Air Pollution Policy
What is the Clean Air Act
What are the impacts of the Clean Air act
What is the Montreal Protocol
How does the Clean Air Act impact climate change
What is the denial machine
What US policies have sought to address climate change
Before the Clean Air act
Skies were much much darker than they are now
Clean Air Act
3 Primary Goals
Reduce outdoor concentrations of air pollutants that cause smog, haze, acid rain and other problems
Reduce emissions of toxic air pollutants that are known or suspected to cause cancer/ other health effects
Phase out the production and use of chemicals that destroy the stratospheric ozone
How it works: regulates emissions from stationary and mobile sources
Like point and non-point sources (most are point source)
Stationary: factories
Mobile: cars
6 criteria
Sulfur dioxide
Burning coal and oil
Emitted by power plants
Nitrogen dioxide
Burning fuel via vehicles
Harmful to ozone
Carbon Monoxide
Colorless, odorless
Vehicles and machinery that burns fossil fuels
Particulate Matter 2.5
Size of pollutant
Smaller and can be inhaled
Ground level ozone
Odorless, colorless
Aboce the earth's surface
Produced when NO's and VOC's react with sunlight and stagnant air
Lead
Ore, processed metals, leaded aviation fuel, incinerators, utilities
We worry less about lead since the clean air act
They used to put lead in gasoline
187 Regulated Air Pollutants
Where do most emissions come from
Stationary fuel combustion
Industry (largest contributor)
Highway vehicles
Non-road mobile
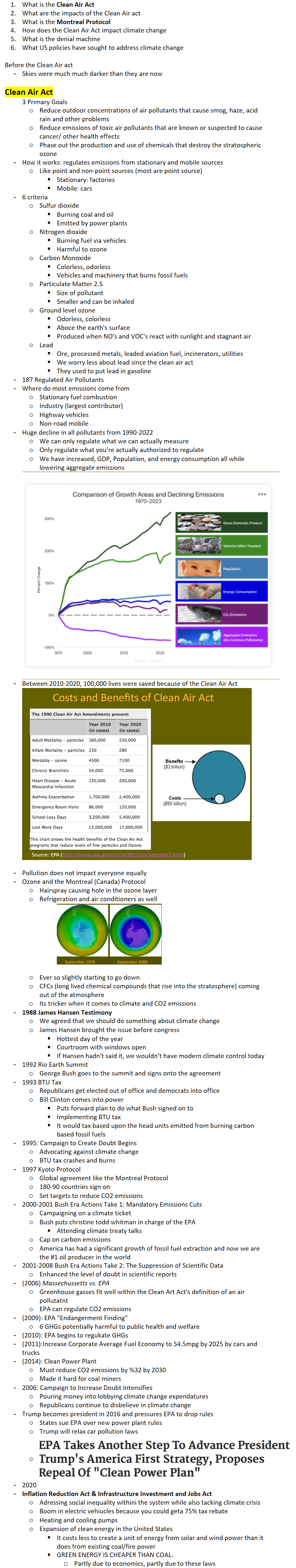
Huge decline in all pollutants from 1990-2022
We can only regulate what we can actually measure
Only regulate what you’re actually authorized to regulate
We have increased, GDP, Population, and energy consumption all while lowering aggregate emissions
Between 2010-2020, 100,000 lives were saved because of the Clean Air Act
Pollution does not impact everyone equally
Ozone and the Montreal (Canada) Protocol
Hairspray causing hole in the ozone layer
Refrigeration and air conditioners as well
Ever so slightly starting to go down
CFCs (long lived chemical compounds that rise into the stratosphere) coming out of the atmosphere
Its tricker when it comes to climate and CO2 emissions
1988 James Hansen Testimony
We agreed that we should do something about climate change
James Hansen brought the issue before congress
Hottest day of the year
Courtroom with windows open
If Hansen hadn't said it, we wouldn’t have modern climate control today
1992 Rio Earth Summit
George Bush goes to the summit and signs onto the agreement
1993 BTU Tax
Republicans get elected out of office and democrats into office
Bill Clinton comes into power
Puts forward plan to do what Bush signed on to
Implementing BTU tax
It would tax based upon the head units emitted from burning carbon based fossil fuels
1995: Campaign to Create Doubt Begins
Advocating against climate change
BTU tax crashes and burns
1997 Kyoto Protocol
Global agreement like the Montreal Protocol
180-90 countries sign on
Set targets to reduce CO2 emissions
2000-2001 Bush Era Actions Take 1: Mandatory Emissions Cuts
Campaigning on a climate ticket
Bush puts christine todd whitman in charge of the EPA
Attending climate treaty talks
Cap on carbon emissions
America has had a significant growth of fossil fuel extraction and now we are the #1 oil producer in the world
2001-2008 Bush Era Actions Take 2: The Suppression of Scientific Data
Enhanced the level of doubt in scientific reports
(2006) Massechussetts vs. EPA
Greenhouse gasses fit well within the Clean Art Act's definition of an air pollutatnt
EPA can regulate CO2 emissions
(2009): EPA "Endangerment Finding"
6 GHGs potentially harmful to public health and welfare
(2010): EPA begins to regukate GHGs
(2011):Increase Corporate Average Fuel Economy to 54.5mpg by 2025 by cars and trucks
(2014): Clean Power Plant
Must reduce CO2 emissions by %32 by 2030
Made it hard for coal miners
2006: Campaign to Increase Doubt Intensifies
Pouring money into lobbying climate change expendatures
Republicans continue to disbelieve in climate change
Trump becomes president in 2016 and pressures EPA to drop rules
States sue EPA over new power plant rules
Trump will relax car pollution laws
2020
Inflation Reduction Act & Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act
Adressing social inequality withini the system while also tacking climate crisis
Boom in electric vehiucles because you could geta 75% tax rebate
Heating and cooling pumps
Expansion of clean energy in the United States
It costs less to create a unit of energy from solar and wind power than it does from existing coal/fire power
GREEN ENERGY IS CHEAPER THAN COAL.
Partly due to economics, partly due to these laws