Equilibria and acids
When ethanoic acid is dissolved in water it forms an equilibrium
CH3COOH(aq) ⇌ CH3COO-(aq) + H+(aq)
This can be expressed for any acid, as follows:-
HA(aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + A-(aq)
For the example of ethanoic acid
HA = CH3COOH
A- = CH3COO-
Ka
HA(aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + A-(aq)
As with any equilibrium we can derive an equilibrium constant, but instead of calling it Kc, we call it Ka
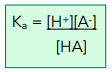
[H+], [A-], and [HA] are when at equilibrium
Ka is the acid association constant
The larger the value of Ka, the higher the strength of the acid
Always has units of moldm-3
Just as we use pH to show the acidity, pH = -log[H+]
The huge range of Ka values mean we often use pKa to show the strength of an acid
pKa = -log(Ka)
Calculating the pH of weak acids
HCOOH(aq) ⇌ HCOO-(aq) + H+(aq)
Given the Ka of methanoic acid what is the pH of a 0.0500M solution?
Ka = 1.60 × 10-4M
Firstly, assume that the [A-] = [H+]
Ka = [H+]2 / [HA]
Secondly, since only a small proportion of the acid has dissociated we can say that [HA]eqm = initial concentration
Rearrange the equation and substitute the values in
0.05 x (1.6 × 10-4) = [H+] 2
Take the square root to find the pH