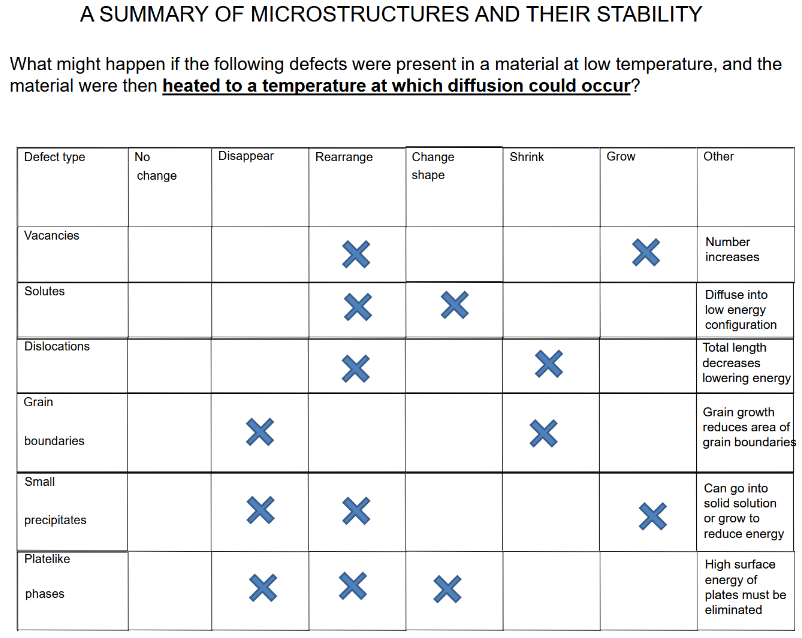
(5 - 6) microstructures qwq
Chapter 5 microstructures introduction (point defects, diffusion)
3 Types of Bonds:
Metallic: sea of electrons + metallic cations (two metals)
Covalent: sharing electron (two nonmetals)
Ionic: transfer of electrons (nonmetal + metal)
Rare Crystal Structure:
Simple Cubic: atom at each corner of a cube → repeating square lattice
Common Crystal Structures:
fcc (face centered cubic) → corners + faces (highly packed)
HCP (hexagonal close packed) → hexagon top + bottom + 4 faces (highly packed)
bcc (body centered cubic) —> corners + center
bct (body centered tetragonal) → corners + center (elongated)
Microstructure Approximate Size:
Atoms: 10-9
Microstructure: 10-4
Processing → Microstructure → Properties
Defects in crystals
Phases
Defects:
Point Defects
Vacancy (gone) → Schottky
Self interstitial atom (displaced same) → Frenkel
Interstitial impurity atom (small foreign squeezes itself in)
Substitutional impurity atom (foreign replaces)
Dislocations (line defects)
Edge
Screw
Grain Boundaries (plane defects)
What do defects do to the material?
Elastic stress
Increase free energy (unstable)
favorable to REMOVE defects but requires thermal activation (slow)
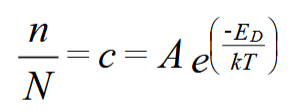
n is number of defects, N is number of atoms, A is a constant, k is Boltzmann’s constant
k = 1.38 × 10-23 J / K
ED is energy of formation for defect
Self Diffusion: only one component due to movement of vacancies
Chemical Diffusion: more than one chemical species (high concentration to low)
Chapter 6: Line Defects (Dislocation) and Planar Defects
Burger’s Vector: vector of lattice distortion bc of dislocation
Glide (slip) bc of sheer stress ALONG slip plane
Climb bc of atomic diffusion PERPENDICULAR slip plane
no equilibrium concentration
due to plastic deformation
How to get rid of line defects:
Recovery
Recrystallisation
Mixed Dislocation (screw + edge): Loops
Types of Planar Defects:
Surfaces (different phases)
Boundaries between solids
Grain boundary: same phase, different orientation due to angle
Interface (same phase, but aligned either perfectly, messy, not not at all)
Coherent
Semicoherent
Incoherent
Twin boundaries (reflection in hcp metals)
Breaking or distorting atomic bonds → energy increase + inc in reactivity
Calculations:
Light Equations:
E = hv
c = λv
c = 3 × 10^8
h = 6.626 × 10^-34
1 Amstrong = 10-10 m
Know this silly chart: