20.Virginity and pregnancy
Virginity, Pregnancy and Delivery, Legitimacy and Paternity
Virginity
Definition of Virginity: A woman who has not experienced sexual intercourse.
Loss of Virginity(Defloration) (UQ): Occurs when a woman engages in sexual intercourse, resulting in the tearing of the hymen.
Types and Structure of Hymen (UQ):
Hymen is a fold of mucous membrane about 1mm thick at the vaginal outlet.
Variations:
Annular: Round or oval opening, common.
Semi-lunar/Crescentic: Crescent shape.
Infantile: Small linear opening.
Cribriform: Multiple small openings.
Vertical: Vertical opening.
Septate: Two lateral openings.
Imperforate: No opening.
Fimbriate: Fimbriated margin that may be misinterpreted as a rupture.
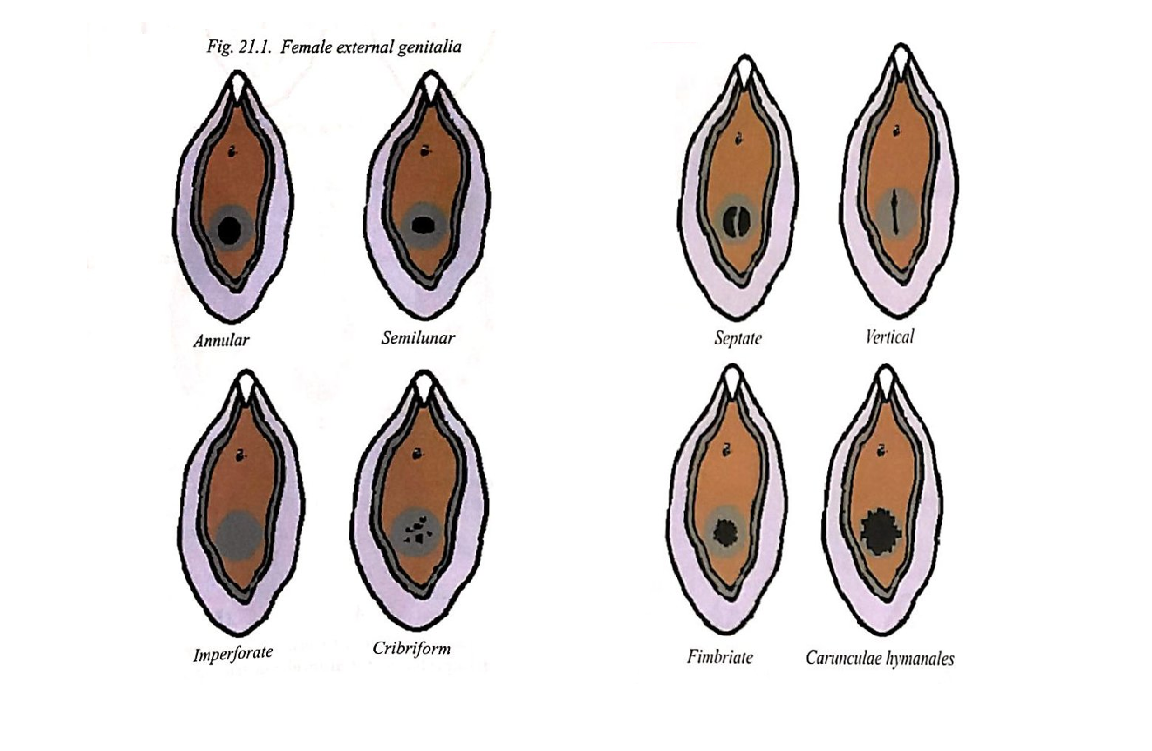
After delivery, only remnants of hymen will be seen at the rim called carunculae hymenales or myrtiformes.
Common site of rupture :both sides of midline on posterior aspect (5 o’clock - 7 o’ clock)
Signs of Virginity (UQ)
Physical Characteristics:
Breasts: Firm, elastic, small nipples, may reveal dark pigmentation in certain skin types.
External Genitalia: Labia majora and minora in normal position, vagina tight and narrow, hymen intact.
False Virgin (UQ): A woman who has experienced sexual intercourse but presents an intact hymen, often elastic and tough.
Differences Between True Virgin and False Virgin
Feature | True Virgin | False Virgin |
|---|---|---|
Basic Difference | Not experienced sexual intercourse | Experienced sexual intercourse |
Hymen | Intact and inelastic | Intact but loose, thick, tough, and fleshy |
Labia Majora | Apposing and closing vaginal orifice | Not apposing, not closing vaginal orifice |
Labia Minora | Small and covered by labia majora | Enlarged and exposed |
Vagina | Narrow with marked rugosity | Capacious with loss of rugosity |
Fossa Navicularis | Present | Disappears |
Fourchette | Intact | Torn, may show healed scar |
Vestibule | Narrow | Gaping and wide |
Clitoris | Small | Enlarged |
Posterior Commissure | Intact | May be torn |
Extra-genital Signs | Small and firm breasts | Large, pendulous breasts |
Areola | Pink | Pigmented |
Nipples | Small and pink | Enlarged and pigmented |
Pregnancy
Definition: A physiological condition where a female's ova is fertilized by spermatozoa, leading to embryo or fetus development.
Legal Implications:
Pregnancy can affect court appearances, with women potentially excused in later stages.
Reduction of capital punishment ( CrPC 416)
May influence divorce settlements and claims for alimony.
Can be falsely feigned for property distribution.
Suicide/Homicide
Maternity leave
Relevant in cases related to infanticide, criminal abortion, and maternal negligence.
Signs and Symptoms of Pregnancy (UQ)
Presumptive signs
Amenorrhea: A missed period, often the first sign.
Morning Sickness: Nausea typically resolves by the third month.
Breast Changes: Enlargement and pigmentation of areola and Montgomery's tubercles by the second month.
Chadwick's Sign: Bluish discoloration of vaginal mucosa by the eighth week.
Quickening (UQ): First fluttering movements felt by 16-20 weeks.
Palmer’s Sign: Rhythmic contractions detectable during bimanual exam as early as 4-8 weeks.
Probable signs
Goodell’s Sign: Softening of the cervix noted in initial pregnancy stages.
Hegar's Sign: Softening of lower uterine segment observed between the second and fifth month.
Abdominal Enlargement: Progressive changes with the formation of linea nigra, striae gravidarum, striae albicans.
Braxton hick’s sign: intermittent painless uterine contractions
Ballottement
Fetal cells in mother’s blood
Uterine Soufflé: A heart-synchronous murmur by the sixteenth week.
Biological Tests: Detect levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) as a pregnancy indicator.
Tests include Ascheim-Zondek and other animal-based tests, though less common today due to modern methods.
Immunological tests: Detects HCG
Prognosticon tube test
Direct Latex Test
Procedure: A simple immunological test to detect HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) in urine.
Latex Reagent: Composed of particles coated with anti-HCG antibodies.
Agitation:
If HCG is present, it binds to the antibodies causing agglutination (Positive Test).
If no HCG is present, no agglutination occurs (Negative Test)
Rapid Chromatographic Immunoassay
Description: A more advanced method using a device with a membrane pre-coated with anti-HCG antibodies.
Procedure: Adding two drops of urine allows it to move by capillary action, producing a pink band (in addition to the control band) if positive.
Timing: Becomes positive approximately two weeks after a missed menstrual period; remains positive throughout pregnancy and becomes negative about a week after termination or abortion.
Interpretation:
A negative test during pregnancy may indicate fetal death.
False Positives: Can occur in ectopic gestation, hydatidiform mole, and pituitary tumors (about 2%).
False Negatives: Occurs in about 7% of normal pregnancies
Positive signs (UQ)
Palpable fetal parts
Fetal movements
Fetal Heart Sounds: Audible usually from the fifth month, indicating successful pregnancy.
Placental souffle: blowing sound by fetal circulation
X-ray
Ultrasound Confirmation: Gestational sac visible as early as five weeks; fetal developmental abnormalities assessed.
Pseudocyesis (Phantom Pregnancy)
Description: A condition where a woman believes she is pregnant and exhibits symptoms.
Characteristics:
Typically affects women nearing menopause or those with a strong desire to be pregnant.
Symptoms may include abdominal enlargement and lactation.
Diagnosis: Ultrasound and pregnancy tests often reveal no actual pregnancy.
Corpus Luteum
Roles: Present during both pregnancy and menstruation; not solely confirmatory of pregnancy.
Can be present in non-pregnant women or absent in some pregnant cases.
Period of Gestation
Standard Duration: Recognized as 280 days (40 weeks) from the last menstrual period.
Variations: Can extend to 320-350 days in cases of post-maturity.
Period of Viability
Definition: Refers to the ability of a fetus to survive outside the womb.
Viability Threshold: Generally accepted at 210 days of gestation for legal purposes, with some children born at 180 days possibly being viable.
Superfecundation (UQ)
Definition: Fertilization of two separate ova from the same period by different acts of coitus.
Example: Can result in non-identical twins with different fathers.
Notable Case: Hybrid twins born to a black woman married to a black man.
Medicolegal Aspects of Superfecundation: Variations in appearance of twins can raise questions of infidelity.
Superfoetation (UQ)
Definition: Fertilization of a second ovum while already pregnant, leading to two fetuses of different developmental stages.
Nutritional Disparity: One fetus may receive more blood supply than another.
Outcome: May result in different sizes at birth.
Twin Pregnancy Complications
States: In twin pregnancies, one fetus may be aborted or retained, leading to conditions known as 'fetus compressus' or 'fetus papyraceus'.
Faternal vs Identical Twins:
Fraternal twins (dizygotic) result from two eggs fertilized.
Identical twins (monozygotic) arise from a split fertilized egg.
Vanishing Twin Syndrome
Description: Multifetal gestation with one or more fetuses disappearing, increasingly identified due to sonography.
Fecundation ab Extra
Concept: Pregnancy can occur without coitus; sperm deposited near the vagina can migrate and cause conception.
Pre-Conception and Prenatal Diagnostic Techniques (PC & PNDT) Act 1994 (Amended 2012)
Regulation: Prohibits sex determination of the fetus.
Prenatal Diagnostic Tests: Include amniotic fluid analysis, ultrasound, etc.
Permitted Cases:
Clause 2
(1) Chromosomal abnormalities
(2) Genetic metabolic disorders
(3) Hemoglobinopathies
(4) Sex- linked genetic diseases
(5) Congenital anomalies
(6) Any other abnormalities specified by the Central Supervisory Board
Clause 3
(1) Spontaneous abortions or fetal loss
(2) History of exposure to radiation, chemicals or teratogenic drugs
(3) Pregnant woman aged more than 35 years
(4) Pregnant woman or her spouse has a family history of mental retardation or physical deformity
(5) Any other condition specified by the Central Supervisory Board
Punishment
Doctor punished with 3 years rigorous imprisonment and fine up to Rs. 10,000/- and suspension of his name for a period of 5 years for the first offence
For the subsequent offence permanent removal, imprisonment for 5 years and fine Rs. 50,000.
Any person, who seeks the aid of genetic counselling laboratory/clinic or doctor for this purpose punished with imprisonment up to 3 years and fine up to 50,000 rupees
For subsequent offence, imprisonment up to 5 years and fine up to one lakh rupees.
Delivery
Definition: Expulsion of the fetus from the uterus.
M/L significance:
Infanticide
Concealment of birth
Feigned delivery
Abortion
Legitimacy
Nullity of marriage
Divorce
Blackmail
Signs of Recent Delivery in Living (UQ)
General Physical State: Fatigue, paleness, increased pulse.
Breast Changes: Enlarged breasts with colostrum post-delivery.
Abdomen Changes: Lax, pendulous with pink striae gravidarum(striae rubra) and linea nigra.
Genitalia Changes: Swollen labia, soft and dilated cervix.
Uterus Size: Initially contracted, progressively involution occurs.
Lochia Discharge (UQ):
Discharge from uterus after delivery
Disagreeable puerperial odour
If the discharge is offensive it indicates infection
For 1 — 4 days the discharge will be bright red with blood clots (lochia rubra).
From 5—9 day it will be pale and serous (lochia serosa).
From 10—15 days it will become yellowish-white and turbid (lochia Alba) and then disappears
Discharge will stop by about 15 days.
Signs of Recent Delivery in Dead (UQ)
Characteristics: Uterine size reduction and changes similar to living signs post-delivery.
Signs of Remote Delivery in Living
Breasts: pendulous and enlarged with Montgomery’s tubercles.
Abdomen : Abdominal wall lax with silvery striae albicans.
External Genitalia and Cervix
Labia majora will not be apposing and labia minora will be seen exposed
Hymen will be absent or caranculae hymenales
Cervix will show healed lacerations
External os will be dilated and slit like.
Differentiation Between Nulliparous and Parous Uterus
Feature | Nulliparous Uterus | Parous Uterus |
|---|---|---|
Weight | 50 gm | 100 gm |
Upper border | At level of broad ligament | Above broad ligament |
Inner Margin | Convex | Concave |
Cavity | Triangular | Rounded |
Cervix | Conical | Cylindrical |
Os | Circular | Transverse |
Cervical canal | Circular | Transverse |
Abor vitae | Present | Absent |
Scar of placental attachment | Absent | Absent |
Legitimacy and disputed paternity
Legal Definitions:
Legitimate child: Conceived during valid marriage or within 280 days of dissolution of marriage by death of the husband or divorce-as per Sec 112 IEA.
Illegitimate child: Born out of wedlock or not fitting within legal timeframes.
Medicolegal Significance
Inheritance: Legitimacy affects inheritance rights.
Nullity of Marriage: Affects the validity of the marriage contract.
Divorce: Illegitimacy can be grounds for divorce.
Affiliation Cases: Legal claims for paternity support.
Posthumous Child: Addressing legitimacy after the father’s death.
Supposititious Child: Claims of false pregnancy.
Atavism: Resemblance to grandparents as proof of legitimacy.
Paternity Tests: Blood group and DNA testing to establish paternity.
Marriage
Contract between a man and a woman which implies physical union by coitus
Nullity of Marriage and Divorce
Divorce is the legal dissolution already existing marriage contract.
According to Sec. 11, 12 and 13 of the Hindy marriage Act - Grounds for Divorce:
Adultery
Cruelty
Desertion
Apostasy: Change in religion
Unsoundness of mind
Sexually transmitted diseases including HIV/ AIDS
Renouncing the world
Bigamy
Impotence
Additional grounds for women: Husband convicted of rape, sodomy or bestiality
 Knowt
Knowt