steroid hormone signalling
oestradiol and progesterone:
oestradiol and progesterone are made in the overies
there are oestradiol receptors in the hypothalamus
the hypothalamus controls activity of the pituitary gland
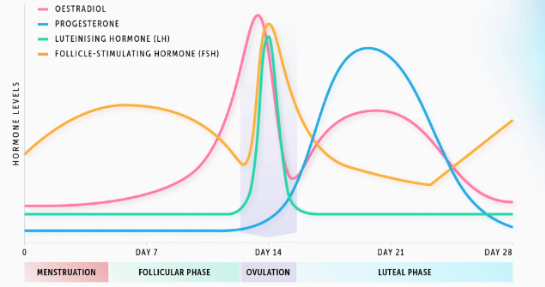
oestradiol causes the pituitary gland to release FSH and LH
progesterone has direct effects on the lining of the uterus
progesterone causes thickening and increased blood vessel formation in endometrium
at the end of the menstrual cycle progesterone levels drop leading to shedding of the endometrium
if embryo implants in endometrium, progesterone levels stay high
 negative feedback = a stimulus causes a response that decreases the stimulus
negative feedback = a stimulus causes a response that decreases the stimulus
if blood sugar rises beta cells secrete insulin causing cells to uptake glucose converted to glycogen or fat which decreases blood sugar levels
if blood sugar levels drop alpha cells secrete glucagon causing a breakdown of glycogen in to glucose which raises blood sugar levels.
positive feedback = a stimulus causes a response that increases the stimulus
Fruit ripening:
ethylene is produced by ripe fruit.
ethylene gas is detected by nearby fruit
nearby fruit begins to ripen causing it to release ethylene gas
Fever:
body temperature increases in response to infection
increased body temp increases metabolism
increased metabolism increases body temperature
this continues until fever breaks