The Endocrine System
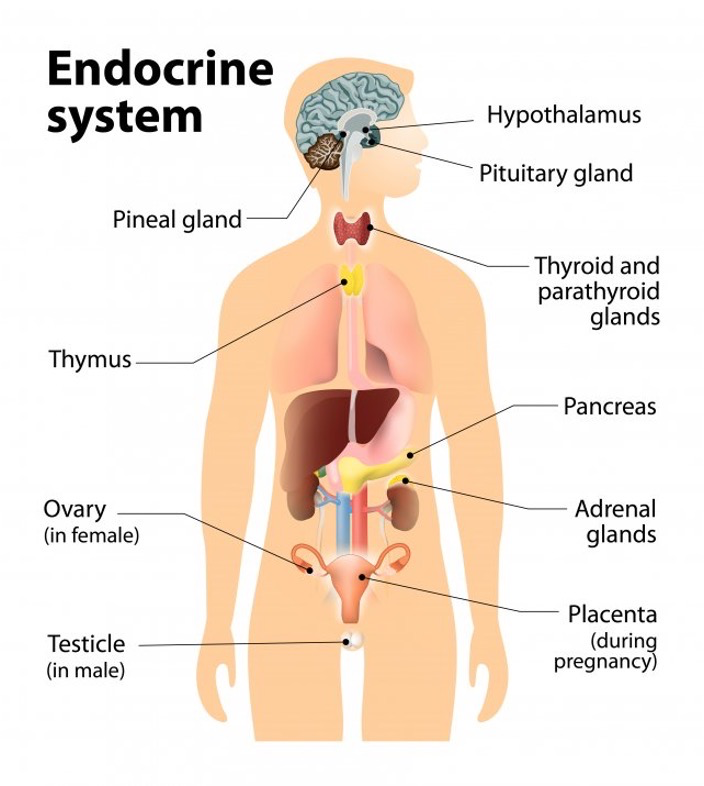
Consists of a series of glands
All glands secrete hormones into the blood
--> spread through the body via the blood stream
Tissues have receptors specific to the hormones
Pituitary gland (master gland)
Thyroid gland: produces thyroxine
--> regulates rate of metabolism as well as growth and development
Adrenal Gland: releases adrenaline
Pancreas: produces insulin
--> regulates blood glucose concentration
Testes (males): produce testosterone and sperm
Ovaries (females): produce progesterone and oestrogen
Endocrine system works closely together with the nervous system
Hormones: chemicals released by glands or tissues
Glands secrete hormones directly into the blood
Each hormone only interacts with specific receptors on some cells to cause a specific response
Circulating hormones: travel around the body in the blood
Local hormones: act on neighbouring cells without entering the bloodstream
Gland | Location (description) | Hormones | Function of the hormone |
Hypothalamus | Brain above pituitary gland | Dopamine, Growth Hormone, Oxytocin | Control center to maintain homeostasis |
Pituitary Gland | Brain below the hypothalamus | Cortisol, growth hormone, pregnancy hormone | Controls other glands |
Pineal Gland | Center of the brain | Melatonin, Serotonin | Regulates the sleep cycle |
Thyroid Gland | Throat | Calcitonin | Controls metabolic rate, heart rate and digestion |
Adrenal Gland | Above Kidneys | Adrenaline, cortisol, testosterone | Immune system/metabolism |
Pancreas | Middle of the body | Insulin | Regulates blood sugar levels and the digestive system |
Testes | Male reproductive organs | Testosterone | Promotes male secondary sexual characteristics and produces sperm |
Ovaries | Female reproductive organs | Oestrogen and progesterone | Promotes female secondary sexual characteristics, produces eggs and role in the reproductive cycle |