Chapter 19 - Saving, capital formation & financial markets
Saving and wealth
Saving: current income minus spending on current needs.
Saving rate: saving divided by income.
Wealth: value of assets minus liabilities.
Assets: anything of value that one owns.
Liabilities: debts one owes.
Balance sheet: list of an economic unit's assets and liabilities on a specific a date.
Flow: measure that is defined per unit of time.
Stock: measure that is defined at a point in time.
Capital gains: increases in the value of existing assets.
Capital losses: decreases in the value of existing assets.
National saving and its components
National saving: saving of the entire economy, equal to GDP less consumption expenditures and government purchases of goods and services, or Y - C - G.
Transfer payments: payments the government makes to the public for which it receives no current goods/services in return.
Private saving: saving of the private sector of the economy is equal to the after-tax income of the private sector minus consumption expenditures (Y - T - C)
- It can be further broken down into household saving and business saving.
Public saving: saving of the government sector is equal to net tax payments minus government purchases (T - G).
Government budget surplus: excess of government tax collections over government spending (T - G)
- It equals public saving.
Government budget deficit: excess of government spending over tax collections (G - T).
Why do people save?
Life-cycle saving: saving to meet long-term objectives such as retirement, college attendance, or the purchase of a home.
Precautionary saving: saving for protection against unexpected setbacks such as the loss of a job or a medical emergency.
Bequest saving: saving done for the purpose of leaving an inheritance.
Investment and capital formation
- Any of the following factors will increase the willingness of firms to invest in new capital:
- Decline in the price of new capital goods
- Decline in the real interest rate
- Technological improvement that raises the marginal product of capital
- Lower taxes on the revenues generated by capital
- Higher relative price for the firm's output
Bonds, stocks and the allocation of savings
Bond: legal promise to repay a debt, usually including both the principal amount and regular interest, or coupon, payments.
Principal amount: amount originally lent.
Maturation date: date at which the principal of a bond will be repaid.
Coupon payments: regular interest payments made to the bondholder.
Coupon rate: interest rate promised when a bond is issued; the annual coupon payments are equal to the coupon rate times the principal amount of the bond.
Stock (or equity): claim to partial ownership of a firm.
Dividend: regular payment received by stockholders for each share that they own.
Risk premium: rate of return that financial investors require to hold risky assets minus the rate of return on safe assets.
Diversification: practice of spreading one's wealth over a variety of different financial investments to reduce overall risk.
Mutual fund: financial intermediary that sells shares in itself to the public and then uses the funds raised to buy a wide variety of financial assets.
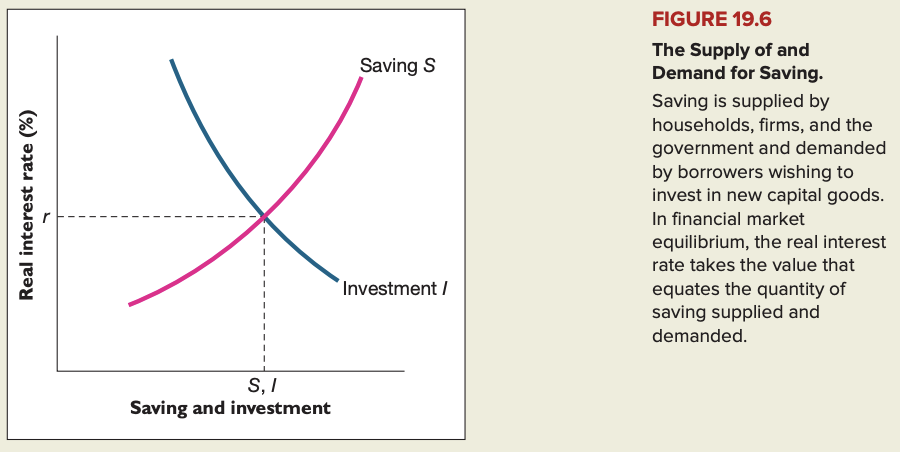
Saving, investment and financial markets
Any of the following factors will shift the demand for savings (I) to the right:
- Decline in the price of new capital goods
- Technological improvement that raises the marginal product of capital
- lower taxes on the revenues generated by capital
- Higher relative price for the firm's output
- Supply of savings will shift right if national saving, private and/or public saving, is increased.