Mild Traumatic Brain Injuries
- Concussions
- What is a Concussion?
- A mild brain injury resulting from a direct blow to the head resulting in physiological changes in brain function
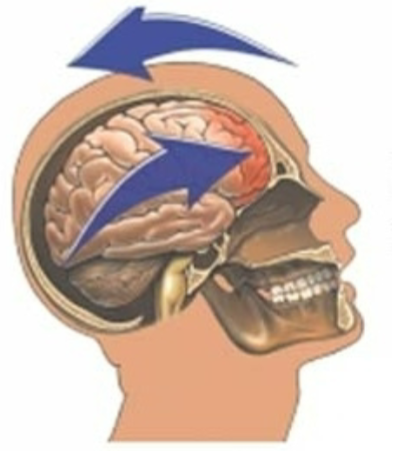
- Causes
- Hitting your head
- Being hit in the head
- Rapid acceleration/deceleration where the brain ricochets in the skull – whiplash
- Blast waves from explosions
- S&S
- Can be grouped into 4 subcategories:
- Physical Symptoms
- Headaches
- Visual problems
- Dizziness
- Noise/Light sensitivity
- Nausea
- Cognitive Symptoms
- Attention problems
- Memory dysfunction
- “Fogginess”
- Fatigue
- Cognitive slowing
- Emotionality
- More Emotional
- Sadness
- Nervousness
- Irritability
- Sleep Disturbance
- Difficulty falling asleep
- Sleeping less than usual
- Amnesia
- Retrograde – Can’t recall events preceding the trauma
- Question about date, score, location, play, breakfast
- Anterograde – Can’t recall events that occurred after event
- Question about impact, coming off field
- Retroanterograde – Reversing/confusing order of events
- Why Are Concussions so Dangerous?
- Survivors are often unaware of their injury
- Willingness to report
- Immediate diagnosis of a concussion is based on self-report
- An athlete who sustains a concussion is 4-6 times more likely to sustain a second concussion
- Second Impact Syndrome and Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
- Second Impact Syndrome
- Occurs in athletes with prior concussion following relatively minor second impact
- Second impact has been shown to occur up to 14 days post-injury
- Athlete returns to competition before resolution of symptoms
- Catastrophic increase in intracranial pressure
- Vasomotor paralysis, edema, massive swelling, herniation, death
- Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
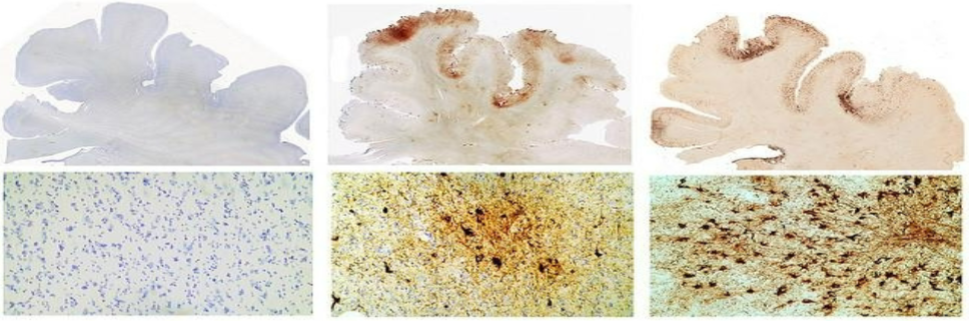
- Multiple head injuries affect neurological functioning
- CTE is characterized by the build-up of a toxic protein called tau
- The build up of these proteins cause behavioral, psychological, and physical changes, including emotional lability and anger issues
- Treatment of a Concussion
- The best way to prevent problems with concussion is to manage them effectively when they occur
- Immediate removal from activity
- Educate your athlete
- Referral to physician
- No athlete should return to play while experiencing symptoms of concussion
- Follow your institutions return from concussion protocol: ImpACT, Standardized Assessment of Concussion (SAC), etc.
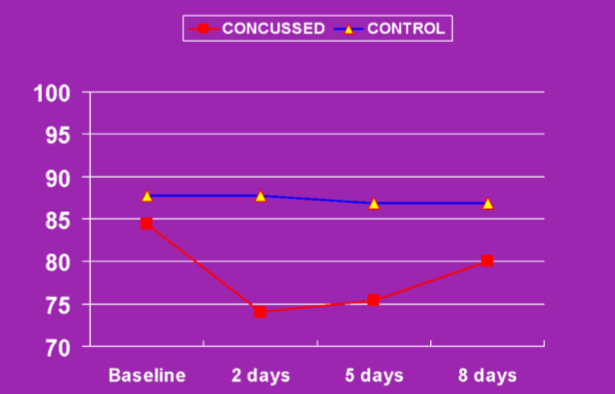
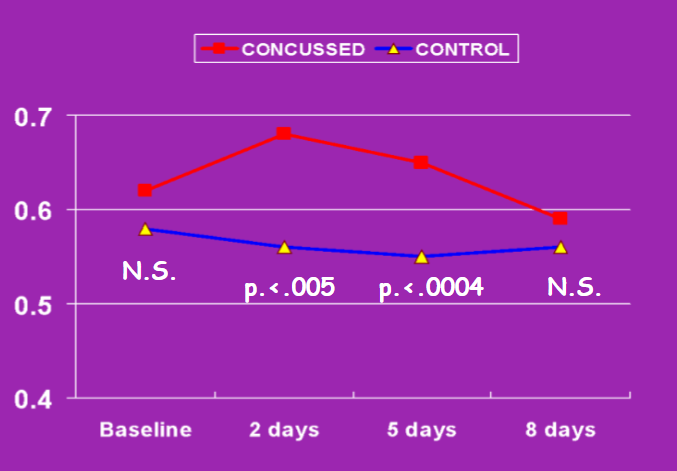
- Recovery Time
- (Time vs Memory)
- (Time vs. Reaction Time)