(5) Hair shape modulation
Hair styling
An operation to deform hair shaft in two possible ways:
Permanent waving (PW): adding wave or curl.
Relaxing: removing curls/waves.
“Relaxer” and “Rebonding” are terms usually applied to products intended for kinky hair treatment only. While "“Straightener” refer to products used for curly and straight hair treatment (PW).
L’Oreal curl classification is able to quantitatively describe hair’s curl degree from numbers 1—8. Thermal techniques can straighten all curl types, however, curl types above 5 need hydroxide-based systems if permanent straightening is desired.
Principle of hair modulation
An alteration of the cortex, temporary or permanent, must occur to change hair shape. What happens is that chemical bonds (hydrogen or disulfide bonds) of the keratin 3D protein structure are broken and mechanically or chemically fixed in the new form. So, the hair doesn’t return to its natural form unless wetted or replaced.
Types of hair styling
Choosing hair treatment is based on many factors:
Degree of curl (most influential)
Degree of desired curl/straightness
Convenience
1. Temporary hair modulation
Involves lower energy processes to disrupt and rearrange hydrogen bonds and salt linkages (weak) through water or heat.
Thermal processing
Hair has to be pre-wetted to break the hydrogen bonds of keratin and permit temporary opening of original hair structure.
During straightening/flat ironing: hydrogen bonds of the alpha keratin polypeptide chains are broken, by heat or water, into beta keratin. The greater the heat used; the more bonds are broken.
After cooling, as long as tension is maintained, hydrogen bonds reform and keep hair in the styled form.
Disadvantages:
It’s a temporary process, but it can irreversibly denature hair at temp.:
155-160 for wet hair.
235-250 for dry hair
Exposure to moisture (perspiration, humidity, etc) will revert hair back to its natural state.
Split ends in the cuticle layer occur and scales lift.
Dry, damaged looking hair.
Vulnerable to environment
More negative charges and flyways.
A very damaged condition of “bubble hair” could occur (water becomes steam inside hair).
Heating hair above boiling point of water/100C results in more free-radicals than UV-irradiation.
2. Permanent styling (chemical treatment)
A more permanent modulation/styling of hair by altering disulfide bonds of keratin.
Curly hair can be chemically straightened by two ways:
Straightening/waving: two-step chemical process with reduction and oxidation
Relaxing: one-step chemical process applying strong alkali.
The chemistry of hair straightening involves two steps:
Disulfide bonds are cleaved in a reducing step—→ Oxidation to form new disulfide bonds.
The difference between straightening and waving procedures with reducing agents is how the hair is set (configuration) before oxidation (to ‘lock in’ the new form').
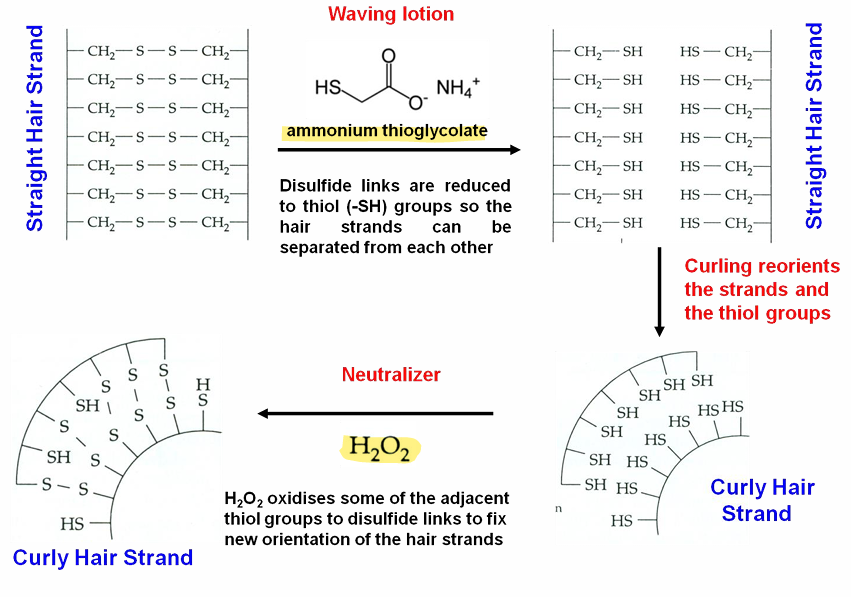
For waving: the reducing agent/product is usually liquid, and hair is curled with rollers before oxidizing.
For straightening: product is usually a thick cream, which assists in holding hair fibres for further configuration or form manipulation.
Most common reducing agents: ammonium thioglycolate (thiols) and sulfite.
Oxidizing agent, hydrogen peroxide, reforms CyS—SCy bonds.
Hair relaxing
pH of relaxers: 11 to 14.
The high pH causes swelling of the fiber, cuticle abrasion, and increase in porosity.
Fast processing time.
Lye relaxers
Mostly used and based on NaOH.
Non-lye relaxers
Guanidine hydroxide, KOH, lithium hydroxide.
The chemistry of hair relaxing involves an irreversible step of a monosulfide bridge, lanthionine, formation during the alkaline treatment.
Furthermore, there’s a partial hydrolysis of protein chains building up the backbone of the hair fibers (irreversible, damaging).
The neutralizer, after rinsing, stops the action of any chemical relaxer that may remain in the hair.
Hair straightening
Formaldehyde/glutaraldehyde/methylene glycol | (Brazilian) keratin hair straightening |
Disrupt the tertiary structure of hair proteins. | Newer, more popular treatments include Nano Keratin system. |
Even though it’s banned at any concen., it’s cheap and quick and leaves shiny strands so it’s still used. | Products are intended to:
|
Brazilian Sanitary Surveillance Agency (ANVISA) prohibited the substance’s use anywhere. | Many of these treatments contain hydrolysed keratin extracted from wool of sheep. |
Substances with >0.05% formaldehyde must be labelled “contains formaldehyde”. So, tricks to the consumer can be done here. Max formaldehyde allowed in beauty products is 0.2%. | The small molecules diffuse into hair cortex to react with hair keratin. Amino acids (hydrolysed keratin |
Has carcinogenic, teratogenic potential and may damage tissues of upper respiratory tract when inhaled.
| Heating of the hair (blow drying) enhances formaldehyde’s ability to react with keratin, allowing it to cross-link the hydrolysed keratin in the solution to the natural keratin in the hair fibers, and seals the cuticle. |
Can irritate the eyes and nose, cause allergic reactions of the skin, eyes and lungs |
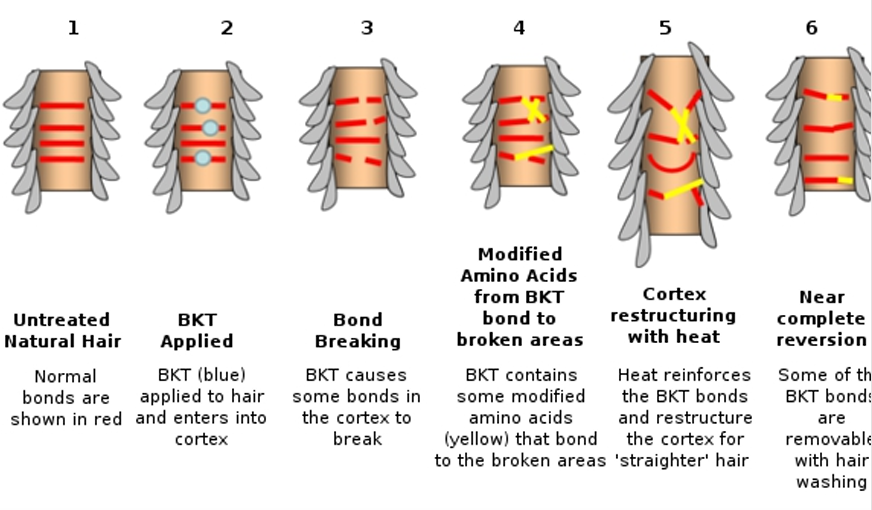
Non-formaldehyde containing keratin-treatment
Non-formaldehyde containing straightening products/ Safe keratin treatments (SKT)
Introduced to market as KeraLuxe.
Main ingredients are hydrolysed keratin combo. with glyoxyloyl carbocysteine, glyoxyloyl keratin amino acids, silicone derivatives, and fatty acids.
These ingredients weaken hydrogen and salt hair bonds and allow interaction with the cysteine bonds.
As the hair is heated, the cysteine bonds are strengthened, which holds the keratin amino acids in the hair shaft.
Cystine system
Straightens hair through a sulfite/urea active complex, heat and protecting/restructuring proteins.
The complex works on the disulfide bonds of the hair to gently relax hair fiber.
The system uses high concen. of cystine, a major component of human hair.
Under heat, the silanol cross-links with the hair fiber to provide a protective shield on the surface of the hair, while the amino acids enhance the longevity of the treatment by aiding in the restructuring of the disulfide bonds. The result is sleeker, smoother hair that requires less time and effort to dry and style.
 Knowt
Knowt