
APUSH Review🏛️🦅🍔🏈🌎5️⃣
Legislation
Marbury v. Madison. Year: 1803 Established Judicial Review
Gibbons v. Ogden. Year: 1824. Federal Government controls interstate commerce
Dred Scott v. Sandford. Year: 1857. Slaves weren’t citizens, they were property, and just traveling to a free area couldn’t free them.
Plessy v. Ferguson. Year: 1896. Separate but equal (segregation)
Korematsu v. US. Year: 1944 Japanese internment camps.
Brown v. Board of Education. Year: 1954. Undo Plessy v. Ferguson (end segregation)
Gideon v. Wainwright. Year: 1963. right to an attorney
Miranda v. Arizona. Year: 1966. Miranda rights
Continuity and Change🔄🔀️
Time Period | Continuity | Change |
1-1491-1607 4-6% | Coerced Labor, Native Resistance, Gold God and Glory, | Native pop. decline, Europeans in Americas, Colombian Exchange, Expansion of Slave trade. |
|---|---|---|
2-1607-1754 6-8% | Loyal to British, Conflict with natives/native resistance, resource competition. | Enlightenment, 1st Great Awakening, Colonial challenges to imperials. |
3-1754-1800 10-17% | Loyal to British, limited natural rights, Conflict with natives. | France driven out of north America, Enlightenment, Abolition in North, Political Parties, Republican Motherhood, Pop. inc. |
4-1800-1848 10-17% | Conflict with natives, Republican Motherhood → Cult of Domesticity, Opinions on Slavery by region, American Isolationism, Great Awakening, Conflicts with Britian. | Market Revolution, Romanticism → Transcendentalism, American Culture, Utopian communities. |
5-1844-1877 10-17% | Nativism, violence against Black People, War →Suppression of Rights, Westward Expansion, Conflict with natives | Industry-N, Agri-S, Abolition of Slavery, Expansion of Fed, Civil rights amendments, |
6-1865-1889 10-17% | Nativism, violence against Black People, role of gov debates, Westward Expansion, Conflict with natives, Gov supports Business, Women involved in reform. | Rise of Middle class, Growth of Philanthropy, Child Labor, immigration Laws, Growth of Large corporations, Conservation and Preservation. |
7-1890-1945 10-17% | Nativism, violence against Black People, role of gov debates, Gov supports Business, Women involved in reform and war, War →Suppression of Rights, | Women’s suffrage, Gov regulates economy, Active in foreign affairs. |
8-1945-1980 10-17% | Nativism, decline in unions, conservative backlash, tech innovations, Discrimination, Debates of gov role, gov regulate environment. | federal support for civil rights, Cold war, Distrust of Gov, gay rights, fed Highway system, military industrial complex. |
9-1980-2008 4-6% | Nativism, decline in unions, conservative backlash, tech innovations, Discrimination, Debates of gov role, gov regulate environment, US intervention in foreign affairs, Gov as a social safety net. | End of cold war, Gay rights, Impeachment, Campaign spending, polarization, tech access. |
Timeline ⌛
Time Periods
1491-1607 4-6%
1607-1754 6-8%
1754-1800 10-17%
1800-1848 10-17%
1844-1877 10-17%
1865-1889 10-17%
1890-1945 10-17%
1945-1980 10-17%
1980-2008 4-6%
1491- Last year before European Contact in Americas
1492: Columbus’ first voyage to the Americas.
Colombian Exchange
West gives Corn, potatoes, beans, squash.
East gives diseases, livestock, horses, fruits.
1588: The destruction of the Spanish Armada.
1607: The founding of Jamestown.
Start of British Colonies
1620: “The Pilgrims” founded Plymouth.
The 1630s: The Puritan “great migration” to New England.
Religious freedom, Pilgrims
1676: Bacon’s Rebellion, and King Philip’s War was also happening.
Bacon’s Rebellion
Indentured Servant uprising about not getting land after time is up. Made plantation owners start choosing slaves. (Trans-Atlantic slave trade)
Metacom’s War
Native American resistance to British control, ultimately unsuccessful
1688: The “Glorious Revolution.”
Exile of king James leading to William and Mary. Gave more power to parliament versus the monarchy.
The 1730s: The height of the Great Awakening.
Great Awakening is a religious revival in the United States.
1754-1763: The Seven Years’ War.
British and French debates over land in Ohio River Valley, War is blamed on Colonists, and they are taxed as such. Taxes lead to American Revolution. End of Salutary Neglect.
1775-1783: American Revolution
Causes: Proclamation of 1763, Taxes, and Quartering act. Boston Massacre. Revolutionaries inspired by enlightenment. British were better funded and more experienced, but USA used guerrilla warfare led my George Washington.
Effects: American Independance, Articles of Confederation, everything else in this class.
1776: The Declaration of Independence.
United States of America Created.
1781: The Articles of Confederation / the Siege of Yorktown.
First Form of Government in US. Yorktown was last major battle, US won made British decide to give up Colonies.
1789: George Washington became the first POTUS.
Unanimous election. Government created.
Farewell address
Willingly give up power, sets precedence for 2 terms, warn of partisanism and foreign affairs.
1800 Election of 1800
Thomas Jefferson VS Aaron Burr. 1st peaceful transition of party power.
1812-1815: The War of 1812.
Causes: England impressment of American Ships and arming Native Americans.
Effects: Stalemate but Andrew Jackson won a battle after treaty signed making it a slight USA victory.
1820: The Missouri Compromise.
Missouri enters US a slave state and Maine as a free one. Outlawed slavery above 36 30 lines.
The 1830s: The height of the Second Great Awakening.
Religious Revival emphasis on the decay of morality and faith. Personal faith. Sparks ideas about individual liberties. Joseph Smith.
1835-1836: Texan War
Causes: US Immigrants to Mexico, conversion to Catholicism ✝, manifest destiny, slavery abolished in Mexico. Alamo.
Effects: Texas Independence
1844: Election of James K Polk
Ran on platform of expansion and manifest destiny,
1840’s: Gain North land from Great Brittian
US Canada Border along 49th parallel.
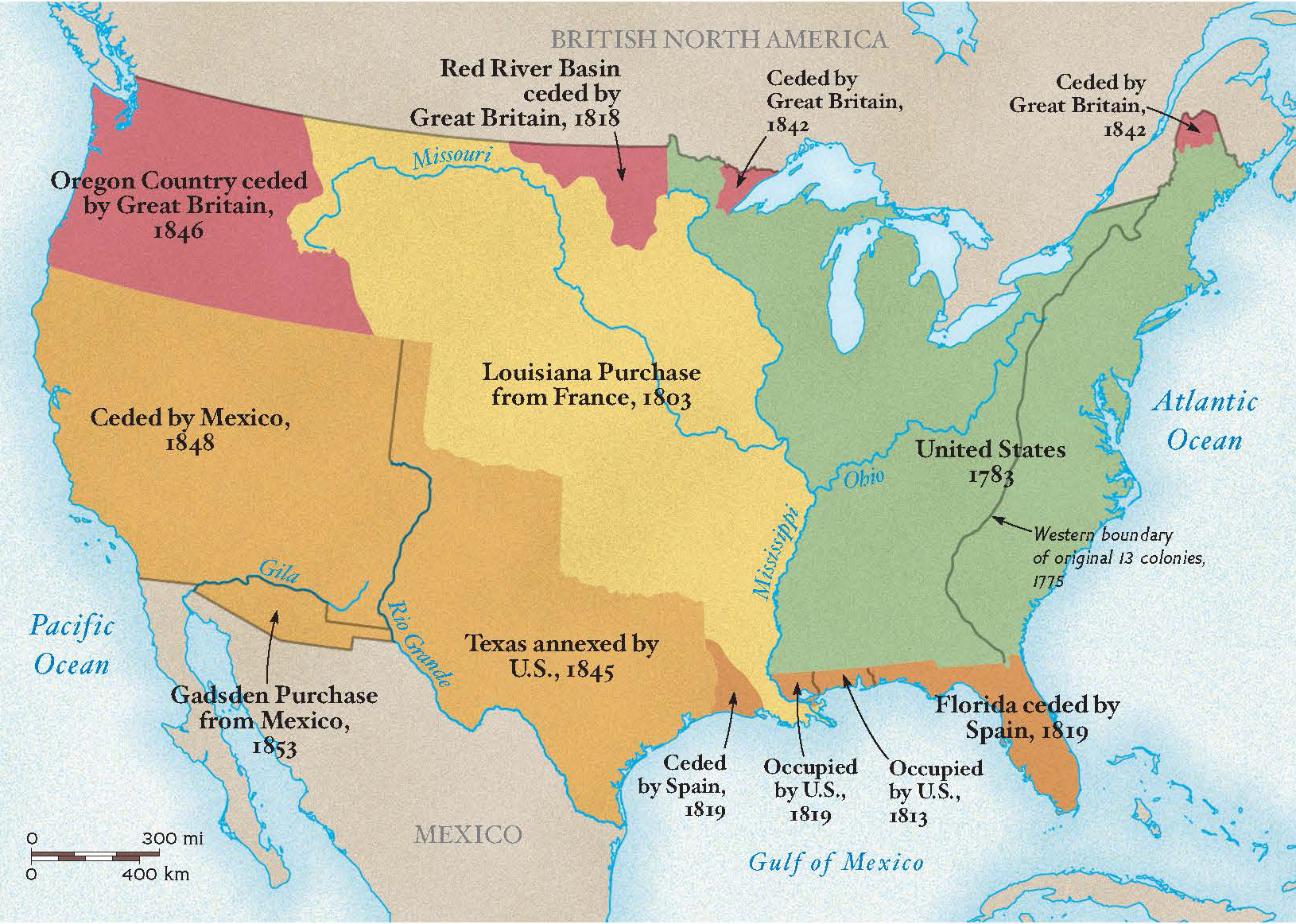
1846-1848: Mexican American War
Causes: Manifest Destiny, Texas Independence, Border dispute (Rio Grande vs Nueces Rivers)
Effects: Treaty of Guadalupe Hildago gives US California, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, Arizona, and parts of Colorado and Wyoming. Kansas-Nebraska Act: Decide slavery in new territories.
1849- California Gold Rush
Westward expansion, Manifest Destiny
1861-1865: The Civil War
Causes: Direct- Lincoln’s Election 1860 caused South Carolina to secede. Lincoln sends troops to Fort Sumter troops attacked by Confederacy Civil War begins. General- Slavery in new territories (Bleeding Kansas), Economics (Cotton is king), State vs Federal rights (Nullification Crisis)
Advantages
Union- Industry, transport, Population, money
Confederacy- “Home field advantage, Committed, supported by Europe at first, military leadership.
Effects: Reconstruction of south, Lincoln’s assassination, racism (KKK), south industrializes, Gilded age begins.
1869: Transcontinental railroad completed
Westward expansion, manifest destiny
1877: The end of Reconstruction.
Reconstruction to fix South after Civil War.
Lincoln’s 10% Plan- 10% of South takes a loyalty Oath to the United States, Improve state government with black people, permanent freedom for black people.
Freedman’s Bureau- aid and educate poor people in south.
Johnson’s plan-
1898: Spanish American War
Causes: Imperialism, U.S.S. Maine, Yellow Journalism.
Effects: Cuban Independance, Spanish empire ends, American empire begins, America gains Puerto Rico, Guam, Philippines.
1890: end of Gilded Age/ Start of Progressive era
1914-1918: World War I.
Causes: Direct- assassination of Franz Ferdinand. General- Militarism, alliances, imperialism, nationalism.
US Cause: Zimmerman, total submarine warfare (Lusitania had US citizens)
Effects: German reparations, League of Nations, 1st Red Scare, Isolationist America, Post war economic boom.
1930s: The Great Depression.
1939-1945: World War II.
Causes: German reparations, appeasement (Hitler’s invasion of Poland).
US Cause: Pearl Harbor
Effects: Ends great depression, Cold War begins, Germany divided in E & W, 2nd Red Scare (McCarthyism), Post-war economic boom.
1950-1953 Korean War
Causes: Cold War
Effects: Communism Contained at 38th parallel.
1955-1975 Vietnam War
Causes: North invades South
Effects: Kent state (Protesting college student killed), Johnson’s Great Society, 26th amendment,
1980: Election of Ronald Reagan
Regan-omics, conservative, ends Cold War.
1991: The end of the Cold War
2001: Terrorist attacks of 9/11
2008: Election of Barak Obama
Immigration and Migration⛵🚂
Pre 1492
Bering Land Bridge- Native Migrations
1492-1776: European Colonization
British-East Coast (Most Colonizers)
Spanish-Florida and Latin America
French-Canada
Dutch-New York
1776-1820: Early America
Northwestern Europe (England, Scotland, Germany, and Scandinavia) Very Protestant
Africa-Transatlantic Slave Trade
1820-1860: Antebellum
US Citizens go settle in Mexican Texas, Indian Removal Act-Trail of Tears
Wave of Irish ✝ ([Nativism and Know Nothing Party] Boston, NYC, Philadelphia) and German (Farmers Pennsylvania and Midwest) Immigrants.
1840-1890: Wild West
Manifest Destiny- Oregon Trail, LDS Pioneers, California Gold Rush.
Chinese immigrants work in California on transcontinental railroad.
1890-1920: Progressive Era
Industrialization and Urbanization- Southern and Eastern Europeans (Italy, Poland, Greece, and Russia ✝☦✡) Increase in Nativism because of lack on English and skills. Progressives like Jane Addams make settlement houses. Public Education became about citizenship/.
1920-1960 WW’s
1st Red Scare- Fear of Immigrants starting Communism in the US. Radical immigrants deported.
Great Migration- African American migrate north to escape racism and to find jobs.
Immigration Quota Acts- Based on National Origins, prioritized NW Europe.
Sacco and Vanzetti Trial- Immigrants convicted of robbery and murder. Defenders said it was nativism.
1960-Present
Internal Migration to Sunbelt
1960’s National Origins Quota changed to encourage immigrants from developing world, no longer favoring white people. 1965 prioritized skilled immigrants and refugees. 1990 Lifted restrictions on homosexual immigrants.
State Origins
Serial | State | Date (admitted or ratified) | How? |
|---|---|---|---|
1. | Delaware | December 7, 1787 | 1st to ratify U.S. Constitution. |
2. | Pennsylvania | December 12, 1787 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
3. | New Jersey | December 18, 1787 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
4. | Georgia | January 2, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
5. | Connecticut | January 9, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
6. | Massachusetts | February 6, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
7. | Maryland | April 28, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
8. | South Carolina | May 23, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
9. | New Hampshire | June 21, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
10. | Virginia | June 25, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
11. | New York | July 26, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
12. | North Carolina | November 21, 1789 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
13. | Rhode Island | May 29, 1790 | Originally rejected Constitution then Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
14. | Vermont | March 4, 1791 | Split from NY and NH |
15. | Kentucky | June 1, 1792 | Split from Virgina. |
16. | Tennessee | June 1, 1796 | Split from North Carolina. |
17. | Ohio | March 1, 1803 | 1st state from Northwest Territory |
18. | Louisiana | April 30, 1812 | Louisiana Purchase |
19. | Indiana | December 11, 1816 | Northwest Territory |
20. | Mississippi | December 10, 1817 | Mississippi Territory |
21. | Illinois | December 3, 1818 | Illinois Territory |
22. | Alabama | December 14, 1819 | Mississippi Territory |
23. | Maine | March 15, 1820 | Split from Massachusetts |
24. | Missouri | August 10, 1821 | Missouri Compromise |
25. | Arkansas | June 15, 1836 | Louisiana Purchase |
26. | Michigan | January 26, 1837 | Northwest Territory |
27. | Florida | March 3, 1845 | Acquired from Spain |
28. | Texas | December 29, 1845 | Annexed from Lone Star Republic of Texas |
29. | Iowa | December 28, 1846 | Louisiana Purchase |
30. | Wisconsin | May 29, 1848 | Northwest Territory |
31. | California | September 9, 1850 | Acquired from Mexico in Treaty of Guadalupe Hildago |
32. | Minnesota | May 11, 1858 | Minnesota Territory |
33. | Oregon | February 14, 1859 | Oregon Territory |
34. | Kansas | January 29, 1861 | Kansas-Nebraska Act |
35. | West Virginia | June 20, 1863 | Split from Virgina during Civil War |
36. | Nevada | October 31, 1864 | Utah Territory |
37. | Nebraska | March 1, 1867 | Kansas-Nebraska Act, Nebraska Territory |
38. | Colorado | August 1, 1876 | Kansas Territory |
39. | North Dakota | November 2, 1889 | Dakota Territory |
40. | South Dakota | November 2, 1889 | Dakota Territory |
41. | Montana | November 8, 1889 | Montana Territory |
42. | Washington | November 11, 1889 | Oregon Territory |
43. | Idaho | July 3, 1890 | Idaho Territory |
44. | Wyoming | July 10, 1890 | Dakota, Idaho, and Utah Territories. |
45. | Utah | January 4, 1896 | Utah Territory |
46. | Oklahoma | November 16, 1907 | Indian and Oklahoma Territory |
47. | New Mexico | January 6, 1912 | New Mexico Territory |
48. | Arizona | February 14, 1912 | Arizona Territory |
49. | Alaska | January 3, 1959 | Acquired from Russia |
50. | Hawaii | August 21, 1959 | Annexed by US. |
Sources📚💻📜
Wars
https://washingtonlee.apsva.us/wp-content/uploads/sites/38/2016/08/war_causes_and_effects.docx
APUSH Review🏛️🦅🍔🏈🌎5️⃣
Legislation
Marbury v. Madison. Year: 1803 Established Judicial Review
Gibbons v. Ogden. Year: 1824. Federal Government controls interstate commerce
Dred Scott v. Sandford. Year: 1857. Slaves weren’t citizens, they were property, and just traveling to a free area couldn’t free them.
Plessy v. Ferguson. Year: 1896. Separate but equal (segregation)
Korematsu v. US. Year: 1944 Japanese internment camps.
Brown v. Board of Education. Year: 1954. Undo Plessy v. Ferguson (end segregation)
Gideon v. Wainwright. Year: 1963. right to an attorney
Miranda v. Arizona. Year: 1966. Miranda rights
Continuity and Change🔄🔀️
Time Period | Continuity | Change |
1-1491-1607 4-6% | Coerced Labor, Native Resistance, Gold God and Glory, | Native pop. decline, Europeans in Americas, Colombian Exchange, Expansion of Slave trade. |
|---|---|---|
2-1607-1754 6-8% | Loyal to British, Conflict with natives/native resistance, resource competition. | Enlightenment, 1st Great Awakening, Colonial challenges to imperials. |
3-1754-1800 10-17% | Loyal to British, limited natural rights, Conflict with natives. | France driven out of north America, Enlightenment, Abolition in North, Political Parties, Republican Motherhood, Pop. inc. |
4-1800-1848 10-17% | Conflict with natives, Republican Motherhood → Cult of Domesticity, Opinions on Slavery by region, American Isolationism, Great Awakening, Conflicts with Britian. | Market Revolution, Romanticism → Transcendentalism, American Culture, Utopian communities. |
5-1844-1877 10-17% | Nativism, violence against Black People, War →Suppression of Rights, Westward Expansion, Conflict with natives | Industry-N, Agri-S, Abolition of Slavery, Expansion of Fed, Civil rights amendments, |
6-1865-1889 10-17% | Nativism, violence against Black People, role of gov debates, Westward Expansion, Conflict with natives, Gov supports Business, Women involved in reform. | Rise of Middle class, Growth of Philanthropy, Child Labor, immigration Laws, Growth of Large corporations, Conservation and Preservation. |
7-1890-1945 10-17% | Nativism, violence against Black People, role of gov debates, Gov supports Business, Women involved in reform and war, War →Suppression of Rights, | Women’s suffrage, Gov regulates economy, Active in foreign affairs. |
8-1945-1980 10-17% | Nativism, decline in unions, conservative backlash, tech innovations, Discrimination, Debates of gov role, gov regulate environment. | federal support for civil rights, Cold war, Distrust of Gov, gay rights, fed Highway system, military industrial complex. |
9-1980-2008 4-6% | Nativism, decline in unions, conservative backlash, tech innovations, Discrimination, Debates of gov role, gov regulate environment, US intervention in foreign affairs, Gov as a social safety net. | End of cold war, Gay rights, Impeachment, Campaign spending, polarization, tech access. |
Timeline ⌛
Time Periods
1491-1607 4-6%
1607-1754 6-8%
1754-1800 10-17%
1800-1848 10-17%
1844-1877 10-17%
1865-1889 10-17%
1890-1945 10-17%
1945-1980 10-17%
1980-2008 4-6%
1491- Last year before European Contact in Americas
1492: Columbus’ first voyage to the Americas.
Colombian Exchange
West gives Corn, potatoes, beans, squash.
East gives diseases, livestock, horses, fruits.
1588: The destruction of the Spanish Armada.
1607: The founding of Jamestown.
Start of British Colonies
1620: “The Pilgrims” founded Plymouth.
The 1630s: The Puritan “great migration” to New England.
Religious freedom, Pilgrims
1676: Bacon’s Rebellion, and King Philip’s War was also happening.
Bacon’s Rebellion
Indentured Servant uprising about not getting land after time is up. Made plantation owners start choosing slaves. (Trans-Atlantic slave trade)
Metacom’s War
Native American resistance to British control, ultimately unsuccessful
1688: The “Glorious Revolution.”
Exile of king James leading to William and Mary. Gave more power to parliament versus the monarchy.
The 1730s: The height of the Great Awakening.
Great Awakening is a religious revival in the United States.
1754-1763: The Seven Years’ War.
British and French debates over land in Ohio River Valley, War is blamed on Colonists, and they are taxed as such. Taxes lead to American Revolution. End of Salutary Neglect.
1775-1783: American Revolution
Causes: Proclamation of 1763, Taxes, and Quartering act. Boston Massacre. Revolutionaries inspired by enlightenment. British were better funded and more experienced, but USA used guerrilla warfare led my George Washington.
Effects: American Independance, Articles of Confederation, everything else in this class.
1776: The Declaration of Independence.
United States of America Created.
1781: The Articles of Confederation / the Siege of Yorktown.
First Form of Government in US. Yorktown was last major battle, US won made British decide to give up Colonies.
1789: George Washington became the first POTUS.
Unanimous election. Government created.
Farewell address
Willingly give up power, sets precedence for 2 terms, warn of partisanism and foreign affairs.
1800 Election of 1800
Thomas Jefferson VS Aaron Burr. 1st peaceful transition of party power.
1812-1815: The War of 1812.
Causes: England impressment of American Ships and arming Native Americans.
Effects: Stalemate but Andrew Jackson won a battle after treaty signed making it a slight USA victory.
1820: The Missouri Compromise.
Missouri enters US a slave state and Maine as a free one. Outlawed slavery above 36 30 lines.
The 1830s: The height of the Second Great Awakening.
Religious Revival emphasis on the decay of morality and faith. Personal faith. Sparks ideas about individual liberties. Joseph Smith.
1835-1836: Texan War
Causes: US Immigrants to Mexico, conversion to Catholicism ✝, manifest destiny, slavery abolished in Mexico. Alamo.
Effects: Texas Independence
1844: Election of James K Polk
Ran on platform of expansion and manifest destiny,
1840’s: Gain North land from Great Brittian
US Canada Border along 49th parallel.
1846-1848: Mexican American War
Causes: Manifest Destiny, Texas Independence, Border dispute (Rio Grande vs Nueces Rivers)
Effects: Treaty of Guadalupe Hildago gives US California, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, Arizona, and parts of Colorado and Wyoming. Kansas-Nebraska Act: Decide slavery in new territories.
1849- California Gold Rush
Westward expansion, Manifest Destiny
1861-1865: The Civil War
Causes: Direct- Lincoln’s Election 1860 caused South Carolina to secede. Lincoln sends troops to Fort Sumter troops attacked by Confederacy Civil War begins. General- Slavery in new territories (Bleeding Kansas), Economics (Cotton is king), State vs Federal rights (Nullification Crisis)
Advantages
Union- Industry, transport, Population, money
Confederacy- “Home field advantage, Committed, supported by Europe at first, military leadership.
Effects: Reconstruction of south, Lincoln’s assassination, racism (KKK), south industrializes, Gilded age begins.
1869: Transcontinental railroad completed
Westward expansion, manifest destiny
1877: The end of Reconstruction.
Reconstruction to fix South after Civil War.
Lincoln’s 10% Plan- 10% of South takes a loyalty Oath to the United States, Improve state government with black people, permanent freedom for black people.
Freedman’s Bureau- aid and educate poor people in south.
Johnson’s plan-
1898: Spanish American War
Causes: Imperialism, U.S.S. Maine, Yellow Journalism.
Effects: Cuban Independance, Spanish empire ends, American empire begins, America gains Puerto Rico, Guam, Philippines.
1890: end of Gilded Age/ Start of Progressive era
1914-1918: World War I.
Causes: Direct- assassination of Franz Ferdinand. General- Militarism, alliances, imperialism, nationalism.
US Cause: Zimmerman, total submarine warfare (Lusitania had US citizens)
Effects: German reparations, League of Nations, 1st Red Scare, Isolationist America, Post war economic boom.
1930s: The Great Depression.
1939-1945: World War II.
Causes: German reparations, appeasement (Hitler’s invasion of Poland).
US Cause: Pearl Harbor
Effects: Ends great depression, Cold War begins, Germany divided in E & W, 2nd Red Scare (McCarthyism), Post-war economic boom.
1950-1953 Korean War
Causes: Cold War
Effects: Communism Contained at 38th parallel.
1955-1975 Vietnam War
Causes: North invades South
Effects: Kent state (Protesting college student killed), Johnson’s Great Society, 26th amendment,
1980: Election of Ronald Reagan
Regan-omics, conservative, ends Cold War.
1991: The end of the Cold War
2001: Terrorist attacks of 9/11
2008: Election of Barak Obama
Immigration and Migration⛵🚂

Pre 1492
Bering Land Bridge- Native Migrations
1492-1776: European Colonization
British-East Coast (Most Colonizers)
Spanish-Florida and Latin America
French-Canada
Dutch-New York
1776-1820: Early America
Northwestern Europe (England, Scotland, Germany, and Scandinavia) Very Protestant
Africa-Transatlantic Slave Trade
1820-1860: Antebellum
US Citizens go settle in Mexican Texas, Indian Removal Act-Trail of Tears
Wave of Irish ✝ ([Nativism and Know Nothing Party] Boston, NYC, Philadelphia) and German (Farmers Pennsylvania and Midwest) Immigrants.
1840-1890: Wild West
Manifest Destiny- Oregon Trail, LDS Pioneers, California Gold Rush.
Chinese immigrants work in California on transcontinental railroad.
1890-1920: Progressive Era
Industrialization and Urbanization- Southern and Eastern Europeans (Italy, Poland, Greece, and Russia ✝☦✡) Increase in Nativism because of lack on English and skills. Progressives like Jane Addams make settlement houses. Public Education became about citizenship/.
1920-1960 WW’s
1st Red Scare- Fear of Immigrants starting Communism in the US. Radical immigrants deported.
Great Migration- African American migrate north to escape racism and to find jobs.
Immigration Quota Acts- Based on National Origins, prioritized NW Europe.
Sacco and Vanzetti Trial- Immigrants convicted of robbery and murder. Defenders said it was nativism.
1960-Present
Internal Migration to Sunbelt
1960’s National Origins Quota changed to encourage immigrants from developing world, no longer favoring white people. 1965 prioritized skilled immigrants and refugees. 1990 Lifted restrictions on homosexual immigrants.
State Origins
Serial | State | Date (admitted or ratified) | How? |
|---|---|---|---|
1. | Delaware | December 7, 1787 | 1st to ratify U.S. Constitution. |
2. | Pennsylvania | December 12, 1787 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
3. | New Jersey | December 18, 1787 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
4. | Georgia | January 2, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
5. | Connecticut | January 9, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
6. | Massachusetts | February 6, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
7. | Maryland | April 28, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
8. | South Carolina | May 23, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
9. | New Hampshire | June 21, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
10. | Virginia | June 25, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
11. | New York | July 26, 1788 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
12. | North Carolina | November 21, 1789 | Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
13. | Rhode Island | May 29, 1790 | Originally rejected Constitution then Ratified U.S. Constitution. |
14. | Vermont | March 4, 1791 | Split from NY and NH |
15. | Kentucky | June 1, 1792 | Split from Virgina. |
16. | Tennessee | June 1, 1796 | Split from North Carolina. |
17. | Ohio | March 1, 1803 | 1st state from Northwest Territory |
18. | Louisiana | April 30, 1812 | Louisiana Purchase |
19. | Indiana | December 11, 1816 | Northwest Territory |
20. | Mississippi | December 10, 1817 | Mississippi Territory |
21. | Illinois | December 3, 1818 | Illinois Territory |
22. | Alabama | December 14, 1819 | Mississippi Territory |
23. | Maine | March 15, 1820 | Split from Massachusetts |
24. | Missouri | August 10, 1821 | Missouri Compromise |
25. | Arkansas | June 15, 1836 | Louisiana Purchase |
26. | Michigan | January 26, 1837 | Northwest Territory |
27. | Florida | March 3, 1845 | Acquired from Spain |
28. | Texas | December 29, 1845 | Annexed from Lone Star Republic of Texas |
29. | Iowa | December 28, 1846 | Louisiana Purchase |
30. | Wisconsin | May 29, 1848 | Northwest Territory |
31. | California | September 9, 1850 | Acquired from Mexico in Treaty of Guadalupe Hildago |
32. | Minnesota | May 11, 1858 | Minnesota Territory |
33. | Oregon | February 14, 1859 | Oregon Territory |
34. | Kansas | January 29, 1861 | Kansas-Nebraska Act |
35. | West Virginia | June 20, 1863 | Split from Virgina during Civil War |
36. | Nevada | October 31, 1864 | Utah Territory |
37. | Nebraska | March 1, 1867 | Kansas-Nebraska Act, Nebraska Territory |
38. | Colorado | August 1, 1876 | Kansas Territory |
39. | North Dakota | November 2, 1889 | Dakota Territory |
40. | South Dakota | November 2, 1889 | Dakota Territory |
41. | Montana | November 8, 1889 | Montana Territory |
42. | Washington | November 11, 1889 | Oregon Territory |
43. | Idaho | July 3, 1890 | Idaho Territory |
44. | Wyoming | July 10, 1890 | Dakota, Idaho, and Utah Territories. |
45. | Utah | January 4, 1896 | Utah Territory |
46. | Oklahoma | November 16, 1907 | Indian and Oklahoma Territory |
47. | New Mexico | January 6, 1912 | New Mexico Territory |
48. | Arizona | February 14, 1912 | Arizona Territory |
49. | Alaska | January 3, 1959 | Acquired from Russia |
50. | Hawaii | August 21, 1959 | Annexed by US. |
Sources📚💻📜
Wars
https://washingtonlee.apsva.us/wp-content/uploads/sites/38/2016/08/war_causes_and_effects.docx
 Knowt
Knowt