chapter 3: a&p (cells)
What is a cell?
Cell theory:
- The cell is the smallest unit of life.
- All organisms are made of one or more cells.
- Cells only arise from other cells.
- Trillions of cells in the body divided over 250 cell types
- 2 micrometers to over 1 meter long nerve cells
- All share: plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus
Extracellular Materials
- Extracellular Fluid (ECF): includes interstitial fluid, blood plasma, cerebrospinal fluid
- dissolves & transports fluids
- Cellular Secretions: such as gastric & intestinal fluids (digestion), saliva & mucus (lubricants)
- Extracellular Matrix (ECM): mesh assembled from proteins and polysaccharides that bind cells together
- particularly abundant in connective tissues
Lipids
- Phospholipid Bilayer:
- thin, fluid
- embedded proteins
- cholesterol → add structure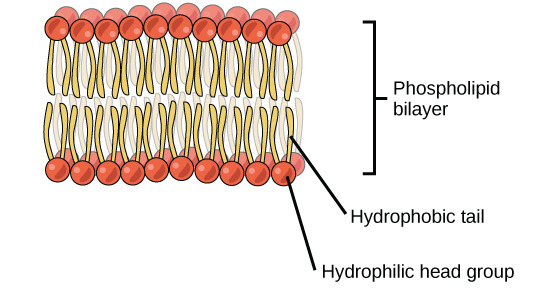
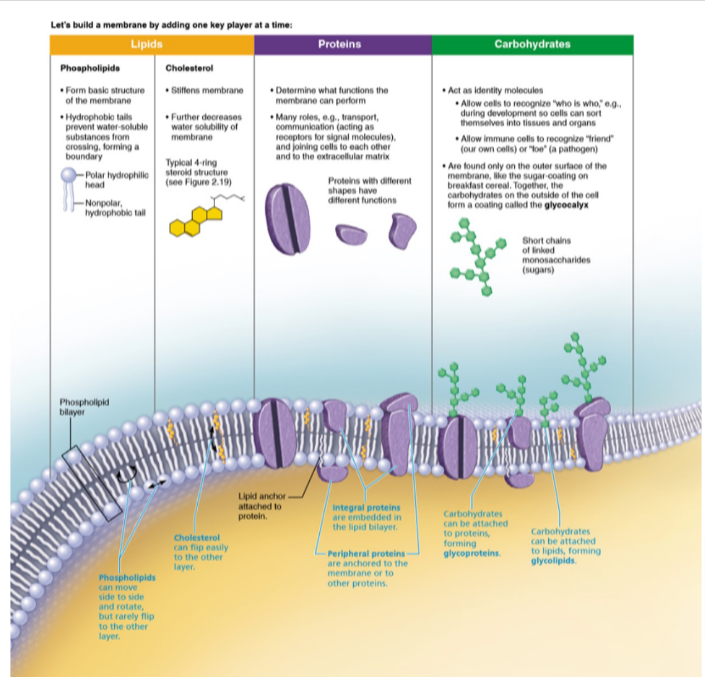
Proteins
- transport substances in & out cells
- receptors: sense materials (1 side communicate to other 🔁)
- enzymes: catalyze reactions
- ECM attachment anchor to cell membrane to surrounding matrix
- cell to cell contact
- no tissue sheets to hold together
Carbohydrates
- glycocalyx
- glycoprotein
- glycolipid
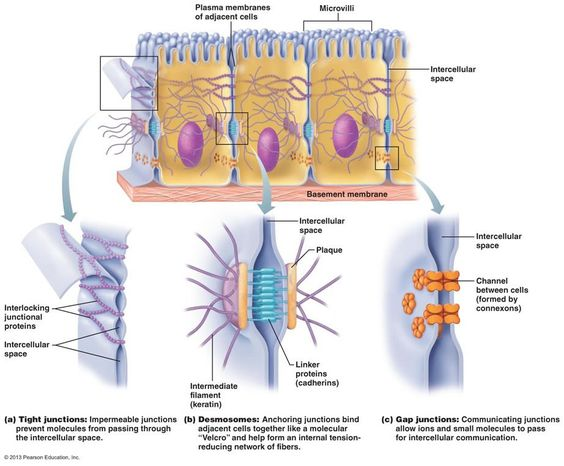
Cell Junctions
1. tight junction:
- tightly fused, impermeable, no passing of other materials, prevent movement
(ex: intestinal tract)
2. desmosomes:
- anchoring junctions, distribute tension, & prevent stretching
(ex: stretching muscle & skin)
3. gap junctions:
- communicating junctions (protein channels) thats allow material exchange
(ex: cardiac cells & other contract)
Membrane Transport:
- Selective Permeability: only substances meeting certain criteria can pass through unaided
- hydrophobic
Passive Transport: movement across a membrane without expended cellular energy (along concentration gradient) (high to low)
1. simple diffusion → C2, O2
2. facilitated diffusion → helper protein → carrier (or) channel mediated → leakages (or) gated
3. osmosis → H2O against (aquaporin)
Tonicity: 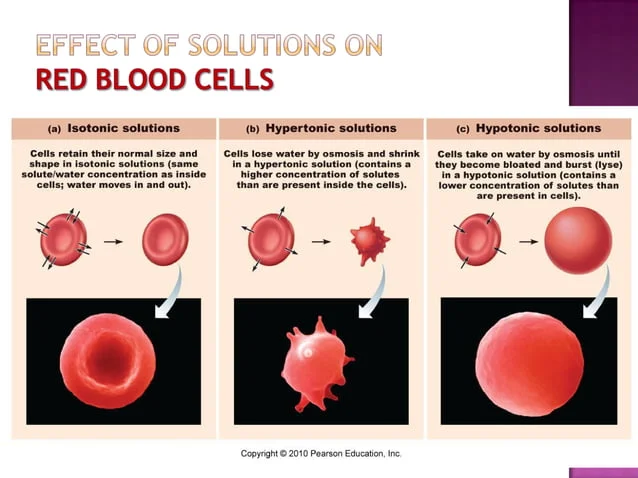
Active Transport: movement across a membrane that requires ATP
1. primary & secondary
- sodium potassium pump (protein) pump splits ATP & moves substances
- co-transporter to use energy of concentration gradient (moving against crowd)
2. vesicular transport
- endocytosis & exocytosis
- phagocytosis (cannibalism)
- pinocytosis (take in fluid)
- receptor mediated endocytosis
Membrane Potential
- Voltage across membrane
- Voltage: electrical potential energy from separation of charge particles
- Established by diffusion, maintained by active transport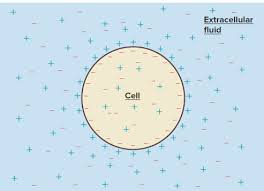
1. Leakage Channels = K+ Loss from Cell
2. Some K+ moves back into cell, attracted to - charge of inner membrane
3. Balanced K+ gradient occurs at -90 mV
Plasma Membranes:
- Cell Adhesion Molecules (CAMs): glycoproteins that maintain cell anchors, move migrating cells, send SOS signals after damage, transmit environmental information
- Membrane Receptors:
- Contact Signaling: cell-cell recognition, important in development & immunity
- Chemical Signaling: extracellular ligands bind to receptors to initiate a response (e.g., hormones, neurotransmitters); response is cell-type specific
- Initiate release of G proteins from receptors into cells, & activate different types of responses
Cytoplasm
- Cytoplasm: internal contents of a cell
- Cytosol: jelly-like filling; fluid medium for biochemical reactions
- Inclusion: additional chemical substances
- Organelle: membrane-enclosed bodies for a specific function
- Nucleus: central organelle holding DNA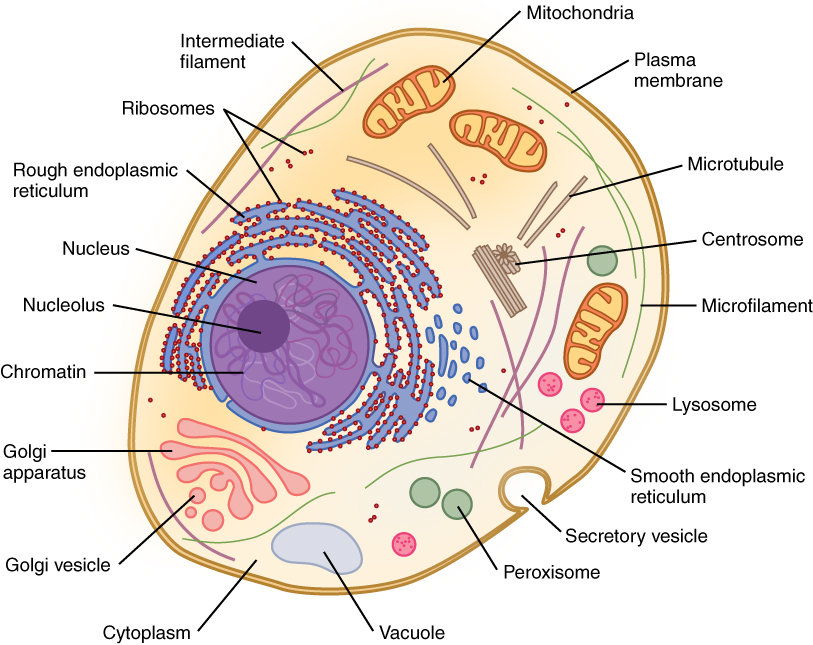
Endomembrane System
- system of organelles that work together to produce, store, and export biological molecules
1. Nucleus
2. ER (Rough & Smooth)
- Rough: protein synthesis for outside cell
- Smooth: lipid synthesis (phospholipid, cholesterol)
- steroid hormones
- store calcium
3. Golgi Apparatus
- postal service of cell
- modify molecules
4. Exocytosis OR Lysosomes
- digestive enzymes & clean out (autophagy) autolysis: cell death/destruction
5. Peroxisomes
- detoxify & neutralize free radicals (ROS); highly reactive products of cellular processes that contain oxygen (OH, H2OO2, O2)
- Oxidative stress: damage caused by ROS
6. Mitochondria
- provide majority of ATP
- High density in cells with high energy needs
- Smooth outer membrane and folded inner membrane with cristae
- Metabolism occurs in internal matrix
7. Ribosomes
- protein synthesis
- Built of two subunits
- Free or membrane-bound
Cytoskeleton
1. Microtubules: thick filaments, tubulin
- Cilia & flagella
- resist compression
- centrioles
2. Microfilaments: thin filaments, actin
- contraction & cell division
3. Intermediate Filaments: keratin
- cell adhesion
- resist tension
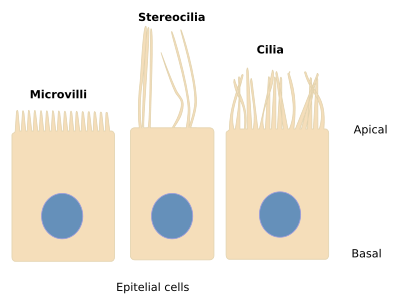
Cellular Extensions:
- Cilia: whiplike extensions to move substances across cell surfaces
- Flagella: substantially longer than cilia to propel a cell
- Only present in humans in sperm cells
- Microvilli: finger-like projections that increase cell surface for absorption (not movement)
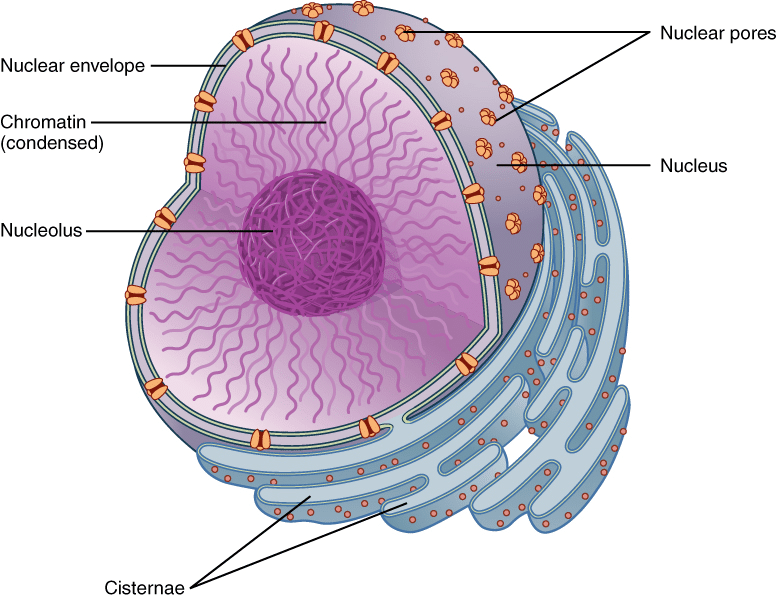
Nucleus:
- stores genetic information
(ex: DNA)
- Multinucleated: multiple nuclei
- Anucleate: no nucleus
Nuclear Envelope: lipid bilayer with passages called nuclear pores
Nucleolus: manufactures ribosomes
Chromosomes
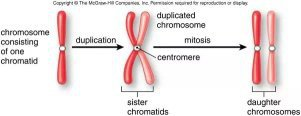
Cell Cycle
- Interphase
G1: prep for DNA replication
S: DNA replication
G2: prep for cell division
- Mitosis (Cell Divide)
1. Prophase
- condense chromosomes
- lose nucleus & activate centrioles
2. Metaphase
- chromosomes line up in the middle
3. Anaphase
- chromatids pull apart
- moved by centrioles
4. Telophase/Cytokinesis
- 2 nuclei form
- cytoplasm, membrane divide
- Cytokinesis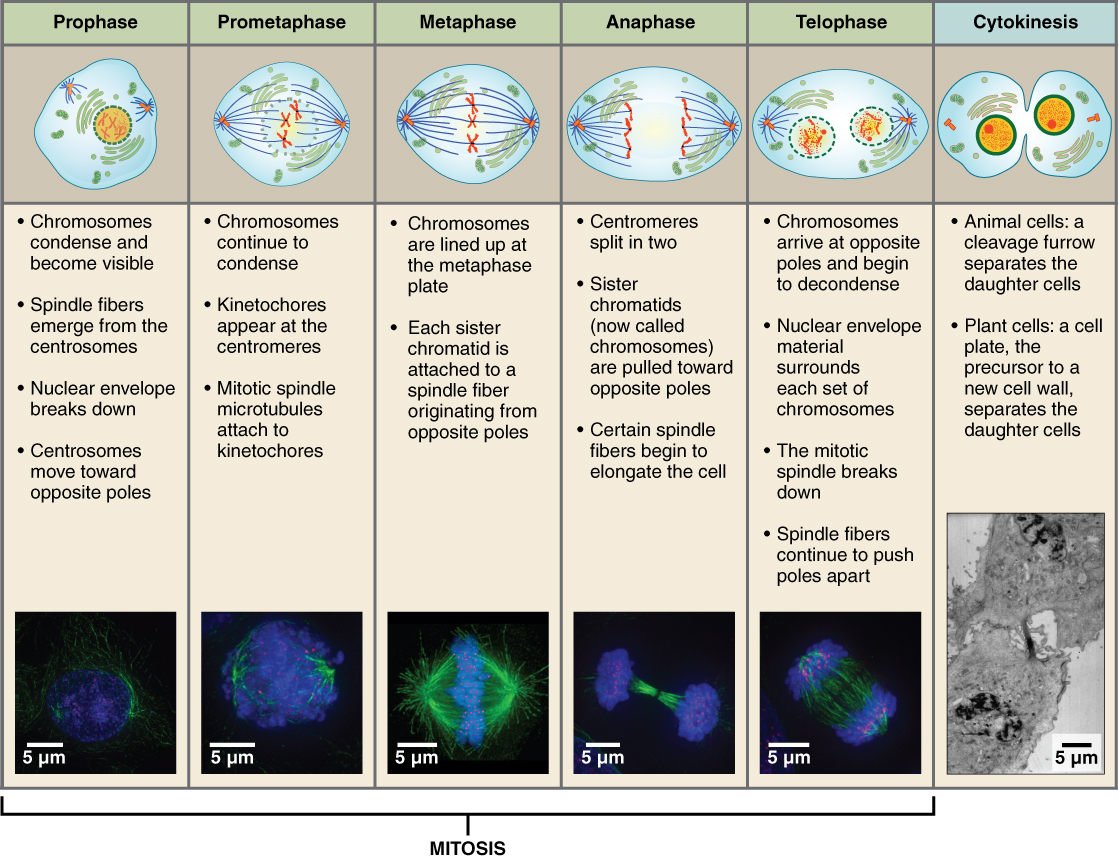
G0: rest phase between cell divisions or in cells that cannot divide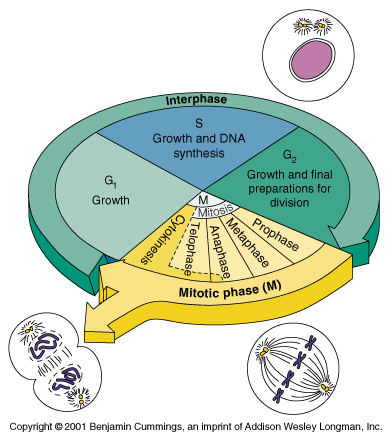
Control of Cell
- ratio of SA:V ⬆ Cell ⬇ Movement
- chemical signal
- space to grow
- interphase checkpoints ruled by cyclins (mitosis) & cyclin dependent kinases (cdks)
* Contact Inhibition:
- no space to put new cells so mature tissue & control growth
Central Dogma
(Nucleus) (Ribosomes)
DNA (genetic code) → RNA (messenger) → Protein
transcription translation
Transcription: DNA → RNA
1. Initiation: proteins bind to designated gene promoter
2. Elongation: RNA polymerase unwinds DNA and writes mRNA along one strand
3. Termination: terminator sequence causes RNA to unbind DNA and RNA pol
RNA processing
- Exon: portion of transcript that codes for proteins
- Intron: non-coding parts in-between
- Splicing: removal of non-coding transcript sequence
Translation: RNA → Protein
1. Initiation: ribosomes binds to mRNA
2. Elongation: tRNA matches amino acid to RNA sequence
3. Termination: tRNA reaches the stop codon and releases the peptide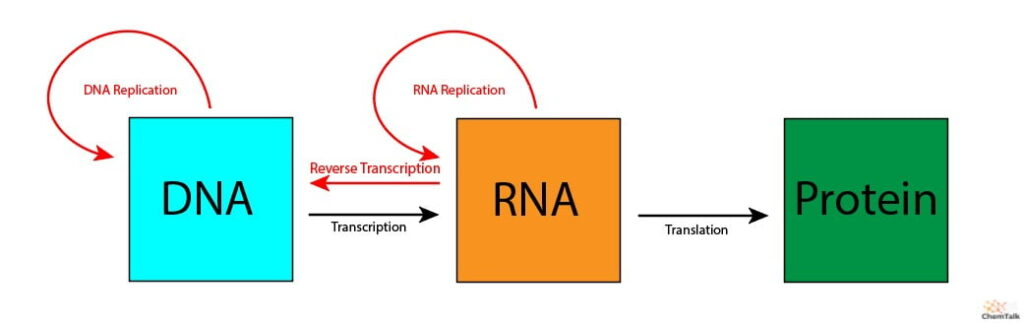
DNA Replication:
1. Initiation: helicase & other enzymes unwind DNA
- Helicase
- Unzip DNA strand
- Promoter / Ribosome
2. Elongation: DNA polymerase builds the complementary strand along each template
- Primase
- keep DNA apart through primase
- DNA polymerase
- replace primer & new DNA
- RNA polymers' unwind DNA
- tRNAs
3. Termination: two new strands are complete & each fused to an original strand
- Ligase
- connect & ligase new DNA strand
- Terminator
- Stop Codon
- Semiconservative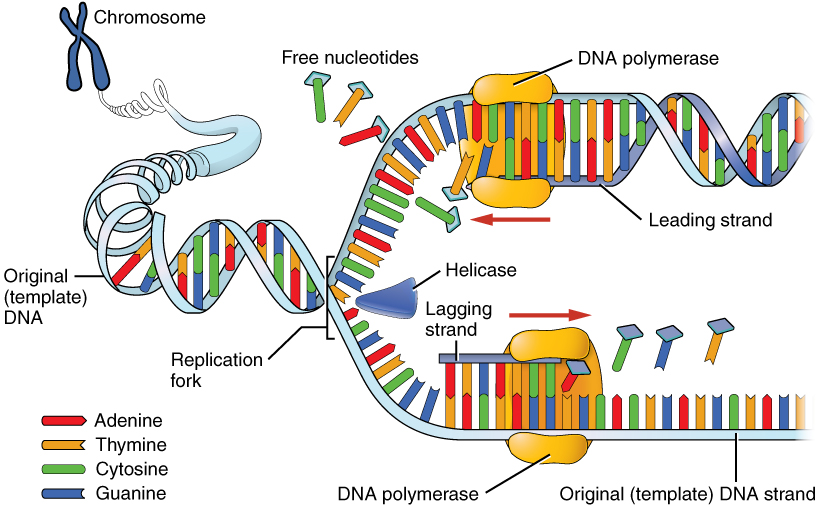
Messenger RNA
- Gene: segment of DNA with instructions to build one polypeptide
- copied from DNA to mRNA, then from mRNA to protein
- made up of exons and introns
- Encoded in there base-long triplets
- mRNA
carry protein code
- rRNA
form ribosome
- tRNA
build proteins
Autophagy & Apoptosis
- Autophagy: removal of unnecessary, damaged, or stressed cell components
- Allows removal of unneeded proteins & structures
- Cannibalizes portions of cells during starvation & stress
- Restructures cells during development
- Ubiquitin-proteasome Pathway: marks & destroys misfolded or damaged proteins
- Apoptosis: programmed cell death to remove cells with limited life spans
- Mitochondria leak factors that trigger caspases to digest internal components