chapter 12 (political ideology & shaping beliefs)
12.1
Party Ideology
Objective: Describe the different ideologies of the Republican & Democratic Parties.
Introduction
u.s is a diverse society with public policies reflecting citizen attitudes
policymakers must balance competing ideologies due to the diversity of the population
preferences vary between policies emphasizing order and stability versus those promoting individual liberties
social and economic issues, such as welfare policies and immigration reform, reflect party differences
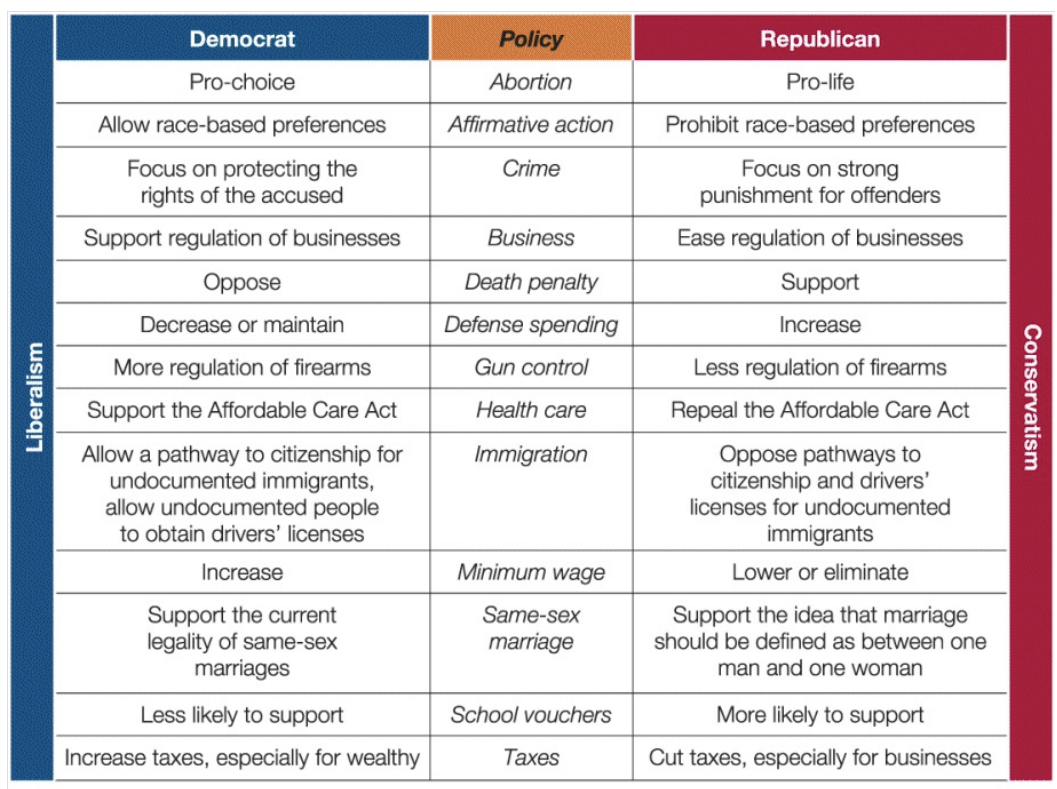
party ideology: a party’s philosophy about the proper role of government and its set of positions on major issues
party identification: an individual’s attachment to a political party
republican party: associated w/ conservatism
conservatism: an ideology favoring more control of social behavior more, fewer regulations on businesses, and less government interference in the economy
republicans favor liberty in business, pro-life, order in immigration, and strong punishments for criminal offenders
republicans support tax cuts for businesses, fewer business regulations, and individual property rights
democratic party: associated w/ liberalism
liberalism: an ideology favoring less government control over social behavior and more greater regulation of businesses and of the economy
democrats prioritize sexual and marital privacy, pro-choice, support less strict immigration policies, and civil liberties when determining criminal sentences
democrats favor tax increases for the wealthy, more business regulation, and restrictions on property use for community protection
libertarianism: an ideology favoring very little government regulation and intervention
beyond protecting private property and individual liberty
not the same as liberalism!!!!
party ideology and identification are distinct, influenced by various factors such as family, education, and life experiences
parties attract members by focusing on issues and policies aligned with specific ideologies
both parties display partisanship, emphasizing ideological contrasts and criticizing opponents
right: something guaranteed, that the government cannot take away
privilege: something a person may obtain or receive, but that the government can take away
12.2
Ideology & Economic Policymaking
Objective: Describe liberal and conservative perspectives on economic policymaking.
Government Intervention in the Economy
1776: adam smith wrote a book advocating for a free-market economy
smith argued that national economic prosperity is best achieved through individuals freely pursuing their economic interests in a competitive marketplace
laissez-faire economy minimizes government intervention in economic transactions, allowing individuals and businesses to operate freely; means "let us do it" or to leave alone
governments have historically intervened in the economy for broad policy goals (ex. building the transcontinental railroad in 19th century)
command-and-control economy: economic policy in which government dictates much of a nation’s economic activity, including the amount of production and price for goods
u.s.s.r used command-and-control practices until its collapse in the early 1990s
china transitioned to a mixed market system in the 1980s
u.s. has a mixed economy, where individuals and businesses make many economic decisions, with government regulations in place
Monitoring the Health of the Economy
gross domestic product (GDP), unemployment rate, & inflation rate are key indicators monitored by the federal government to assess the health of the economy
gdp: the total value of goods and services produced by an economy
decline or stagnation in GDP may signal an economic recession
economic recession: a period of decline in economic activity, typically defined by two consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth
unemployment rate: the percentage of people actively looking for work who cannot find jobs
inflation: the rise in the prices of goods and services
consumer price index (CPI):the cost of a fixed basket of goods and services over time, used to measure the cost of living
inflation can impact workers' purchasing power, and programs like social security may adjust based on changes in the CPI
often a trade-off between inflation and unemployment
republicans: usually more willing to accept higher unemployment for lower inflation
democrats: may tolerate inflation to reduce unemployment
Business Cycles & Theories of Economic Policymaking
policymakers have diverse perspectives on defining and solving economic problems
even when they acknowledge an economic issue, policymakers may differ in explaining its causes and proposing solutions
"business cycle": term used by economists to describe the cyclical nature of economic activity
despite a generally upward trend in positive GDP growth, economies may still experience periods of contraction and expansion
monetary theory: gov’t should control the money supply to encourage economic growth and restrain inflation
Keynesianism
keynesianism: the government can use monetary & fiscal policies to stabilize the economy and prevent recessions
keynes, in his influential work ("the general theory of employment, interest, and money" (1936)), provided a theory of business cycles
published during the great depression
keynes argued that individual decisions regarding saving and spending drive business cycles
expansion: people get too confident, make risky investment decisions, making the economic boom worse
contraction: people get too pessimistic, cut spending and investment, making it worse and possibly leading to an economic depression
keynes advocated for government intervention to counterbalance economic contractions by injecting more money into the economy
democrats often support keynesian policies, exemplified by the creation of public works projects during the great depression as part of the new deal
during the 2007–2009 recession: president obama proposed a massive public works project with the goal of creating 2.5 million jobs
Supply-Side Theory
supply-side theory: emphasizes the demand for goods & services and the role of supply in fostering economic growth'
proposes lower taxes on individuals and businesses as the most effective tool to combat economic downturns
contrastst keynesian theory
often associated with "reaganomics”
critics of supply-side theory use the term "trickle-down economics" to describe it
they argue that these policies primarily benefit the wealthy, and the benefits are unlikely to reach individuals not directly impacted by lower tax rates
proponents argue that excessive taxation hampers economic growth by impeding business development
republicans have generally supported supply-side economics
december 2017: trump administration successfully enacted legislation to cut individual and business taxes to boost economic growth
fiscal policy: government use of taxes and spending to attempt to lower unemployment, support economic growth, and stabilize the economy
theory | gov’t approach | general supporters |
|---|---|---|
monetary theory | match the growth of the money supply to the growth in economic productivity | … |
keynesianism | stimulate the economy during times of economic recession by spending money to encourage economic growth | democrats |
supply-side theory | stimulate the economy by cutting taxes to encourage businesses to grow and taxpayers to spend more money | republicans |
Guiding the Nation’s Economy through Taxing & Spending Decisions
republicans often support budgets that increase military spending and decrease taxes
ex. the bush tax cuts (2001 and 2003) reduced income tax rates for wealthy americans and those with below-average incomes, while military spending increased for the wars in iraq and afghanistan
president obama's fiscal policy focused on tax increases for the wealthiest americans and government spending programs to stimulate the economy
president trump's federal budget for 2018 projected a budget deficit exceeding $1 trillion
deficit was mainly due to a combination of tax cuts and increases in military and defense spending
although democrats & republicans differ on how to use taxing and spending to influence the economy, managing the budget is challenging
deficits are likely to persist well into the future
12.3
Monetary Policy
Objective: Describe monetary policy and how the Federal Reserve uses the money supply to regulate the economy.
Introduction
primary driver of monetary theory and business cycles is supply of money in an economy, including available credit for borrowing
more money availability can lead to inflation - too much money chasing too few goods
monetarists oppose fine-tuning the economy through Keynesian or supply-side policies
they advocate matching money access to economic productivity growth
monetary policy can have powerful and destructive effects.
countries in financial distress may print money without financial backing
germany, austria, and hungary post-ww1 misused monetary policy, leading to hyperinflation
people needed sacks of currency to buy food.
monetary chaos in societies can lead to anarchy, violence, and political extremism
ex. hyperinflation in germany contributed to the rise of fascism before ww2
Federal Reserve System
federal reserve system: a board of governors, federal reserve banks, & member banks responsible for monetary policy
consists of a 7-member panel of governors, 12 regional federal feserve banks, and 6000 member banks
governors appointed by the president, confirmed by the senate, serving nonrenewable fourteen-year terms (except the chair, who serves a four-year term)
governors, except for cause, cannot be removed, providing some independence in economic decisions
the fed regulates the amount of money in the economy w/ 3 main tools:
buying and selling treasury securities
setting reserve rates, impacting the amount of money banks can loan
influencing interest rates banks pay to borrow from the federal government
lowering the federal funds rate stimulates the economy by encouraging borrowing with lower interest rates
actions of the fed influence interest rates throughout the economy as banks and credit card companies adjust their rates accordingly
monetary policy: a set of economic policy tools designed to regulate the amount of money in the economy.
policies encourage healthy economic growth without causing damaging inflation and aim to prevent economic depression
ex. fed lowered interest rates in 2008 during the economic crisis to prevent a downturn similar to the great depression (1930s)
Challenges & Risks with Conducting Monetary Policy
criticism of the fed:
questions about true independence, especially when pressured by congress or the president
disagreement with the Fed's goal of maintaining a "moderate inflation" around 2%
inflaiton concerns:
critics argue that persistent moderate inflation undermines Americans' spending power if wages don't risk
2% rise in the price of goods and services over time can have a significant impact
despite criticism, international governments, financial firms, businesses, and individuals at home and abroad maintain confidence in the nation's currency
the american dollar remains strong against other nations' currencies
12.4
Ideology & Social Policy
Objective: Describe liberal and conservative perspectives on social policy.
Federal Government & Health Care
medicare: a federal program that provides health insurance to seniors and the disabled
1960s: pres. LBJ’s great society program amended the social security act
creates medicare for senior citizens (age 65+)
1972: president nixon extends medicare benefits to the disabled
medicare: a federal program that provides health insurance to seniors and the disabled
2003: president George W. Bush adds prescription drug benefit to medicare
social security and medicare constitute the largest part of the federal budget
they are expected to increase in the next decade, then level off in 2030
political forces have expanded the government's role in health care
2016: total medicaid spending around $553.5 billion
late 20th & early 21st centuries: both parties agree on the need for health-care system reform
2012: u.s. has the highest medical care costs globally, spending $8,233 per person (more than 2.5 times the average in developed nations)
Patient Protection & Affordable Care Act
2010: approx. 48 million americans were uninsured, leading to the signing of the affordable care act (ACA) on March 23, 2010, by pres. obama
obamacare aimed to overhaul the american health-care system.
key ACA provisions included:
employer health insurance requirements
individual mandates
medicaid expansion
health-care exchanges
coverage for young adults up to age twenty-six
prohibition of excluding preexisting conditions
implementation challenges included website navigation issues, and by 2015-2016, some insurers raised premiums or left the ACA program
despite challenges, over 16 million americans obtained health-care coverage post-ACA
republican attempts to overturn ACA during obama's second term were unsuccessful
supreme ccourt upheld the individual mandate and tax credits in 2012 & 2015
ACA represents a study in liberal and conservative ideologies on health care, with debates over individual mandates, government involvement, and market forces
liberals: support widespread health care, arguing it should be available to all
conservatives: oppose ACA, favoring individual responsibility and market-driven health care
republicans (including pres. trump) succeeded in eliminating the individual mandate through tax overhaul
they still seek further ACA repeal, claiming interference with the free market
School Choice, Competition, & the Markets
republicans and democrats differ ideologically on public education reform, particularly on school-choice initiatives
school-choice reforms allow parents to select their children's schools, fostering competition among schools
advocates (not all conservative) support vouchers, using taxpayer money for private and religious school tuition, blurring public-private school lines
argue vouchers promote competition, improving standards in traditional public schools and benefiting those not using vouchers
pponents fear draining funds from public schools, creating winners and losers
argue supporting religious schools violates the establishment clause
school-choice debate reveals ideological tensions between equality of opportunity and support for individualism and the free market