borrower is typically responsible for paying for the appraisal. The loan approval is based on the lower of the appraised value or the contract sales price to protect the lender from over-financing.
Appraisal Fees vary by location
If the appraisal comes in lower than the estimated value or lower than the purchase contract price, the lower number is always used!
Underwriting notice (Notice of Action Taken) due \le 30 days from \text{ALIENS} :
Under the Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA), a lender must notify an applicant of the action taken (approval, denial, or counteroffer) on their application within 30 days of receiving a complete application (ALIENS).
Closing = consummation: The closing is the final stage where all documents are signed, and the loan is funded. It is also known as consummation for disclosure timing purposes (when the borrower becomes contractually obligated to the lender).
Coordinated by settlement agent:
The settlement agent (e.g., title company, escrow company, attorney) is a neutral third party responsible for overseeing the closing process, preparing final documents, collecting and disbursing funds, and recording deeds and mortgages.
Fees & Cash Calculations
Collect other fees after \text{LE+ITP} : After the Loan Estimate is provided and the borrower has given their Intent to Proceed, the lender can collect fees for third-party services such as appraisal fees, title services, flood determination fees, and other legitimate settlement charges.
Seller concessions limited by program ( \approx 2\%–6\% ): Seller concessions (or seller contributions) are funds a seller pays on behalf of the buyer towards closing costs or discount points. The maximum allowable percentage varies by loan program (e.g., Conventional typically 3-9% depending on LTV, FHA 6%, VA 4%).
Discount points: 1 point = 1\% of the loan amount. Borrowers pay discount points at closing to reduce the interest rate over the life of the loan. This is a form of prepaid interest.
Borrower may raise rate for credit (formerly YSP): A borrower can choose a higher interest rate than the par rate, which results in a lender credit (Yield Spread Premium, now referred to as borrower credit) being given towards closing costs. This can help reduce the out-of-pocket costs at closing.
Cash-to-close formula: \text{Total Acquisition} - \text{Total Credits} = CTC . Total Acquisition includes the purchase price plus all closing costs. Total Credits include the loan amount, earnest money deposit, seller concessions, and any lender credits. The result is the amount of money the borrower needs to bring to closing.
Refi types:
No-cash-out (Rate-and-Term Refinance): A refinance where the new loan amount is primarily used to pay off the existing mortgage and associated closing costs, with little to no cash back to the borrower.
Cash-out (must meet Net Tangible Benefit): A refinance where the new loan amount is greater than the existing mortgage balance, allowing the borrower to receive cash from the equity in their home. The loan must provide a net tangible benefit to the borrower (e.g., lower interest rate, shorter term, payment reduction, debt consolidation).
Occupancy & Credit Types
Occupancy: Primary, Secondary, Investment (all 1!–4 units)
Primary Residence: The property where the borrower lives the majority of the time. This typically offers the lowest interest rates due to lower perceived risk.
Secondary Residence: A second home that the borrower occupies for a portion of the year, not as their primary residence. It must be a reasonable distance from the primary home and not primarily rented out. Rates are typically slightly higher than primary but lower than investment.
Investment Property: A property purchased with the intention of generating income through rent or capital appreciation. These properties carry the highest risk for lenders, resulting in higher interest rates and stricter underwriting requirements.
1-4 Units: All occupancy types can apply to properties with 1 to 4 dwelling units. For 2-4 unit properties, at least one unit must be owner-occupied for it to be considered primary or secondary residence.
Closed-end = lump-sum w/ set term; Open-end (HELOC) = revolving
Closed-End Credit: A type of credit where the loan amount, interest rate, and repayment schedule are fixed at the time of origination. The borrower receives a single lump sum, and the loan is paid off over a set term (e.g., a traditional mortgage or car loan).
Open-End Credit (HELOC): A line of credit that allows borrowers to draw funds as needed up to a certain maximum amount, repay them, and then draw again. The interest rate is often variable, and actual payments depend on the outstanding balance (e.g., Home Equity Line of Credit - HELOC, credit cards).
Security & Lien Basics
Security instrument: Mortgage/Deed of Trust (gives foreclosure right)
Security Instrument: A legal document that secures a real estate loan by giving the lender a lien on the property. In the event of default, it allows the lender to take foreclosure action to recover the debt.
Mortgage: Used in some states (lien theory states). The borrower retains title, but the lender holds a lien. Foreclosures are typically judicial (require court action).
Deed of Trust: Used in other states (title theory states). A third party (trustee) holds the legal title to the property on behalf of the lender until the loan is repaid. Foreclosures are often non-judicial (exercised by the trustee under a power of sale clause).
Note = repayment terms; Deed = ownership
Promissory Note (Note): A legal document that serves as the borrower's promise to repay the debt. It outlines the specific terms of the loan, including the interest rate, payment schedule, and terms of default. It does not provide the lender a right to the property directly, but allows them to sue the borrower if they fail to repay.
Deed (Title): A legal document that transfers ownership interest in real property from one party to another. It provides evidence of who owns the property. The deed is recorded in public records.
Lien priority = recording order; super-liens (taxes, IRS, HOA) jump ahead
Lien Priority: The order in which claims against a property will be satisfied in the event of a foreclosure or sale. Generally, liens are prioritized based on the order in which they are recorded in the public records ("first in time, first in right").
Super-Liens: Certain types of liens, by law, take precedence over other recorded liens, regardless of their recording date. These include:
Property Taxes: Unpaid property taxes always have the highest priority.
IRS Tax Liens: Federal tax liens can sometimes supersede previously recorded mortgages.
Homeowners Association (HOA) Liens: In some states, HOA assessment liens can have super-lien status, taking priority over first mortgages.
Core Ratios & Formulas
LTV = \dfrac{1^{st}\ mtg}{Value}
Loan-to-Value (LTV): A ratio comparing the loan amount to the property's value (purchase price or appraised value, whichever is less). Lenders use LTV to assess risk; a higher LTV indicates higher risk.
CLTV = \dfrac{1^{st}+2^{nd}\ balances}{Value}
Combined Loan-to-Value (CLTV): A ratio comparing the sum of the first mortgage balance and the current balance of any subordinate (second) liens to the property's value. Used when there are multiple loans on a property.
HCLTV = \dfrac{1^{st}+2^{nd}\ LIMIT}{Value}
High Combined Loan-to-Value (HCLTV): Also known as Total Loan-to-Value (TLTV). This ratio includes the full credit limit of open-end credit (like a HELOC), even if the borrower hasn't drawn to the maximum. It's calculated by adding the first mortgage balance to the maximum credit line of the second mortgage and dividing by the property's value. This assesses potential future debt exposure.
Housing payment = PITI + MI + HOA
Housing Payment: The total monthly cost associated with owning a home. It typically includes:
Principal: The portion of the payment that reduces the loan balance.
Interest: The cost of borrowing money.
Taxes: Monthly prorated portion of annual property taxes.
Insurance: Monthly prorated portion of homeowner's insurance.
MI: Mortgage Insurance (PMI, MIP) if applicable.
HOA: Homeowners Association dues if applicable.
Front-end DTI = \dfrac{Housing}{GMI}; Back-end DTI = \dfrac{Housing+Debt}{GMI}
Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratios: Used by lenders to assess a borrower's ability to manage monthly payments and repay debts.
Front-End DTI (Housing Ratio): Compares the total proposed monthly housing payment (PITI + MI + HOA) to the borrower's Gross Monthly Income (GMI). It indicates what percentage of income goes towards housing costs.
Back-End DTI (Total Debt Ratio): Compares the total of the housing payment plus all other recurring monthly debts (credit card minimums, car loans, student loans, child support, etc.) to the borrower's Gross Monthly Income (GMI). This provides a comprehensive view of the borrower's overall debt burden.
ARM Essentials
Components: Index (SOFR, COFI, CMT), Margin (fixed profit), Rate caps (initial, periodic, lifetime, payment)
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARMs): Loans where the interest rate can change periodically. Key components:
Index: A benchmark rate that reflects market interest rates. Common indices include:
SOFR (Secured Overnight Financing Rate)
COFI (Cost of Funds Index)
CMT (Constant Maturity Treasury)
Margin: A fixed percentage point amount added to the index to determine the borrower's interest rate. It represents the lender's profit and remains constant over the life of the loan.
Rate Caps: Limits on how much the interest rate can change:
Initial Cap: Limits how much the rate can change at the first adjustment.
Periodic Cap: Limits how much the rate can change at each subsequent adjustment period.
Lifetime Cap: Sets the maximum (and sometimes minimum) interest rate that can be charged over the entire life of the loan.
Payment Cap: Limits the amount the monthly payment can increase or decrease, even if the interest rate dictates a larger change (can lead to negative amortization).
Fully-indexed rate: Index + Margin
The actual interest rate the borrower pays after the initial fixed period, determined by adding the current index value to the fixed margin.
Hybrid ARMs: 3/1,\ 5/1,\ 7/1,\ 10/1 etc.
ARMs that combine an initial fixed-rate period with subsequent adjustable periods. The first number indicates the number of years the initial rate is fixed, and the second number indicates how often the rate will adjust thereafter (e.g., a 5/1 ARM has a fixed rate for 5 years, then adjusts annually).
Loan Families
Conventional Mortgage: Loans that are not insured or guaranteed by a government agency (like FHA, VA, USDA).
Conforming (FNMA/FHLMC limits) vs Non-conforming (jumbo, sub-prime, etc.)
Conforming Loans: Meet the loan limits and underwriting guidelines set by Fannie Mae (FNMA) and Freddie Mac (FHLMC), making them eligible for purchase by these GSEs. This makes them easier to sell on the secondary market.
Non-Conforming Loans: Do not meet these guidelines.
Jumbo Loans: Exceed the conforming loan limits for a particular area. They are typically held in lender portfolios or securitized by private investors.
Sub-prime Loans: Offered to borrowers with lower credit scores or other risk factors. These often carry higher interest rates and fees.
PMI required when LTV>80\%, cancels at 78\%
Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI): Required on conventional loans when the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio is greater than 80% (i.e., less than 20% down payment). It protects the lender in case of borrower default.
Cancellation: PMI can typically be canceled when the LTV reaches 80% of the original value (either through principal reduction or increased property value, often with an appraisal). Lenders are legally required to automatically cancel PMI when the LTV reaches 78% of the original value, provided the loan is current.
FHA (Federal Housing Administration) Loans: Insured by the FHA, allowing lenders to offer loans with lower down payments and less stringent credit requirements.
Min score 500 (<580 \Rightarrow 10\%\ down; \ge 580 \Rightarrow 3.5\%\ down)
FHA loans allow for lower credit scores. Borrowers with a FICO score of 580 or higher are eligible for the maximum financing of 96.5% LTV (3.5% down payment). Those with scores between 500 and 579 are typically limited to 90% LTV (10% down payment).
MIP: UFMIP=1.75\%; Annual for life if >90\%\ LTV, else 11 yrs
Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP): Required on all FHA loans.
Upfront MIP (UFMIP): A one-time premium of 1.75% of the loan amount, typically financed into the loan.
Annual MIP: A recurring premium paid monthly. The duration depends on the LTV at origination. If the LTV is greater than 90% at origination, annual MIP is required for the life of the loan. If the LTV is 90% or less, annual MIP is typically cancelled after 11 years.
HECM reverse mortgage (\ge62 yrs)
Home Equity Conversion Mortgage (HECM): The FHA's reverse mortgage program available to homeowners aged 62 or older who have significant home equity. It allows them to convert a portion of their home equity into cash without selling the home or making monthly mortgage payments (though property taxes, insurance, and HOA dues still must be paid). The loan becomes due when the last borrower leaves the home permanently.
VA (Department of Veterans Affairs) Loans: Guaranteed by the VA for eligible veterans, active-duty service members, and surviving spouses.
100\% financing: VA loans allow eligible borrowers to purchase a home with no down payment, provided the sales price does not exceed the appraised value.
Guaranty 25\% of loan: The VA guarantees a portion of the loan (typically 25% of the loan amount up to the conforming loan limit), which protects the lender in case of default and eliminates the need for mortgage insurance.
Funding Fee (waived for disabled, etc.): A one-time fee paid by the borrower to the VA to help offset the cost of the program. The amount varies based on down payment, loan type, and prior use of VA benefits. It is waived for veterans with service-connected disabilities or surviving spouses of veterans who died in service or from a service-connected disability.
USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) Loans: Also known as Rural Development loans, aimed at low-to-moderate income borrowers in eligible rural areas.
Rural, income-limited: Properties must be located in designated rural areas, and borrowers must meet specific income limits (typically up to 115% of the median household income for the area).
0\% down: USDA loans allow for 100% financing, meaning no down payment is required.
Guarantee fee financed: Similar to FHA's UFMIP, USDA charges an upfront guarantee fee (currently 1%) which is typically financed into the loan, as well as an annual guarantee fee (currently 0.35%) paid monthly.
fixed-rate only: USDA loans are available only as fixed-rate mortgages, providing predictable monthly payments.
RESPA (Reg. X) “R.E.S.P.A.”
R Referrals: giving/receiving thing‐of‐value = 10k fine/ 1 yr jail
Referrals/Section 8: Prohibits kickbacks, fee-splitting, and unearned fees for referrals of settlement services. No person shall give or accept any part of a charge for services performed or render any service as part of a real estate settlement service other than for services actually performed. Violations can result in fines up to \$10,000 and/or up to 1 year in prison.
E Escrows: 2-month cushion, 50/30 rule; Initial & Annual statements
Escrow Accounts (Impound Accounts): Funds collected by the lender or servicer to pay future property taxes, homeowner's insurance, and sometimes mortgage insurance.
2-month cushion: RESPA allows lenders to collect and hold a cushion equal to no more than two months (1/6th) of the total annual escrow payments.
50/30 rule: Refers to rules related to escrow account analysis, ensuring that balances don't exceed allowed amounts. If there is a surplus of \$50 or more at the annual review, it must be refunded to the borrower.
Initial & Annual statements: An initial escrow statement is provided at closing or within 45 days. An annual escrow statement must be provided within 30 days of the end of the escrow computation year, summarizing account activity.
S Servicing Transfer Notice 15/15/60
Servicing Transfer: If the loan servicer sells or transfers the servicing rights to another company, both the old servicer and the new servicer must provide notice to the borrower.
The notice must be sent at least 15 days before the effective date of the transfer by the transferring servicer, and at least 15 days after by the receiving servicer.
There is a 60-day grace period during which the borrower cannot be penalized for making a timely payment to the old servicer instead of the new one.
P Purchase booklet “Your Home Loan Toolkit” within 3 biz days of ALIENS
Purchase Booklet: For purchase transactions, borrowers must receive "Your Home Loan Toolkit: A Step-by-Step Guide" (formerly "Settlement Costs Booklet") within 3 business days of application completion (i.e., receipt of ALIENS).
A ABA disclosure at referral (ownership %, cost, free to shop)
Affiliated Business Arrangement (ABA) Disclosure: Required when a loan originator refers a borrower to a settlement service provider with whom the originator has an ownership or other beneficial interest.
The disclosure must be given at the time of referral.
It must state the nature of the relationship, an estimated charge for the service, and inform the borrower that they are not required to use the recommended provider and are free to shop for other providers.
TILA (Reg. Z) – CAR
C Cost of credit: disclose APR & Finance Charge; redisclose if APR > 0.125\% change or +\$100 finance charges
Cost of Credit Disclosures: TILA requires lenders to disclose the true cost of credit to consumers.
Annual Percentage Rate (APR): The total cost of the loan expressed as a yearly rate. It includes the interest rate plus certain upfront fees (like origination fees, discount points, mortgage insurance premiums).
Finance Charge: The total dollar amount of all charges payable directly or indirectly by the borrower and imposed directly or indirectly by the creditor as an incident to or a condition of the extension of credit.
Redisclosure Requirements: If the disclosed APR changes by more than 0.125\% (1/8th of a percent) from the original disclosure, or if the finance charge changes by more than \$100 , a new disclosure must be provided to the borrower, and a new waiting period may apply before closing.
A Advertising: trigger terms (#PDF) require full details
Advertising Rules: TILA places restrictions on how loan terms are advertised to prevent misleading consumers.
Trigger Terms: Specific terms in an advertisement that, if used, require the advertiser to disclose additional information. Examples (often remember as "#PDF"):
#: The number of payments
P: The amount of any payment
D: The amount of any down payment
F: The period of repayment (e.g., "30-year loan")
When a trigger term is used, the advertisement must also clearly and conspicuously disclose: the amount or percentage of the down payment, the terms of repayment (including the payment schedule), and the annual percentage rate (APR).
R Rescission: primary-dwelling refinance, 3 biz days, 2 copies; violation = 3-yr window
Right of Rescission: Allows borrowers to cancel certain credit transactions secured by their principal dwelling without penalty.
Applicability: Applies to primary-dwelling refinances and home equity lines of credit (HELOCs), but not to purchase mortgages or investment property loans.
3 Business Days: The borrower has three business days following the later of the signing of the loan documents, receipt of the rescission notice, or receipt of all material disclosures, to rescind the loan.
2 Copies: Each borrower with an ownership interest in the property must receive two copies of the Right to Rescind notice.
Violation = 3-year window: If the lender fails to provide the required rescission notices or accurate material disclosures, the rescission period can be extended from three business days to three years.
TRID Timing
Loan Estimate: within 3 biz days of app AND \ge 7 biz days before close
Provision Timeline: The Loan Estimate (LE) must be provided to the borrower within 3 business days of receiving a complete application (ALIENS).
Waiting Period: The borrower must receive the LE no later than 7 business days before loan consummation (closing). This ensures adequate time for review. If the LE is mailed, it is considered received 3 business days after mailing.
Closing Disclosure: borrower receives 3 biz days before consummation
Provision Timeline: The borrower must receive the Closing Disclosure (CD) no later than 3 business days before loan consummation. This is a strict "waiting period" that allows borrowers to compare the final terms against the LE.
Zero-tolerance fees (credit, origination, appraisal, affiliate, transfer tax)
Zero-Tolerance Fees: Fees that cannot increase from the amount disclosed on the Loan Estimate to the amount charged on the Closing Disclosure. If they do, the lender must cure the discrepancy. These include:
Lender's origination charges (e.g., points, administration fees).
Charges for services for which the consumer is not allowed to shop (e.g., appraisal fee, credit report fee, flood determination fee, tax service fee).
Charges for services provided by an affiliate of the lender.
Transfer taxes.
Ability-to-Repay & Qualified Mortgage
ATR (Ability-to-Repay): must verify 8 factors via docs; no equity-based lending
Ability-to-Repay (ATR) Rule: Mandates that lenders determine a consumer's ability to repay a mortgage loan before extending credit. This rule aims to prevent irresponsible lending.
8 Factors for Verification: Lenders must verify the following factors using reasonably reliable third-party documentation:
Current or reasonably expected income or assets
Current employment status
Monthly mortgage payment for the loan
Monthly payments on any simultaneous loans
Monthly payments for mortgage-related obligations (property taxes, insurance, HOA fees)
Current debt obligations (including alimony and child support)
Monthly DTI ratio or residual income
Credit history
No Equity-Based Lending: The rule explicitly prohibits lending based solely on the equity in a borrower's home, requiring a comprehensive assessment of their financial capacity.
QM (Qualified Mortgage): limits: fees \le3\%, term \,\le30 yrs, points triggers; NO Balloon, Interest-only, Neg-Am
Qualified Mortgage (QM): A category of loans that offer lenders certain legal protections from liability under the ATR rule. QMs are generally considered "safer" loans.
QM Limits/Features: To be a QM, a loan must meet specific criteria:
Fees \le3\%: Generally, the total points and fees charged to the borrower cannot exceed 3% of the total loan amount (with specific thresholds for smaller loans).
Term \le30 yrs: The loan term cannot exceed 30 years.
Underwriting and Points Triggers: Loans must meet specific underwriting standards including DTI limits (though this can be rebuttable for prime loans) and various points and fees thresholds.
NO Risky Features: QMs explicitly prohibit certain risky features:
Balloon Payments: A large payment at the end of the loan term.
Interest-Only Payments: Payments that only cover the interest, with no principal reduction.
Negative Amortization (Neg-Am): Payments that are less than the interest due, causing the loan balance to increase over time.
Privacy & Credit Laws
GLBA (Reg. P): Privacy notices, Opt-out, Safeguards
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA): Also known as Regulation P. Focuses on protecting consumers' nonpublic personal information (NPI) held by financial institutions.
Privacy Notices: Financial institutions must provide customers with a clear and conspicuous notice that explains their information-sharing practices, both at the time an account relationship is established and annually thereafter.
Opt-out Right: Consumers must be given the opportunity to "opt out" (prevent) their financial institution from sharing their NPI with unaffiliated third parties.
Safeguards Rule: Requires financial institutions to develop, implement, and maintain a comprehensive information security program to protect the security, confidentiality, and integrity of customer NPI.
FCRA (Fair Credit Reporting Act): permissible purpose to pull credit; adverse action disclosures
Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA): Governs the collection, dissemination, and use of consumer credit information. Ensures accuracy, fairness, and privacy of consumer credit reports.
Permissible Purpose: Lenders must have a permissible purpose (e.g., in connection with a credit transaction) to obtain a consumer's credit report.
Adverse Action Disclosures: If a lender denies credit or takes other adverse actions (e.g., offers less favorable terms) based in whole or in part on information from a credit report, they must provide an adverse action notice. This notice includes the reason for the adverse action and the name and contact information of the consumer reporting agency (CRA) that provided the report.
USA PATRIOT Act: CIP – collect ID, verify, retain, compare to OFAC
Uniting and Strengthening America by Providing Appropriate Tools Required to Intercept and Obstruct Terrorism Act (USA PATRIOT Act): A federal law enacted after 9/11 to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.
Customer Identification Program (CIP): Financial institutions are required to establish a CIP to verify the identity of customers. This involves:
Collecting ID: Obtaining identifying information (e.g., name, DOB, address, SSN/TIN).
Verifying: Using documents (e.g., driver's license, passport) or non-documentary methods to verify identity.
Retaining: Keeping records of the verification process.
Comparing to OFAC: Checking customer names against lists of suspected terrorists and criminals maintained by the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC).
Discrimination Laws
ECOA (Equal Credit Opportunity Act): protects race, color, religion, national origin, sex, marital status, age, public-assist; Notice of Action within 30 days
Equal Credit Opportunity Act (ECOA): Prohibits discrimination in any credit transaction.
Protected Classes: Lenders cannot discriminate against applicants based on:
Race
Color
Religion
National Origin
Sex
Marital Status (meaning single, married, separated, divorced, widowed)
Age (provided the applicant has the capacity to contract)
Receipt of Public Assistance Income (e.g., Social Security, disability).
Notice of Action within 30 days: Creditors must notify applicants of the action taken on their credit application (approval, denial, or counteroffer) within 30 days of receiving a complete loan application. If denied, the reason for the denial must be provided, along with the ECOA notice.
HMDA (Home Mortgage Disclosure Act): collects data (race, ethnicity, sex); mandatory reporting
Home Mortgage Disclosure Act (HMDA): Requires certain financial institutions to collect and report data about their mortgage lending activity.
Data Collected: Includes information about the applicant (e.g., race, ethnicity, sex, income) and the loan (e.g., loan type, purpose, total loan amount, property location/type).
Mandatory Reporting: This data is publicly disclosed and used by regulators and the public to identify potential discriminatory lending patterns and assess whether financial institutions are meeting the housing needs of their communities.
High-Cost & Higher-Priced Loans
HOEPA (Home Ownership and Equity Protection Act – Section 32): triggers by APR, points/fees, or PPP; counseling; bans PPP, Neg-Am, Balloons (few exceptions)
Home Ownership and Equity Protection Act (HOEPA): An amendment to TILA designed to protect consumers from predatory lending associated with "high-cost mortgages."
Triggers: A loan becomes a high-cost mortgage if its APR, points/fees, or prepayment penalty (PPP) exceed specific thresholds set by regulation.
Mandatory Counseling: Borrowers applying for a HOEPA loan must receive mandatory housing counseling from a HUD-approved counselor prior to closing.
Banned Provisions: HOEPA loans prohibit certain harmful features:
Prepayment Penalties (PPP)
Negative Amortization (Neg-Am)
Balloon Payments (with a few limited exceptions for certain bridge loans)
Others like financing points and fees, extending credit without regard to ATR.
HPML (Higher-Priced Mortgage Loan – Section 35): APR \ge \text{APOR}+1.5\% (first lien); needs ATR, escrow \ge5 yrs; no PPP > 2 yrs, poss. 2nd appraisal
Higher-Priced Mortgage Loan (HPML): Loans with an APR that exceeds the Average Prime Offer Rate (APOR) by a certain percentage. APOR is a benchmark rate based on average prime offer rates for comparable transactions.
APR Trigger: A loan is HPML if its APR is greater than or equal to:
APOR + 1.5\% for first-lien conventional mortgages.
APOR + 3.5\% for subordinate-lien mortgages.
Requirements for HPMLs:
Needs ATR: Subject to the Ability-to-Repay rule.
Mandatory Escrow \ge5 yrs: Lenders generally must establish an escrow account for property taxes and homeowner's insurance for at least five years (unless certain exemptions apply).
No Prepayment Penalties > 2 yrs: Prepayment penalties are generally prohibited for HPMLs, unless they are specifically allowed and limited to the first two years of the loan.
Possible 2nd Appraisal: If the sales price significantly exceeds the seller's acquisition price within a short period, a second, independent appraisal may be required to prevent property flipping.
Essential Disclosure Timeline Cheat-Sheet
Application \rightarrow LE, CHARM, Toolkit, HUD counselor list, SSP list (all 3 biz days)
Loan Estimate (LE): As detailed above, within 3 biz days of application.
Consumer Handbook on Adjustable Rate Mortgages (CHARM) Booklet: Required for all ARM loans, informing borrowers about the risks and features of ARMs, given at application or within 3 business days.
"Your Home Loan Toolkit" (Purchase Booklet): As detailed above, for purchase transactions, within 3 business days of application.
HUD Counselor List: A list of HUD-approved counseling agencies must be provided within 3 business days of application.
Servicing Disclosure Statement (SDS) / Affiliated Business Arrangement (ABA) (SSP list): Also within 3 business days, detailing whether the lender intends to service the loan or transfer servicing, and disclosing any affiliated business arrangements.
Before Closing: ABA (referral), Closing Disclosure (3 biz days PTC)
Affiliated Business Arrangement (ABA) Disclosure: As detailed above, at the time of referral if making a referral to an affiliate.
Closing Disclosure (CD): As detailed above, the borrower must receive it at least 3 business days prior to consummation (PTC).
At Closing: Right to Cancel (where applicable), Initial Escrow Stmt
Right to Cancel (Notice of Right to Rescind): Handed to borrowers at closing for applicable transactions (primary residence refinances, HELOCs).
Initial Escrow Statement: Provided at closing or within 45 days after closing, detailing the initial deposits into the escrow account and the projected payments for the first year.
After Closing: Servicing transfer notice, Annual Escrow & Privacy, PMI annual
Servicing Transfer Notice: As detailed above, within 15$$ days before/after transfer.
Annual Escrow Statement: As detailed above, provided annually for loans with escrow accounts.
Annual Privacy Notice (GLBA): As detailed above, provided annually as long as a customer relationship exists.
PMI Annual Disclosure: Lenders must provide an annual disclosure regarding the borrower's PMI, including information on how to cancel it.