L3: Molecular and Cellular Mechanism of Inflammation
Learning Objectives
Define inflammation
Distinguish between acute and chronic inflammation
Understand the role of cytokines and chemokines in inflammation
Dual roles of cytokines as pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators
Understand the cellular mechanisms of inflammation
Chronic inflammation in autoimmune diseases
Definitions
body’s attemption of removing harmful stimuli and starting the healing process
types of stimuli causing vascularised tissue damage
pathogens
noxious stimuli
chemicals
stings
physicla injury
hypersensitivity and autoimmune disease
Types of inflammation (chronic)
metabolic syndrome
arthritis
alzheimer’s disease
asthma
ulcerative colitis and inflammatory Bowel disease
colon, breasy and lung cancers
eye disorders
cardiovascular disease
gingivitis
symptoms fo acute inflammation
heat: increased blood flow to affected area
redness: capillaries filled with blood
swelling: increased permeability of blood vessels → buildup of fluid and exudation of plasma proteins
pain: increased bradykinin release → stimulate nerve endings
★internal organ inflammation: not many nerve endings → no pain
immobility: loss of function
Process of Inflammation
Recognition of injurious agent
infectious inflammation
signals: PAMPs
extrinsic source
recognised by TLRs (Toll-like receptors) on cell surface of pathogen or infected cell
ligands recognised (bacterial products)
LPS (in Gram-ve bacteria)
LTA (in Gram+ve bacteria)
flagellin
Sterile inflammation
signals: DAMPs
endogenous source
recognised by NOD receptors (nucleotide oligomerisation domain) in cytosol
ligands recognised (released by damaged cells)
heat shock proteins
uric acid crystal
defensins
HMGB1
Recruitment of leukocytes
Blood vessel dilation → increased blood flow
margination: getting close to blood vessel wall
rolling
binding of selectin ligand (on neutrophil) to E- or P-selectin (on endothelium)
binding of chemokine receptor (on neutrophil) to chemokine (IL-1 secreted by macrophage) presented by proteoglycan (on endothelium) → activate neutrophil
adhesion: binding of β2 integrin (on neutrophil) to ICAM-1
diapedesis (facilitated by CD31): endothelial cells contract → increase permeability → transmigrate from blood vessel to tissue
Chemotaxis: cytokines produced by Langerhan cells and macrophage attract neutrophils to site of infection
Removal of causative regents —— Phagocytosis
recognition and attachment: microbes bind to phagocyte receptors
engulfment: engulf pathogens or apoptotic cells by zipping up aroound it
depend on polymerisation of actin filaments → plasma membrane remodelling
fusion of phagosome with lysosome b: form phagosome → fuse with lysosome → phagolysosome
killing and degradation: digested by lysozyme and released as exocytic vesicles
mediated by ROS nitric acid and lysosomal enzymes
★ Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs)
produced by neutrophils and inflammatory mediators
✔︎ chromatin materials + antimicrobial peptides and enzymes
trap miceobes to prevent spreading
Termination/ Resolution
depletion of chemokines
neutrophils apoptosis
induced by ROS, AncA1 and lactoferrin
clearance of apoptotic neutrophils by macrophages
macrophage phenotype switch: fomr pro-inflammatory → resolution-phase
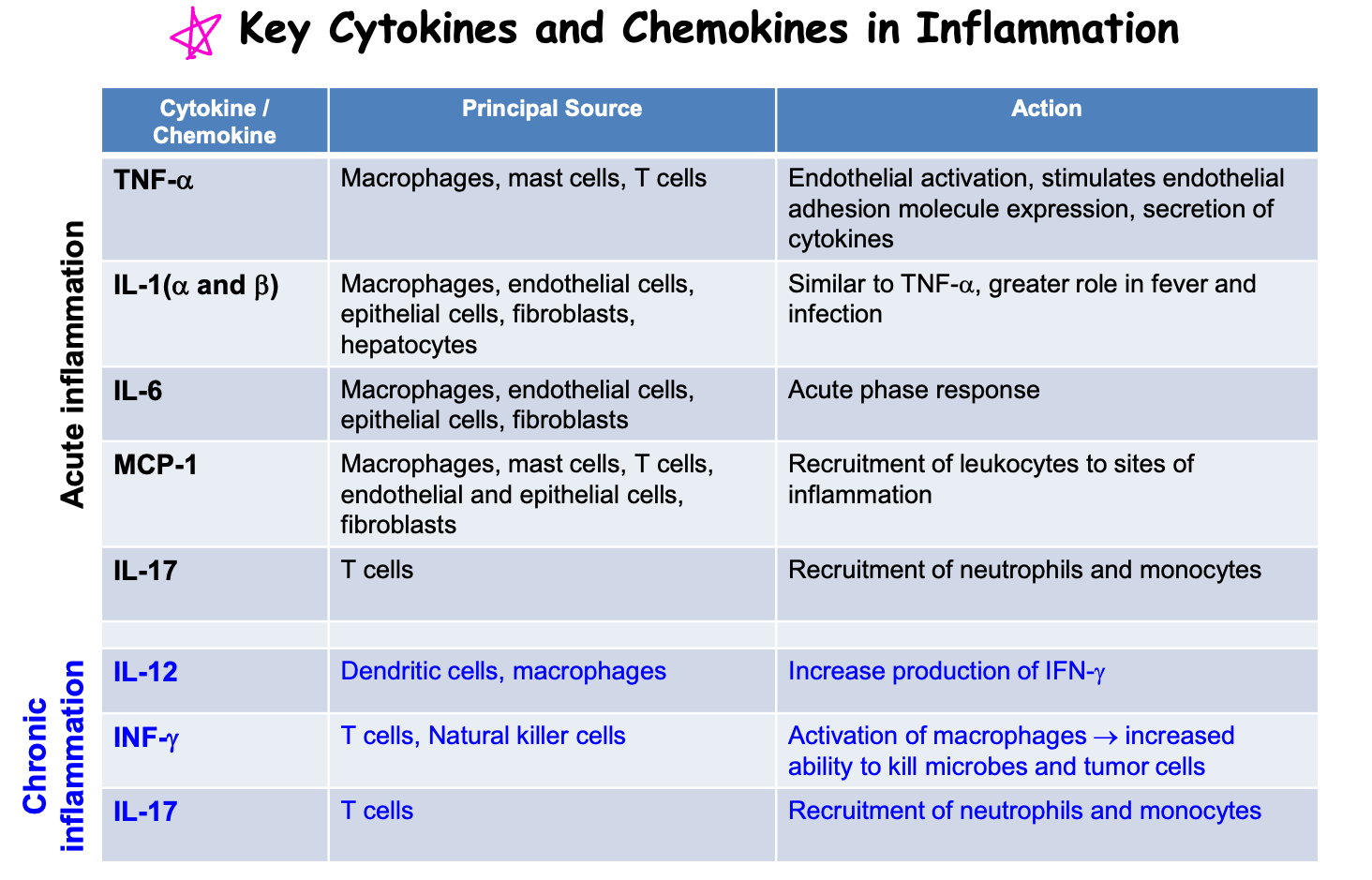
Inflammatory mediators
Cytokines
Role
key modulators
regulators of inflammation
chemical messengers
types
interleukin
tumor nercrosis factors
interferons
chemokines
produced by immune cells and non-immune cells → bind to cell surface receptors
initiate autocrine, paracrine and endocrine effects
functions
T-cell proliferation: IL-2, IL-4, IL-15, IL-21
Pro-inflammatory: TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IFN-γ
Anti-inflammatory: IL-10, TGF-β1, IL-6
Chemokines
family of small cytokines
chemotaxis: secreted by cells primary to recruit leukocyes (macrohages and monocytes) of infection or injury
chemoattractants: adhesion molecules
induce integrin expression: β2-integrin on lymphocytes for attachment
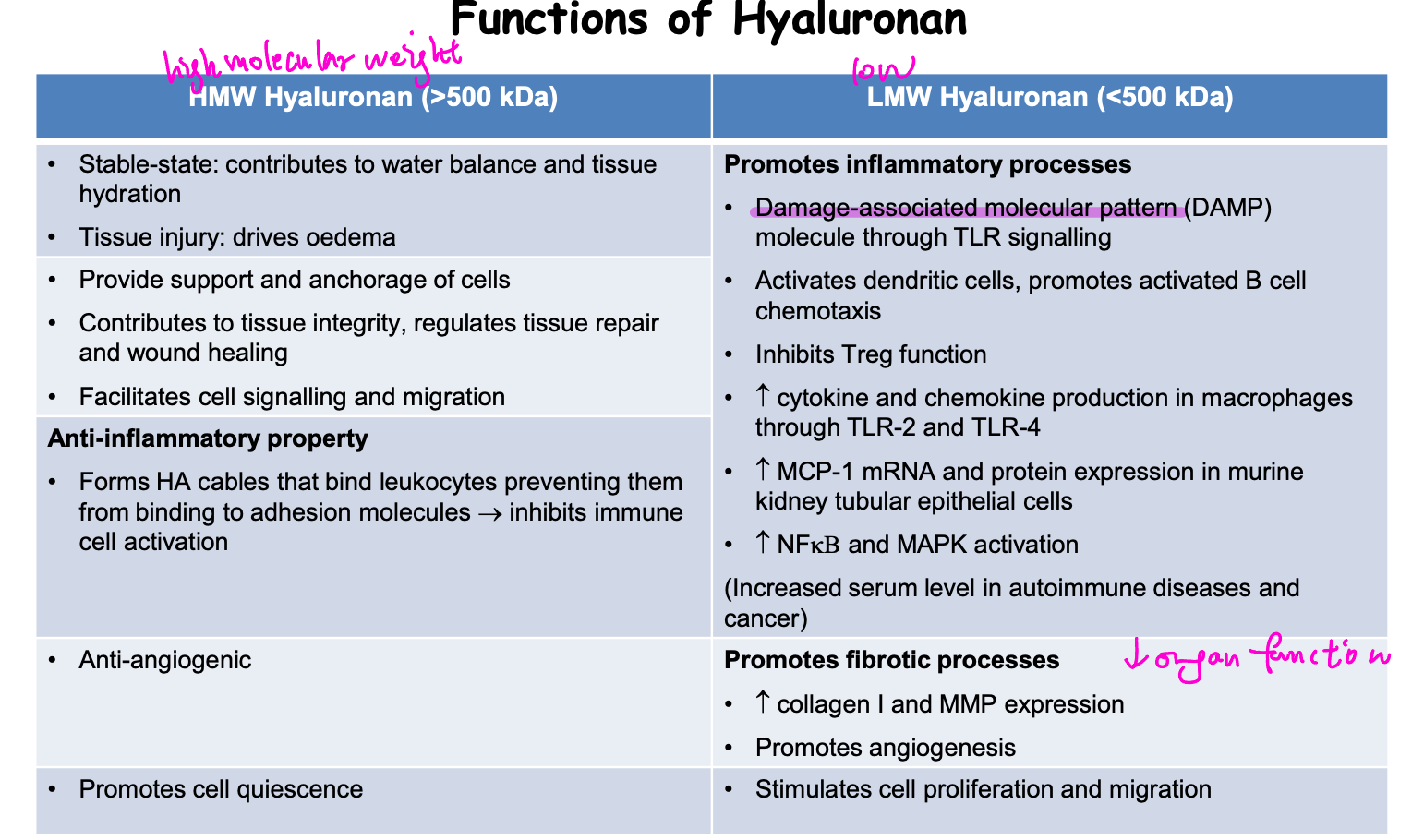
Hyaluronan (HA)
large non-fulfated glycosaminoglycan in extracellular matrix
synthesied by 3 HA synthases (HAS I, II, III) on plasma membrane → secreted to extracellular space
HMW HA: synthesised by HAS I and II
LMW HA: synthesised by HAS III
bind to CD44
functions
Acute and Chronic Inflammation
inducing agent
acute
pathogen
injured tissues
allergens
chronic
non-degradable pathogens
persistant foreign body
autoinmmune response
cells involved
acute
neutrophils
monocytes
macrophage
basophils
eosinophils
mast cells
chronic
monocytes
macrophage
lymphocytes
plasma cells
fibroblast
process
acute
vacular changes
neutrophils recruitment
chronic
angiogenesis
mononuclear cell infiltration
outcomes
acute
resolution
abcess formation
chronic inflammation
chronic
tissue destruction
fibrosis
necrosis
Chronic inflammation in autoimmune diseases
Inflammation and cell senescence
cell senescence= early ageging of cell
increased inflammatory mediators expression
TNF-α
IL-6
IL-1β
caused by age-related frailty or chemical injury
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Type II hypersensitivity
breakdown of self-tolerance → immune-mediated tissue damage
causes
genetic factors
environmental factors
smoking
UV exposure (drive apoptosis)
microbiome or viruses (EBV)
involved immune cells
autoreactivity of T cells
B cells
increased cytokines secretion
IFN-γ: accelerate disease
IL-6: promote terminal B cell differentiation
IL-8 and MCP-1: increase inflammatory cell recruitment
damaged organs
kidney—— lupus nephritis
pathogenesis
acute stage: nephrons damged by B and T cells (treated by immunosuppressive agents)
chronic stage: tubular atrophy and fibrosis (chronic renal impariment → dialysis)
mechanism
indirect binding: chromatin released from dead cells are entrapped in GBM (glomerulus basal membrane) → ‘bridge’ to mediate anti-dsDNA antibody binding → glomerulonephiritis
direct binding: antibody bind to cell surface or extracellular matrix antigen in nephron
skin
lungs
brain
heart