Chapter 17: Microorganisms and their Applications in Biotechnology
Viruses
- Not considered as cells - no protoplasm.
- Live on host cell.
- When they are living on host cell they are considered as living thing.
- They do not feed, respire, excrete, grow or reproduce - but; inside a host cell, virus can reproduce or replicate.
- Viral diseases and our defence system:
- cold, influenza, chickenpox, dengue, haemorrhagic fever, herpes and AIDS.
- can only be destroyed by antibodies produced by our WBCs.
Bacteria
- Living cells.
- Larger than viruses.
- Non-motile.
- Posses hair like threads called flagella.
- ^^Three general types:^^
- Cocci - spherical shaped
- Bacilli - rod shaped
- Spirilla - spiral shaped
- ^^Bacteria can be:^^
- Saprophytic - feeding on decaying organic material.
- Parasitic - causing diseases in plants and animals.
- Autotrophic - able to manufacture food using energy from the sun or inorganic material.
Fungi
- Live as saprophytes.
- Unicellular e.g yeast or multicellular e.g bread mould.
- Parasitic fungi live on the living tissue of their hosts.
Role of microorganisms in decomposition
- ^^Decomposers in nature^^
- Decomposers feed on dead and decaying organisms and their faeces.
- They secrete enzymes which break down complex organic compounds to simple organic compounds.
- They absorb small amount of energy and nutrients; most of the energy is lost as heat and the remaining nutrients are released into surrounding.
- Inorganic compounds compounds release gases like CO2, hydrogen sulphide and water vapour.
- Help maintain life on earth.
- ^^Decomposers in sewage:^^
- Decomposed by saprophytic microorganisms.
- Bacteria in sewage secrete an enzyme to digest solid organic matter into soluble harmless substances.
Biotechnology
- Fermentation
- ^^Yoghurt making^^
- By fermenting milk and using lactobacillus bulgaricus (bacteria).
- In the absence of O2 bacteria respires anaerobically and converts lactose to lactic acid .
- This acid curdles the milk producing yogurt, it can later be flavored or sweetened.
- ^^Cheese making^^
- Use both bacteria and fungi.
- Lactobacillus is used to ferment milk sugar to lactic acid. The mixture curdles milk protein.
- Curdled protein together with the fats in the milk, is removed and acted upon by a mixture of bacteria and fungi to produce cheese.
- By different temperatures and different variation of bacteria and fungi different kind of cheese is produced.
- ^^Production of alcohol^^
- Yeast is used for brewing.
- Yeast is mixed with sugar.
- Yeast starts to respire anaerobically to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide from sugar.
Antibiotics
Complex substances produced by microorganisms.
Used in treatment of bacterial infections.
Commercial production.
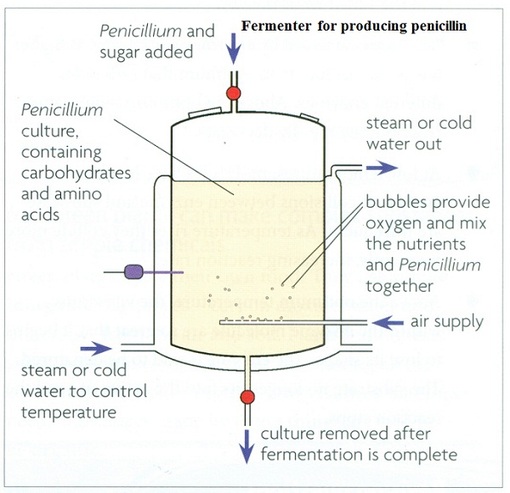
Penicillin production.
Single-cell protein
- eg. bacteria and yeast.
- Help produce animal feed and human food.
Industrial Biotechnology
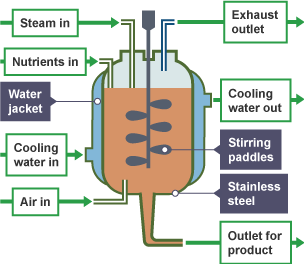
^^Fermenters^^
- Designed to keep its inside environment favourable for the desired biological process.
- Designed for aerobic and anaerobic processes both.
- Important features:
- Cooling system
- Removal of heat during microbial activities.
- aeration system
- For proper mixing ad adequate aeration.