UNIT 6.3-6.5
Market Failure #1: PUBLIC GOODS
Public Sector- The part of the economy that is primarily controlled by the government
Private Sector- The part of the economy that is run by private individuals and companies that seek profit.
Public Goods:
Why must the government provide public goods and services?
It is impractical for the free-market to provide these goods because there is little opportunity to earn profit - this is due to the Free-Rider Problem (Free Riders are individuals that benefit without paying)
The Free Rider Problem
Examples:
People who download music illegally
People who watch a street performer and don’t pay
Teenagers that live at home and don’t have a job
What’s wrong with Free Riders?
Free-Riders keep firms from making profits.
If left to the free market, essential services would be under produced.
To solve the problem, the government can:
1. Find new ways to punish free-riders.
2. Use tax dollars to provide the service to everyone.
Definition of Public Goods
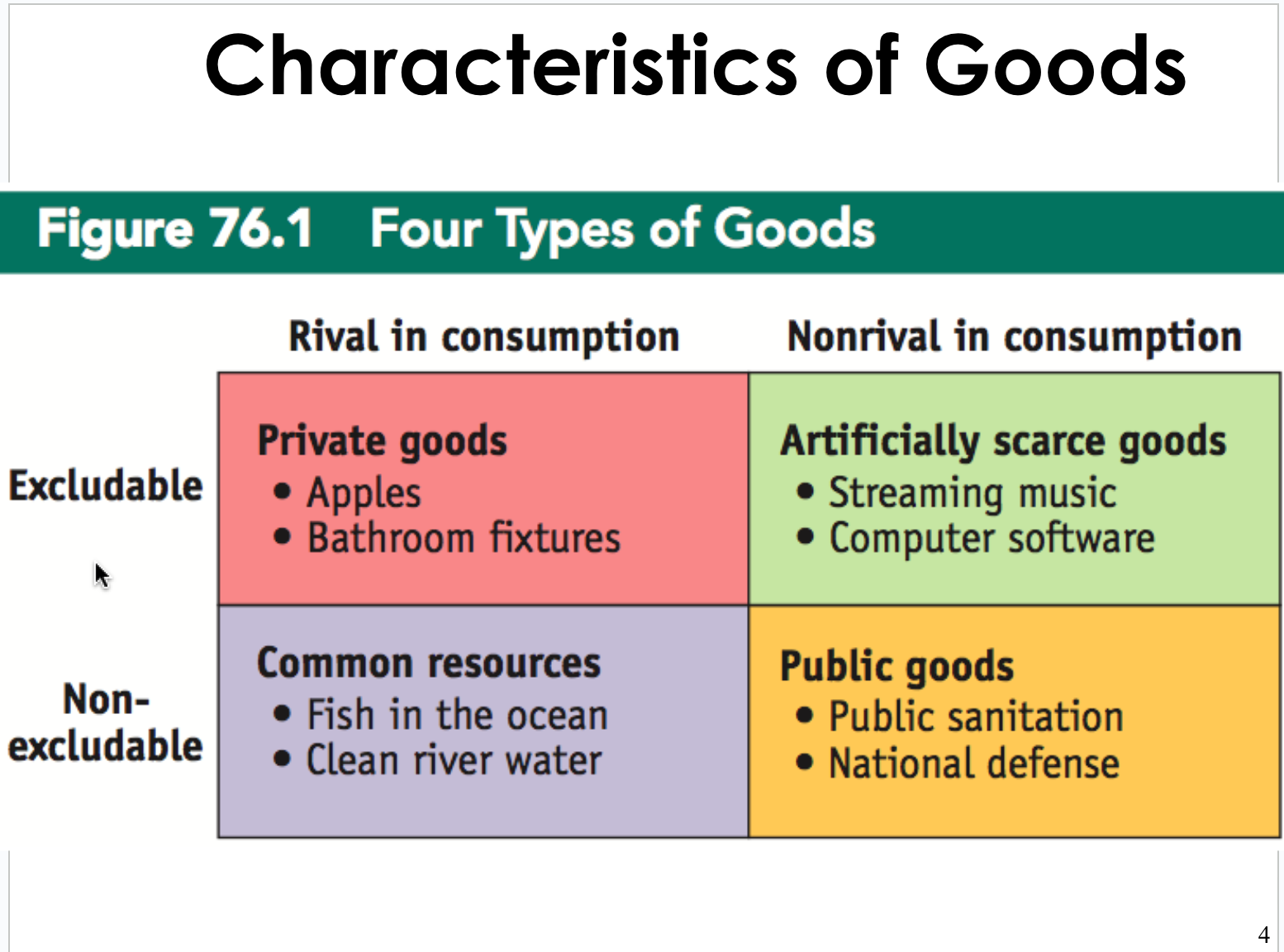
Public goods have two criteria:
1. Non-exclusionary
Everyone can use the good
Cannot exclude people from enjoying the benefits (even if they don’t pay).
Ex: National Defense
2. Shared Consumption (Non-rival)
One person’s consumption of a good does not reduce the usefulness to others.
Ex: City Park
How does the government determine what quantity of public goods to produce?
They use Supply and Demand
Demand for Public Goods-
The Marginal Social Benefit of the good determined by citizens willingness to pay.
Supply of Public Goods-
The Marginal Social Cost of providing each additional quantity.
Government Intervention to correct market failures depends of the Different Market Structures behind the market failures
Market Failure #3: Monopolies
Monopoly Review
Why are monopolies a Market Failure?
Monopolies destroy the key ingredient of the free market system- Competition.
Price Makers
Inefficient (productively and allocatively)
To fix this MARKET FAILURE the government must get involved.
Regulating Monopolies/…
Antitrust Laws
Antitrust Laws- Laws designed to prevent monopolies and promote competition.
After the Civil War, advances in technology and transportation lead to national markets.
Eventually only a few firms began to dominate industries: Railroads, Steel, meatpacking, coal, etc.
Legislative Branch
Passed laws designed to stop monopolies
Sherman Act of 1890- “Every person who shall monopolize …or conspire to monopolize…shall be deemed guilty of a felony.”
Executive Branch
The Federal Trade Commission must approve all corporate mergers. (Like AT&T and…)
When firms use anti-competitive tactics the Department of Justice files suit against them.
Judicial Branch
Supreme Court finds the firm guilty or not guilty and assigns a punishment.
Why Regulate?
Why would the government regulate a monopoly?
To keep prices low
To make monopolies efficient
How do they regulate?
Use Price controls: Price Ceilings NOT Taxes
Why don’t taxes work?
Taxes limit supply and that’s the problem
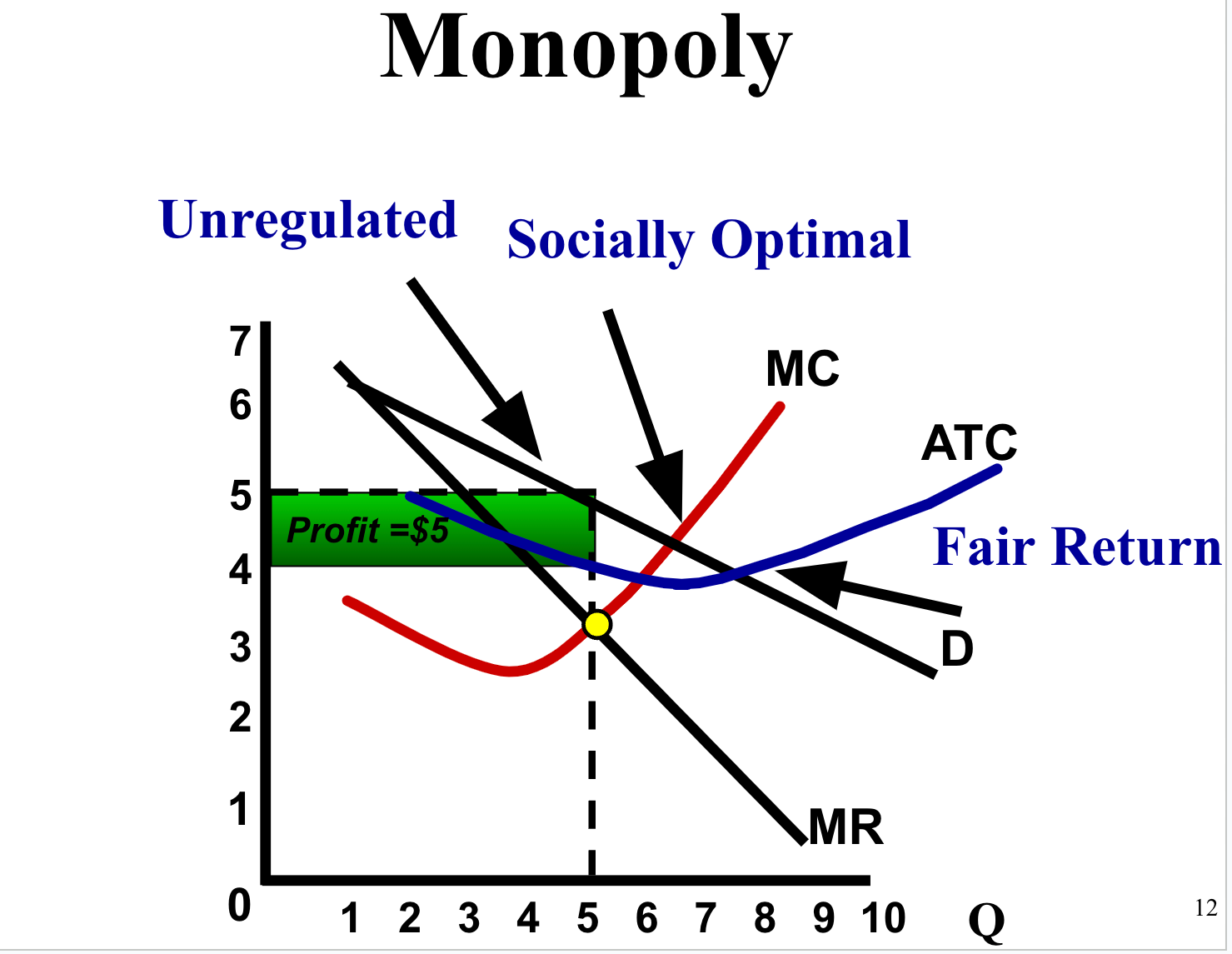
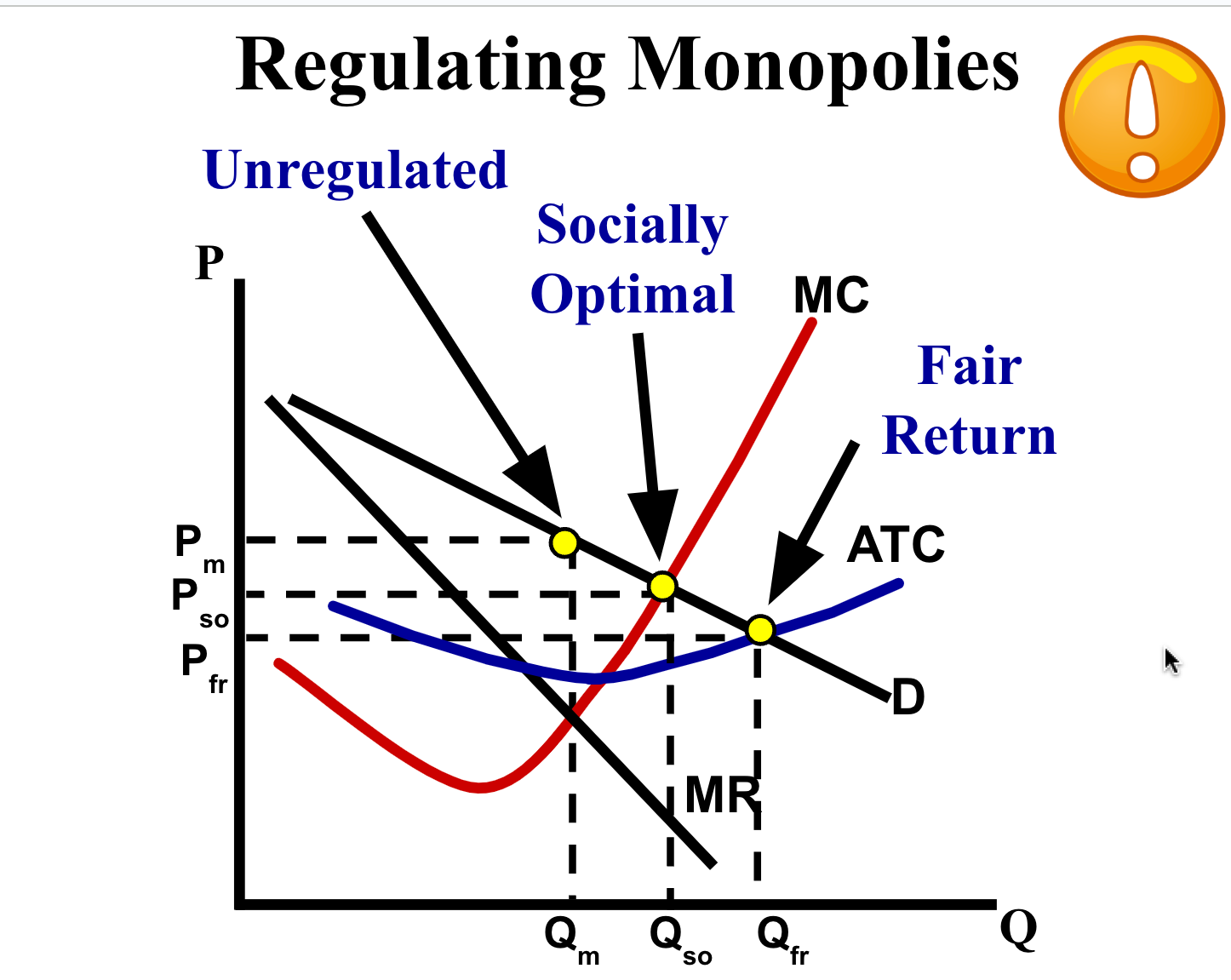
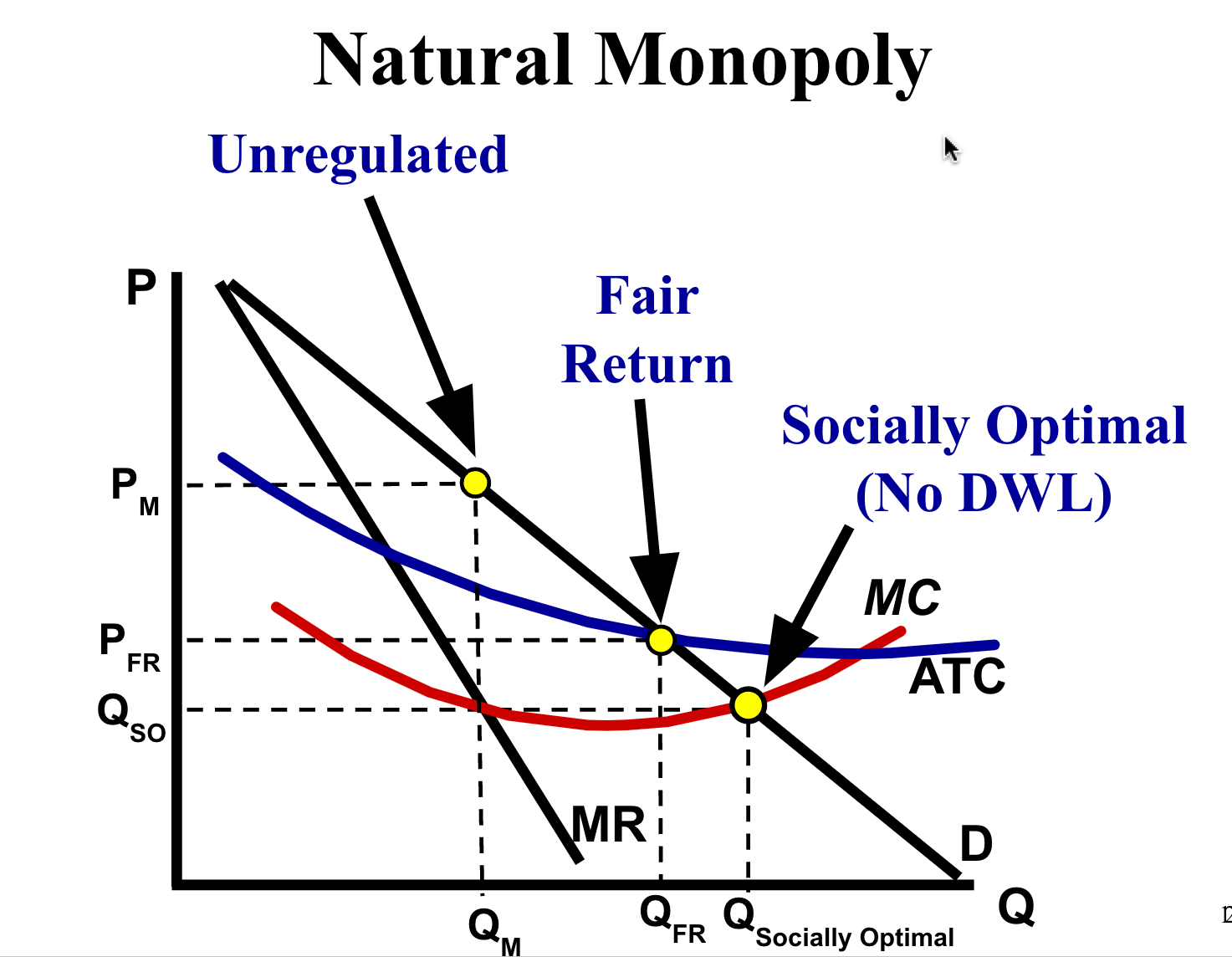
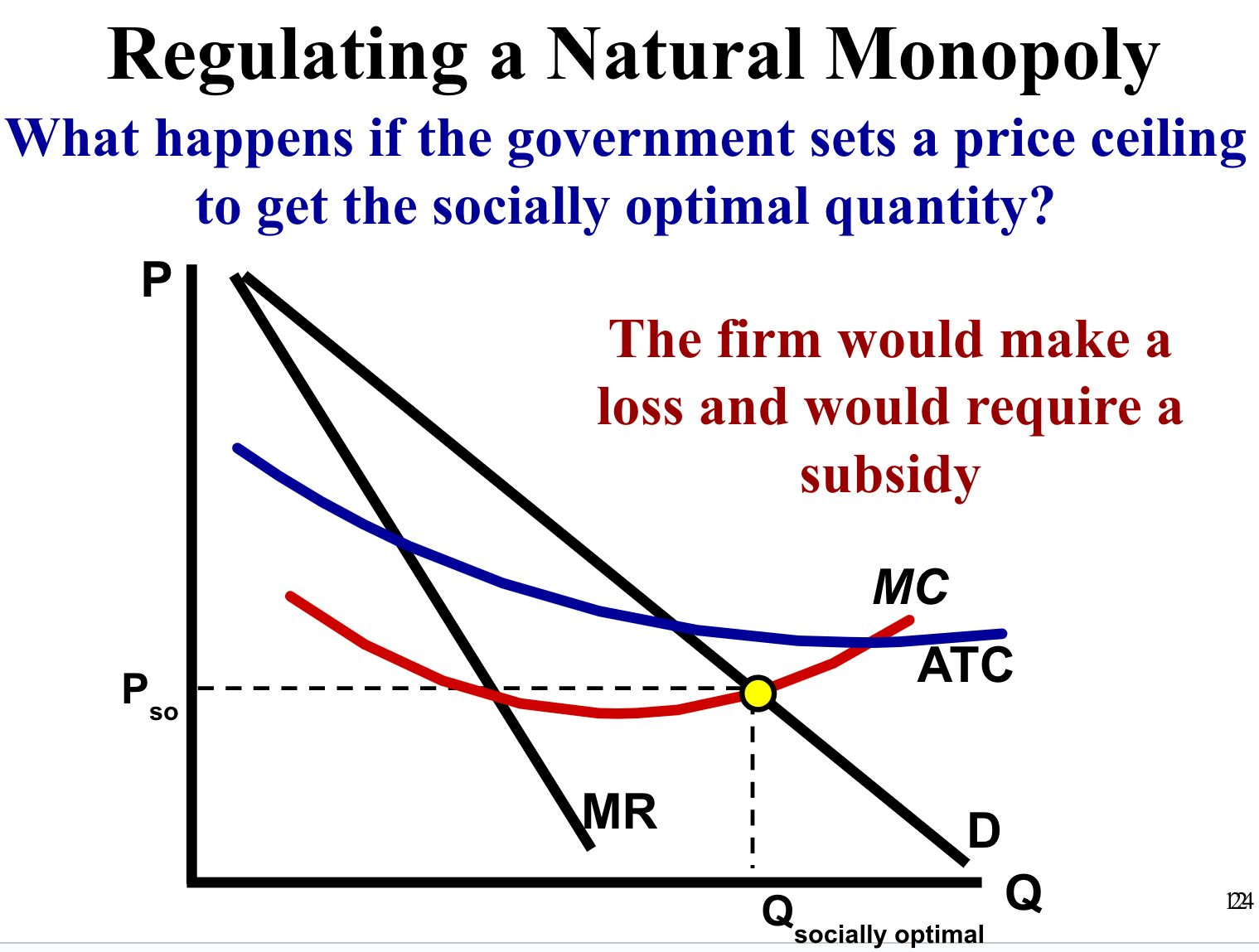
Where should the government place the price ceiling? :
1.Socially Optimal Price
P = MC=D (Allocative Efficiency)
OR
2. Fair-Return Price (Break–Even)
P = D = ATC (Normal Profit)
Socially Optimal = Allocative Efficiency=(d=mc)
Fair Return means no economic profit
 Knowt
Knowt