Factors affecting photosynthesis
Light intensity
Light wavelength
Light duration
Water availability
Humidity (indirect)
Temperature
Carbon dioxide concentration
Amount of chlorophyll
Wind (indirect)
Indirect factors - stress response of plans in these conditions = stomatal closure which affects carbon dioxide concentration
Respiration reduces the overall rate of photosynthesis
Gross rate of photosynthesis - rate of respiration = net rate of photosynthesis
Usually the rate of respiration in plants is quite low and on a sunny day the rate of photosynthesis is much higher than the rate of respiration
Limiting factor: The factor that is present at the lowest or least favourable value (and so is therefore limiting the rate)
The law of limiting factors states that the rate of a metabolic process is limited (prevents the reaction from being faster) by the factor that is at its least favourable value
Light intensity
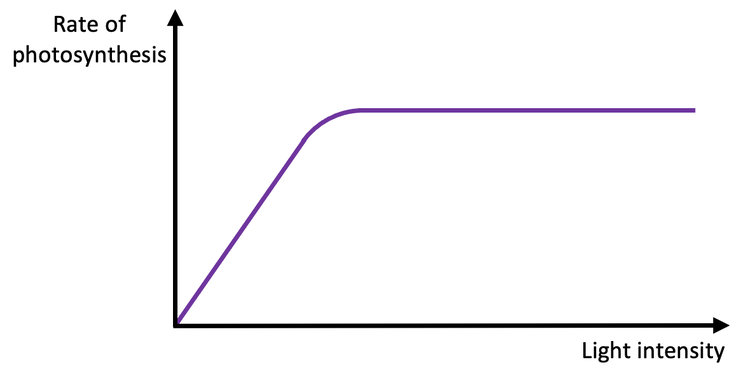
Rate of photosynthesis in mm3CO2cm-2h-1
Describe the effect of increasing light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis
Firstly, the rate increases in a linear fashion - light intensity limiting factor
Then in the non-linear zone, the rate of photosynthesis is increasing at a slower rate - light intensity still limiting factor, but other factors are also starting to be limiting
Finally, the rate plateaus, or becomes constant, while light intensity still continues to increase - light intensity is no longer the limiting factor
Explain
More light is absorbed by photosystems 1 and 2
As light intensity increases, more electrons can be excited out of chlorophyll for non-cyclic and cyclic phosphorylation
More electrons passed down electron transport chain, so more ATP and NADH
More protons being pumped from stroma into thylakoid space
More photolysis of water
More/faster rate of GP → TP → RuBP
Greater rate of fixation of CO2 by ribisco combining CO2 and RuBp
Why does it level off?
Light no longer limiting factor
Most likely carbon dioxide
Rate of fixation of carbon dioxide by rubisco is limited because the collision rate and formation of ESCs with RuBp and carbon dioxide is liited by carbon dioxide conc
Rate of production of GP is limiting
ATP and reduced NADP from LDR is not limiting
How light affects concentrations of GP, RuBP and TP

No light independent stage so no ATP or reduced NADP
RUBp reacts with carbon dioxide, producing GP
GP cannot be converted to TP also cannot regenerate RuBP because ATP and reduced NADP are required from LDR
So GO builds up and plateaus as no more RuBP is made whilst the RuBP falls and then plateaus as it is used up
Low carbon dioxide concentration = low rate/no reaction of RuBP and carbon dioxide so little/no GP made
However ATP and reduced NADP from LDR are available
So GP is used up being converted to TP and then back to RUBp
So GP levels fall and RuBp rise then plateau, once all the GP is used up