Unit 6: Industrialization through Progressive Era
Settlement of the West
Fredrick Jackson Turner → early academic historian
writes a thesis in 1893 claiming, “ the frontier is closed”
closing the frontier & its significance on America and American character
the american government once had land that was un-setteled by white americans but now all land has been setteled
America has crossed a threshold - no place to expand
the frontier had made america what it was but there is no longer a frontier and this is a turning point in history
3 Waves
1) Mining →
1st wave of white american settelers to the west in big numbers
Gold rush
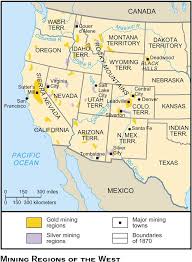
Mining pockets throughout the western territories of gold and silver
short-term wave
mining towns turn into ghost towns because all the wealth has been found
Placer mining → technique of sifting for gold in streams
Comstock Load → tremendous amount of silver pulled from the ground with help from big corporations and big machinary
2) Cattle Industry →
story of the open range →
concluded quickly that a large amount of cattle roam the southern territory
push to get cattle to a market
drive cattle northward towards transcontinental railroad system
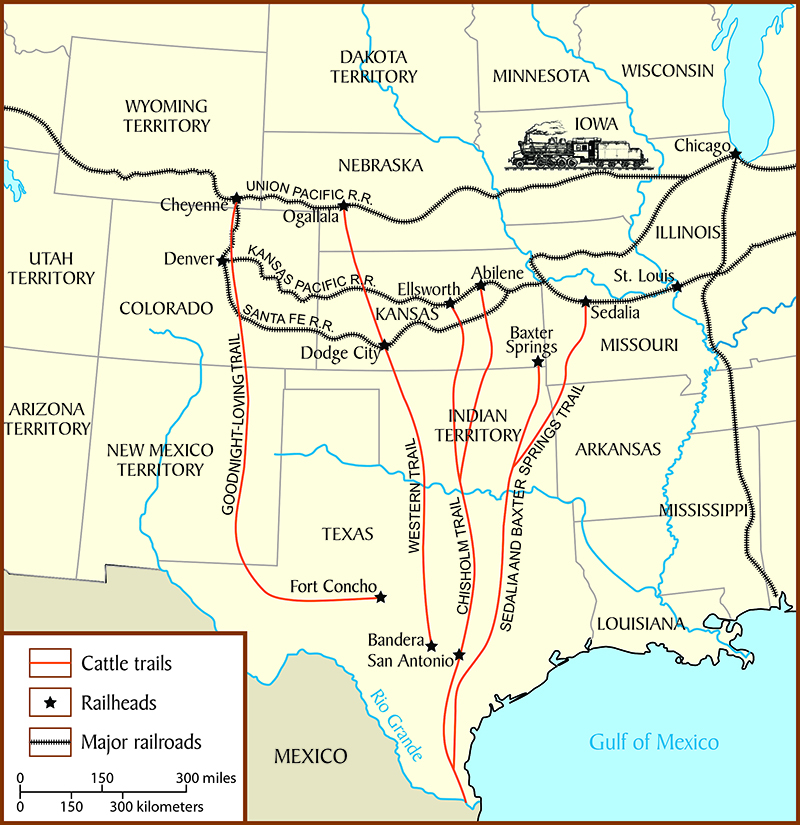
“Long drives”
start of the cow boys
not a long period of time
most rapid spread of domesticated animals
Cowboys
influence of Mexican cattleman
many cowboys were hispanic not white
Positive Impact of Technology →
railroads
refrigeration
barbed wire
Long drives are replaced by Ranching
1887 → harsh winter with lots of cold
hit with blizzard that kills 80-90% of heards
3) Farmers
longest and most perminant wave
Homesteaders → Homestead Act farmers
free land and opportunity → 180 acres
new technology
had to prove that within one year, they could increase the value of that land
crops, home, etc
given land title if you could prove that
Difficulties
droughts
pests
removal from society
Native American Life on The Great Plains
indiginous tribes are living on the land that is going to be setteled by white american settelers
The Horse
Nomadic → mobile for following food
Warfare → increased between tribes
a warrior culture
destruction of more settled groups
The Buffalo
used everything
depended on for survival
followed the herds
Dispersing the Tribes
government originally wanted to make treaties with tibes to create reservations for them to live
Ft. Laramie Treaty of 1868
Treaty does not last long
gold is found on land and the reservation land is changed
By the end of the 1800’s buffalo are almost extinct
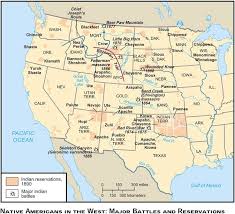
Government Policy
treaties
reservations
Dawes Act (1887) → encourage natives to drop cultural ways of life and adopt white lives
gave 160 acres to each native man in the reservations
leaves Surplus Land
land is put up for sale and bought by white settelers
Assimilation → Americanization
boarding schools
teach english to native children
adopt chrisitanity
learn trades
ensure they don’t speak their native language
remove them from their native relgion
some children would never see their families again
Battles and Conflict
Sand Creek Massacre (1864)
Colonel Chivington’s attack on Cheyenne
150-500 people slaughtered, many of them women and children
the reason of the attack was because there had been attacks on white settelers and they assumed that it had been the Cheyenne tribe
Battle of Little Bighorn (1876)
Black Hills
last stand of George Custer
in charge of enforcing reservations and assimilation
rare occasion when native americans beat americans
Wounded Knee 1890
last armed resistance of plains tribes to government policy
last attempt to resist assimilation and hold onto their culture
America In The Gilded Age: Rise of Big Business, Urbanization & Immigration In The Late 1800s
The Corporation → new innovations in business
people are buying stock to invest into these corporations and businesses
spreads the risk out so it isn’t all on the company
JP Morgan → finds companies and buys them buy owning a majority of their shares
would get a seat on the board of directors for these companies
Cornelius Vanderbilt → shipping industry
Leland Stanford → Owner of the Central Pacific Railway
Jay Gould → Also wealthy in the Railroad industry
The government was not always laissez-faire (“hands off”)
Sweetened incentives for building railroads by giving land for each mile of railroad built
Federal Land Grants
Railroads first made money by selling land to farmers and ranchers
Swift → big in the meat packing industry
used vertical integration
Carnegie → big in the steel industry
cuts out the middle man
owns the mines, and the refineries, etc.
creation of Vertical Integration
Rockefeller → big in the oil industry
Doesn’t own every aspect of the industry but dominates a single part of the industry
dominates the refining industry → horizontal integration
all are big because they are able to out-compete their competetors
Vertical Integration → Owns all steps in the process which allows you to sell your product for cheaper
Horizontal Integration → dominating one part of the industry
“Survival of the Fittest”
Captians of Industry… or Robber Barrons
Urbanization → growth of cities
New pattern of immigration
By the 1880’s → Large number of immigrants are coming from Southern and Eastern Europe
given the title, “new immigrants”
“old immigrants” → come from Northern, Central, & Western Europe
South is still very agriculturally based and have no manufacturing
Immigrants settel where their are jobs and do not move to the South
South also has Black Share-croppers
Social Networks for Immigrants
ethnic neighborhoods → neighborhoods that consisted of groups of the same people in which everyone spoke the same native language and had ethnic stores and
Immigrants are bringing their cultures with them
America expects them to throw away their cultures and become American
Families would arrive in stages
men would come in the first wave and would make enough money to get passage for their family
most typically only make enough to send a few people across but typically don’t make enough to go back home
Nativism → Beleive that the priority should be on those who are already living there
Nativists are anti-immigrants
want to spread their culture and remove those who are comming into the country
Immigrants are met with resistance
Hypocracy → citizencs say they don’t want immigrants yet they were once immigrants or descended from immigrants
WASP → # of americans and culture of Americans who are already here
White
Anglo
Saxon
Protestants
Contrast
contrast between wealth and poverty
Tenement Housing → Where everyon lives in urban areas
very unsanitary
families shoved into these tiny housing units
Wealthy → what people typically see with boulevards and parks
City Planners worked to provide green areas
Leisure → need some type of normalcy
Baseball, Circus, Amusement Parks all emerge
Need to Know Terms
Laissez -Faire →
traced back to eighteenth century French economists
Calls for limited government and competition
No government interference in the economy
Businesses set all of their regulations and rules
Need to have healthy competition for businesses to continue to inovate and produce better products
Laissez-Faire in the Gilded Age →
was the dominat economic doctrine in the Gilded Age
Followers of lassez-Faire were called liberals
Went against unions that tried to regulate big businesses
The Gospel of Wealth → Andrew Carnegie
the weath surplus of the rich should:
not be excessivley spent
not be bequeathed(inherited)
be used to reduce wealth disparity
should be given away to help people and make society better
Carnegie became a philanthropist later in life
donated much of his wealth to libraries, schools, etc.
Knights of Labor
(1869-1886) Terence V Powderly
Goals:
inclusive labor union
regardless of gender, race, or the amount of work that you did
8 hr work day
saftey in factories
equal pay
no child labor
compensation for injury on the job
Yellow Dog Contract
an agreement written to an employer to employee
contracts were used to:
permit workers from joining other labor unions
prohibit participation in other unions by contracts
agreeing to quit the union if apart of another union
caused a dark shadow between workers and employers
caused difficulties for labor unions by restricting workers rights
contract was struck by the supreme court as unconstitutional, and unforcible
The Great Railroad Strike
wage cuts
started in Mattinsburg, West Virginia
spread through large cities like Baltimore, Pittsburgh, and Chicago
Workers responed:
mass walkouts
protests
violence
solidarity
strike ended in failure
Knights of Labor
American Federation of Labor(AFL)
Protective Tariff
post civil war the Union needed to generate money FAST
rapid growth was promised with this tariff
domestic growth was increased
the USA flourished in the industrial industries but the farmers did not agree with them
a lot of the country is still built on farming
Blacklisting
placing union organizers on what was known as a blacklist
list was circulated and those on it would not be hired by other factory owners
was eventually made illegal
Lockouts
refuse to higher by employers
had to agree ro employers terms
could refuse to higher you if you were in a union
would not allow workers to work if their was talk of a strike
workers wouldn’t get payed and they would have to give up the strike to work
Mail-Order Businesses
late 1800s
Sears, Roebuck and Co - 1886
Montgomery Ward - 1872
Mail-Order Catalogs
Impact on Rural America
allows people in rural areas to purchase items even if they don’t live near a physical store
Marketing and sales techniques
Innovation in delivery
Social Darwinism
charles darwin was a biologist who wrote about the process of evolition through natural selection
sociologists took Darwin’s ideas on “survival of the fittest” and used them to justify their corrupt social, economic, and political views—creating Social Darwinism
Sherman Antitrust Act
passed in 1890
aimed to prevent monopolies and promote competition by regulating business practices that unfairly retrained trade or created anti-competitive market conditions
courts struggled to define “restraint of trade” and were hesitant to break up monopolies
In the US v E.C. Knights, the Supreme Court kimited the Acts scope by ruing it did not apply to manufacturing monopolies
Pullman Strike
caused due to unfair budget cuts on Railroad cuts in Pullman, Illinois b the Pullman Company
workers lived in company owned houses and used company owned
Budget cuts due to panic of 1893 were made for workers but rent and everyday needs stayed the same causing tension and strikes among the company
These strikes spread to the American Railroad Union and led to a nation wide strike of the Pullman cars disrupting Railroads all over the country
The Injunction
the railroad was angry so they went to court arguing that the strike violated interstate commerce and delivery of the US mail
on July 2nd, 1984, Chicago court filed an Injunction against the ARU statinf they cannot persuade workers to strike against Pullman
Industrial workes of the world
labor union founded in Chicago in 1905
wanted to create one large union
opposed American Federation of Labor
Beleived all should be allowed in the union despite race, gender, or skill level
Two groups within: sociaolists and anarchists
Anarchists → beleived in forceful, non-political methods: strikes, sabotage
Socialists → beleived IWW should get involved in elections/politics, change from within the system
William Haywood → leader, main founder
Eugene Debs → leader of american socialist party
Daniel De Leon → leader of socialist labor party
American Railway Union
Eugene V. Debs → leader
the american railwau union was one of the largest labor unions
the union welcomed any railray worker that had rank below foreman
lots of strikes were held
great northern railroad strike
Pullman strike
American Federation of Labor
Samuel Gompers was the leader and founder of the American Federation of Labor
he is said to be gifted at orating and assembling strikes and using them as a weapon for his fight
the goal of the AF of L were higher wages, shorter hours, and better conditions. in additon to staying our of politics
The Rise of Populism & Agrarian Discontent (1865-1896)
Beginning of a more involved government
Paul Harvey → radio host for ABC radio
Farmers are the backbone
noble and virtuous profession
The Origins of Agrarian Discontent
Economy:
prices for crops have decreased and farmers are making less
business is booming around these rural communities
wealth gap is growing
Overproduction:
farmers have figured out how to make a large amount of money
have to get your crops to markey
crops can go overseas
farmers start to grow large quantities because it is getting shipped all over
farmers end up with more product than they can sell
surplus
farmers have to sell crops for a lower price to get rid of it
The Populist Consipracy
Farmers look for
scapegoat
Minor Villians
Elevator operators → operators give farmers a ticket price to store grain
beleive that operators are rigging the system to get more money
dock farmers points and won’t give them money
too wet, too dry
Congress → the U.S. senate
democratics and republicans have sold out to big businesses
quid pro-co
US senators are not elected directly by the people
nominated by state legislators
makes the Senate an elite social club
East Coast & Big Business → farmers beleived the wealthy elite —particularly those close to big businesses— controlled the economy
there was even enti-Semitic sentiment, with some farmers blaming Jewish individuals for their struggles
Major Villians
Railroads → to get to a broader market, farmers have to use railroads
areas have to pay the railroad rate if they want to get their product to market
no arguing or haggeling for prices
farmers must pay extremley high prices (200-300% higher)
railroads are close with U.S Senate and Congress
Banks & Farm Foreclosures → interest on everything
farmers constantly borrwoing money
20-40% interest on loans compared to today’s 6%
farmers must take out loans, to afford supplies and crops
farmers must rely on crops to make payments
loss of crop with result in foreclosure
The Gold Standard
every bill has to be backed by a hard currency
sound currency and money
makes it harder for farmers to pay back their debt
farmers start advocating for the free coinage of silver
getting off of the gold standard
by-medilism
silver isn’t accepted because the silver declines in value
creditors v debtors
Agrarian Protest
The Granger Movement
largley a self-help movement
put together dances, lectures, and canning parties
farming can get lonley so they want to make rural small town america a better place to live
Co-ops → all of the farmers ban together to alleiviate some of the economic pain
Co-op would buy supplies and share them between all the farmers in the area to save money
would meet with farming companies to control the price they paid
get political in some states
create granger laws
try to regulate railroad rates in areas
granger laws go up to the supreme court and are struck as unconstitutional
The Alliance Movement
Mary Lease
farmers should pay what they owe banks untill they pay farmers failry for what they are doing
have skin in the game
raise less corn, raise more help
farmers need to get involved if they don’t like laws
run for office if you don’t like the politicians
canidates now trying to help farmers
farmers running in midwest states
The Populist Movement
The Populist Party → the peoples party
fights for farmers not for big business
re-enforcing each other in their comittment to the party
defying the merchants, bankers, lawyers, etc.
Plain talk newspaper
Omaha Platform (1892)
government ownership of railroads is supposed to ensure fair pricing
less wealthy people pay less in taxes
more wealthy people pay more in taxes
the secret ballet → voting wasn’t always private and populist beelived that you should be able to vote your conscious without worrying about repercussions
regulating bank interest rates
pushing for a standardized 8 hour work day
appeal to people in the working class in cities
want sympathy
strengthen numbers by creating support in big cities
majoritie of these ideas become standard in the future
The Election of 1892
Populist party run by Weaver
9% of popular vote
5% if electoral votes
Democrats win the election with Cleveland
Cleveland will not run again
Nebreaska’s Finest: The Great Commoner
Willian Jennings Bryan → chosen to run for the election as the democratic canadite
has populist ideals
given at the 1896 Democratic National Convention (Chicago, IL)
speech claims that cities will fall without the help of farmers
“Shall not cruciy mankind on the cross of gold”
The Election of 1896
Republican McKinley wins Majority popular and elctroal votes
Democratic Bryan will never win the election or any election in the future
Populist party is dead after this election
Democratic party takes some of the Populist ideals and brings them to life
changes the government
Legacy
populist reforms become reality
lays the foundation for the Progressive Movement
The Progressive: Reforming American Society 1890-1920
Who Were They?
not poor western farmers
urbanites/ city dwellers
middle class
educated background
many have attended schoola and many have college experience
W.A.S.P.
White Anglo Saxon Protestants
movement effects both parties and is not set to a single party
What Did They Beleive In?
concerned with the ubanization and beleived that society was in decline
saw growing class conflict
wanted to improve/ advance society for the better
want to remove the ideas of Laissez- Faire & Social Darwinism
challenged that these ideas were not correct and would not help to advance american society
had placed a lot of responsibily on the individual
beleived that the poor victims/ products of their environment
tenemant housing,cities, businesses, etc.
causes them to look at other means to find the problem and solutions
Faith in knowledge
causes them to look at other means to find the problems and solutions
social sciences(history, sociology, etc) are emerging in universities
systimatic intervention
can be used to sovle societies problems
Management & Planning
setting regulations and managing those developments
organizing and investigating the problem to get data
educating the people about the problems and creating solutions
regulations = new laws
Muckrakers
journalists who informed the american people and wrote stories to get the attention of civilization
inform citizens of issues and use managment and solutions
Ita Tarbell → upset with buisness and goes after Standard Oil and Rockefeller
beleived that their business tactics were wrong and tycoons were not acceptable
pushed for the federal government to potentially break up these companies
looked at the rise of big businesses
Riis → wrote stories and gave public talks
used photography to help gather data and to tell the story of the problem
look at urban factory workers and immigrant poor
Wrote “How The Other Half Lives”
Looks at the Tenemants and Tenament owners and Factory owners and bosses
Ita Wells → focuses on blacks in the south
Blacks are being linched in the south
pushes for action to be taken by WASP’s
Steffens → pushes for an end to poor living conditions
wrote “The Shame of the Cities”
Upton Sinclair → looks at immigrant labor
looks at meat packing plants
Wrote “The Jungle”
wants to regulate working conditions
gets the attention of lots of people like Teddy Roosevelt
Settelment House Movement
white middle class reformers want to help create change
bought buildings and renovated them into housing to work with immigrants
Hull House is one of the most notable settelment houses
Jane Addams is the most notable settelment worker
Purpose is to try to adopt and take christian teachings and create solutions to try to help immigrants
want to help immigrant poor
people are taught english and learn new skills that can be used in the workplace
new skills of how to use proper hygene and cooking skills
Help immigrants to find better housing conditions
would report tenament housing to police
Provided child care and pushed for mandatory school
didn’t want to see children playing in the streets or working in factories
Crusade against child labor
Fight Against Child Labor
National Child Labor Committee
Lewis Hine→ educated and photographs these harsh conditions
push to band child labor
child could work at as young as 5 years old
children worked in the fields, canning factories, coal mines, etc.
push for state legislation to take children out of the workforce and put them in schools
Child labor is not a federal law untill the 1930’s
Anti-Saloon League
want to discourage alcohol consumption
Carry A. Nation → well known for her efforts to try and push for state laws to remove saloons
would go into saloons with “supplies” and would destroy them
rocks, bottels, etc covered in paper
evenually started attacking saloons with a hatchet
Womens Christian Temperance Union (WCTU)
movement becomes very popular
19 states will pass prohibition laws by the late 1910’s
Journey to the 18th Amendment
16th amendment → authorized the federal government to create an income tax
government would no longer have to rely on alcohol for taxes
prohibition became a national danger
mass march occured in Washington D.C. on December 10, 1913 to demand a prohbition amendment to the U.S. Constitution
wanted an amendment not a law because it would be in the constitution forever
18th amendment → illegal to manufactur and sell alcohol
Eugenics Movements
Belief → through scientific managment and their geniology, society could improve the quality of the nations population by pruning away the weaker strains
want to ensure that these weaker traits do not replicate in the population to make it stronger
occurs along side the growth in immigrant population
Beleives that we can take human inequities and find the hereditary connection to them to remove them
ERO is the head of the eugenics research
integrated eugenics into popular culture
spawned lots of people who endorsed such things as sterilization
Indiana State Senate is the first to force the sterilization of citizens seen as unfit
12 states put sterilization laws into effect
Buck v Bell
about whether the state laws are constitutional or unconstitutional
Oliver W. Homes → Supreme Court Justice
Case is voted 8-1
claims that the citizens are not having their rights violated
IQ test shows Carrie Buck at a mental age of 9
Carrie and mother confind to an instituion
It is better for all the world, it instead of waiting to execute degenerate offspring for crime, or to let them starve for their imbecility, society can prevent those who are manifestly unfit from their continuing their kind. The Principle that sustains compulsory vaccination is broad enough to cover cutting the Fallopian tubes.
Jacobson v. Massachusetts, 197 U.S. 11. Three Generations of imbeciles are enough
Race Relations
Ida B Wells
W.E.B. DuBois
writer of The Crisis
NAACP
founded to improve and protect black rights
not much is accomplished untill the modern civil rights movement comes foward
Prostitution
white slavery - “white slave trade'“
emerging in cities
Anti-prostitution movement feared immigrants coming into the country
feared that they were runing their christian values
Mann → passes the Mann act
if a male crosses over state lines with the means of prostitution, it is considered a federal crime
Jack Johnson → beats his white opponent in boxing and is well known
often around white women
use the Mann act to go after Johnson
U.S. v. Jack Johnson
Johnson had a companion
companion was a 19 year old white prostitue
Mother beleived that Johnson was using hyptonic powers to force her daughter into that position and wanted Johnson to pay
Progressives in the White House
3 presidents are known as Progressive era presidents
President Teddy Roosevelt → Republican
1901-1908
goes after the monopolies that are bad for american consumers
known for the “square deal”
wanted to provide a fair government that would treat all citizens equally
known as the conservation president
important for the natinal government to manage the conservation of land
President William Taft → Republican
1909- 1912
goes after trusts like the Standard Oil Trust
does not accomplish much during his term
President Woodrow Wilson → Democrat
1913-1920
movement dies after Wilsons terms
goes after big monopolies
Clayton Anti-Trust Act
exempts labor unions from being declared as trusts
goes after tariffs
in favor of the 16th amendment
lowers tariffs
in favor of the income tax
creates the federal reform
institution that will regulate the money supply
banking reform