Sociology Flashcards
Karl Marx-
German philosopher and sociologist
revolutionary sociologist and advocated for communism.
Marxism: Social and political theory that explores capitalization and labour. Socioeconomic classes are defined by struggle (Bourgeois and Proletariat). Analyzes the impact of the ruling class on the working class.
Labour Theory of Value: Economic value of a service is proportional to the amount of necessary labour to produce it.
Conflict Theory: Social theory that addresses the perpetual conflict which occurs because of competition of limited resources within a society. social order and status are maintained by dominance and power. Upper class maximize their wealth and suppress the poor and less powerful. The bourgeoisie and proletariat.
Class Consciousness: Individuals are aware of their class and social situations. i.e. being exploited.
Max Weber
Theory of Religion: Research on how religion impacts social change (Emergence of capitalism). Undermined the idea of social stratification, and the religious idea that those being wealthy were blessed by god. If a group is acting on religious grounds we must try to understand the basis of their religion as they are just fulfilling their need for the belief in a higher power.
Social Stratification: Societies categorize people based on rankings, whether wealth, caste system, income, education etc.
Theory of Rationalization: Societies of change from reliance on tradition to rationality and science. Common in bureaucracies.
Classification of Authority:
-Charismatic Authority: Leader who inspires
-Traditional Authority: Leader given power by tradition
-Rational-Legal Authority: Leader given power through rules and procedures i.e. election.
Theory of Bureaucracy: System of government where most of the important decisions are made by state officials rather than elected representatives. Rigid hierarchy of individuals governed by strict rules and regulations.
-Specialization and division of labour
-Formal Written Records
-Competence for job appointments
-Standard operating procedures
-Impersonality in bureaucracy
Social Action Theory; Accepts and assumes that humans vary their actions according to social contexts and how it will affect other people.
-Rationally Purposeful Action
-Traditional Action
-Value-Rational Action
-Affective Action
Dorothy Smith
Feminist Standpoint Theory: Feminist view on the Marxist Standpoint theory, which describes how the oppressed class (Proletariat) had knowledge that was not accessible by the privileged class (Bourgeois).
Critiqued sociology field for excluding women from their research, and how women need to be active in sociology to provide their perspective and how there many consequences to not having female perspectives that inhibit progress.
Ethnography: Research method that focuses on a culture’s social relations, describing life as it is and experienced.
Betty Friedan
Feminine Mystique: Term to describe the myth that women can only be fulfilled or be successful by being a housewife or taking on a domestic role, and how their identity needs to be defined by their motherhood.
Nuclear Family: Ideal family structure post WWII that had a male breadwinner and female caregiver, with dependent children.
Bioessentialism: Idea that one’s important characteristics are determined by their biology and they cannot change. i.e. women are meant to be caregivers and are “wired” to be nurturers.
Intersectionality: A term to describe how parts of our identity overlap and create unique interactions and forms of oppression. i.e. misogynoir
Reginald Bibby
Project Canada- survey conducted to compare adult and teen samples as close as possible
Ibn Khaldun
Anthony Giddens
Influence on how we see identity and social change.
Author of Modernity and Self Identity, the third way: the renewel of social democracy, sociology
Emile Durkheim
Functional Sociologist:looks at how different parts of society contibute and work together
Structural Functionalism: Society as a complex system whose parts work together for stability and to promote solidarity. For example, crime, that reinforces our morals
Anomie: Social instability resulting from a breakdown of values and morals.
Division of Labour in Society: The division of labour is proportional to a society's moral or dynamic density. He describes it as a combination of a group's or society's population density and level of socialisation.
Collective Consciousness: The reason why and how individuals who are different can come together and form a society. This is because collective consciousness refers to a set of common beliefs, values, and behaviors that are found within a society. Essential for the development and bond of a society as it allows individuals to act for the interests of the whole community.
George Herbert Meade
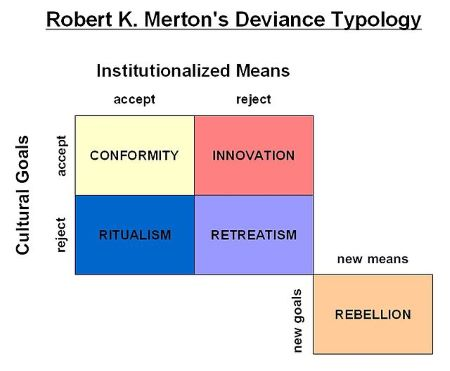
Robert K. Merton
Brown vs., Board of education helped against desegregation
Strain Theory: Pressure derived from social factors, such as lack of income or lack of quality education, drives individuals to commit crime.
-Conformity: Accepts approved goals, pursues them through approved means.
-Innovation: Accepts approved goals, uses unapproved means.
-Ritualism: Abandones society’s goals, conforms to approved means
-Retreatism: Abandons approved goals and means.
-Rebellion: Challenges approved goals and means.
 Focus Groups
Focus Groups
Self-fulfilling Prophecy: Coined the term to describe the phenomenon whereby a person's or a group's expectation for the behavior of another person or group serves actually to bring about the prophesied or expected behavior.
Defiance
Biological Theories: Brains being wired differently, not being able to feel empathy or having opposition defiant disorder.
Psychological Theories
-Early psychoanalyst studies suggest that crimianls cannot control their aggression..
-Behavioral psychologists argue that as children, criminal deviant behavior is warded or reinforced which leads them to become criminals.
George Herbert Mead
Theory of the emergence of mind and self: The emergence of mind is contingent upon interaction between the human organism and its social environment; it is through participation in the social act of communication that the individual realizes her (physiological and neurological) potential for significantly symbolic behavior (that is, thought).
Social Behaviorism: Social interaction and environment impact how w einteract with the world.
Thought on the self: Not present at birth, but developes thrpugh soicla interaction. The self arises through a process of social experience and activity where individuals engage in symbolic communciation.
Communication Process
-Phase 1: Conversation of Gestures: Unconscious Communication
-Phase 2: Conversation of Significant Gestures: Conscious Communication
Gesture: An action that implies a reaction. The reaction is the meaning of the gesture.
Symbolic Interactionism
Edward Said
Palestinian Adovocaism
Orientalism: Coined the term to describe how prejudice and racism is perpetuated even when people have never been to this place. Especially how colonial forced protray middle eastern culture in academics.
George Dei
Dropout: published book on how socio economic problems can impact rates of dropping out or put students at risk for not completing their education.
Afrocentricity: Incorporation of african history and culture into school curriculum. Making sure to center cultural diversity especially to dismantle eurocentric biases in school.