Noah Hart - Ch 3 Outline
- Federalism Preview
- Under AOC, most authority in states
- COnstitution divided power between state and national govt.
- Exclusive or shared
- System called federalism
- Did not define boundaries clearly
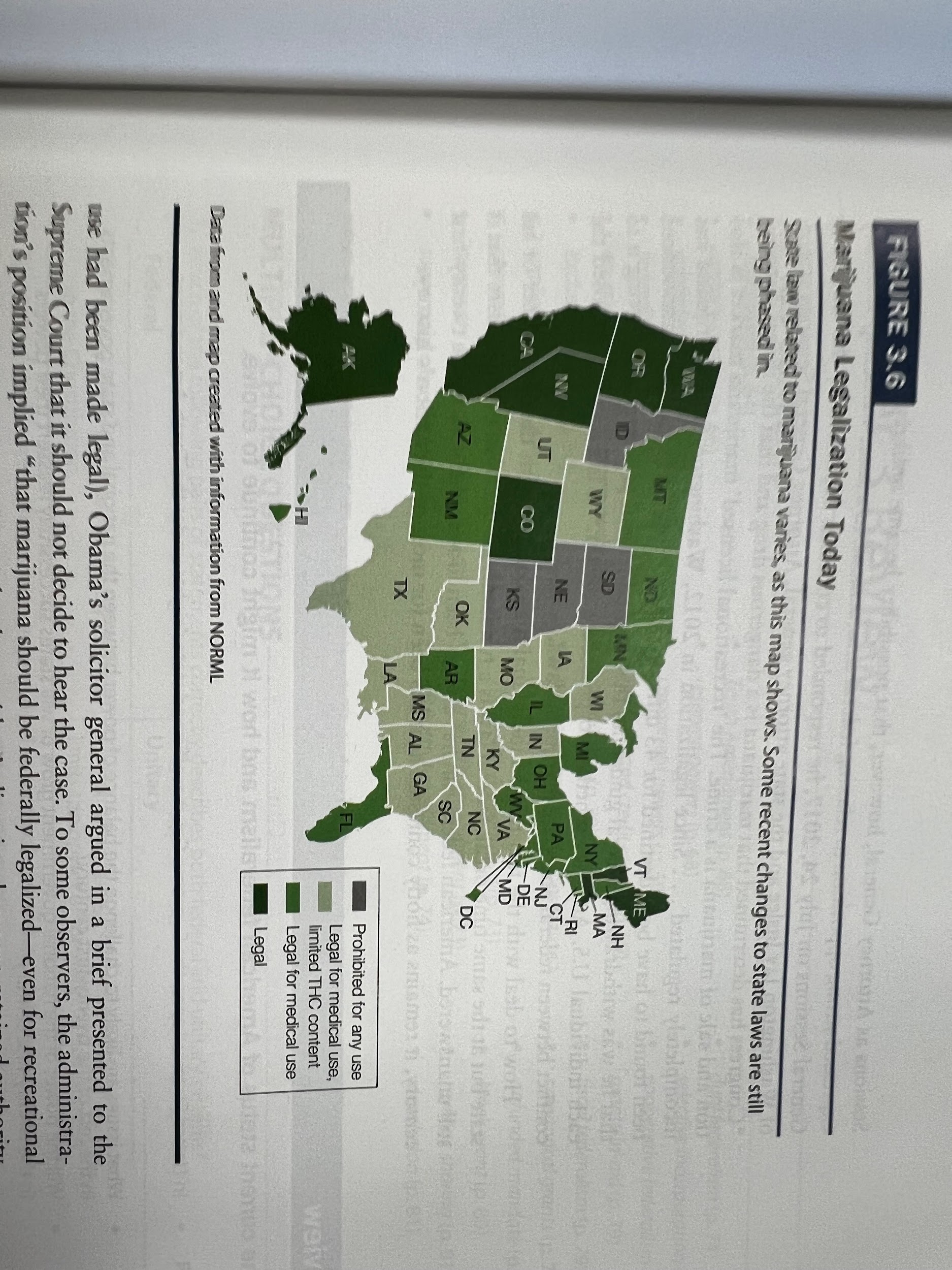
- What was the conflict over Medical Marijuana
- Two sued US govt, use protected by states, federal illegal
- Using Marijuana for medical purposes
- Possession illegal under CSA
- Federal agents destroyed weed plants
- Up to supreme court
- One on many that helped established lines in federalism
- Federalism and the Constitution
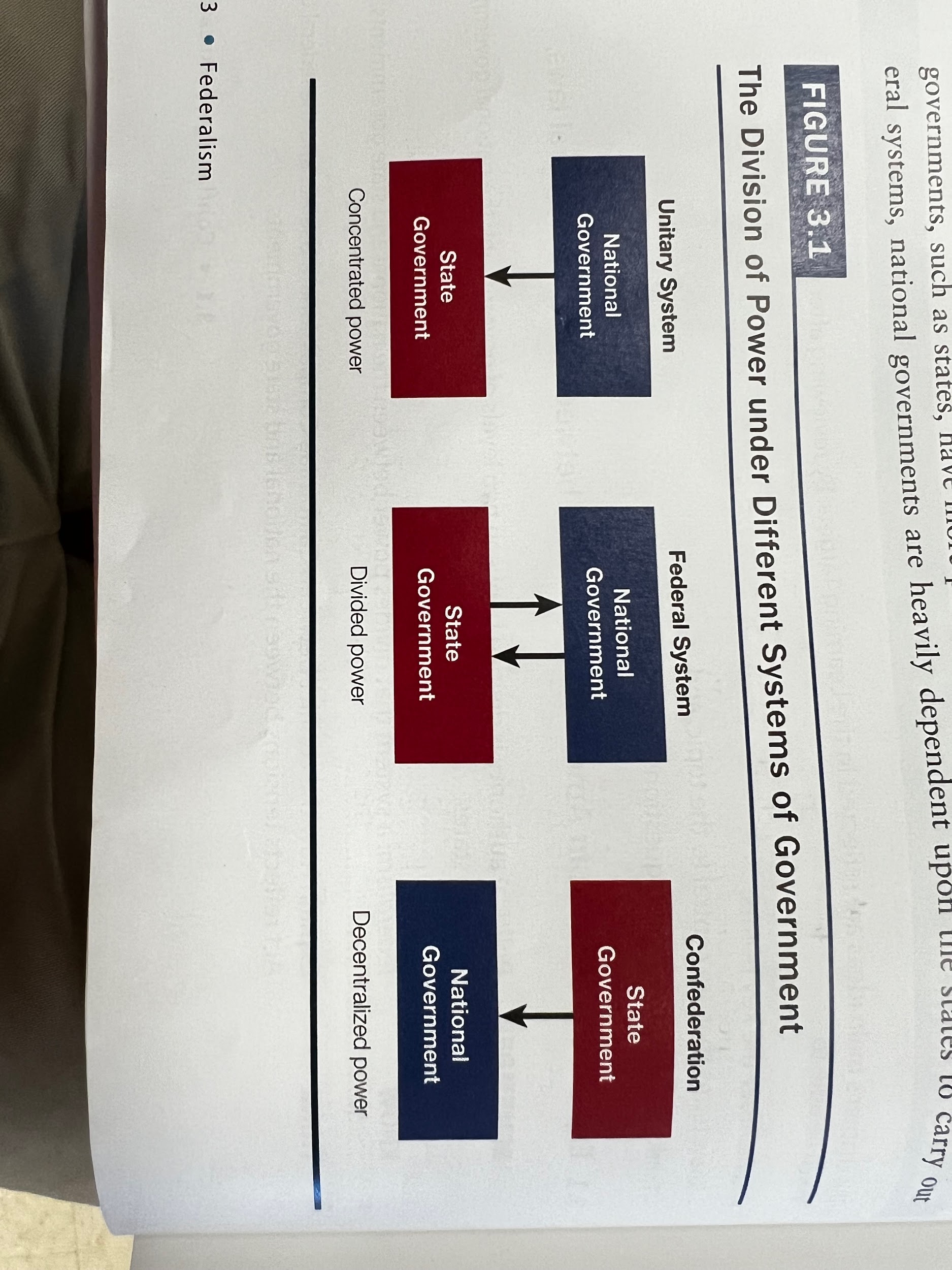
- What are the systems of government?
- Unitary, central power executes control over others
- Can delegate/or take back power
- China, UK, Iran, Most Govts,
- Opposite Confederal system
- National govt. Reliant on states
- Example AOC and switzerland
- Federalist constitutional innovation
- Divided power
- Some powers denied and granted
- US, Mexico, Nigeria, Russia
- What are the national and state powers?
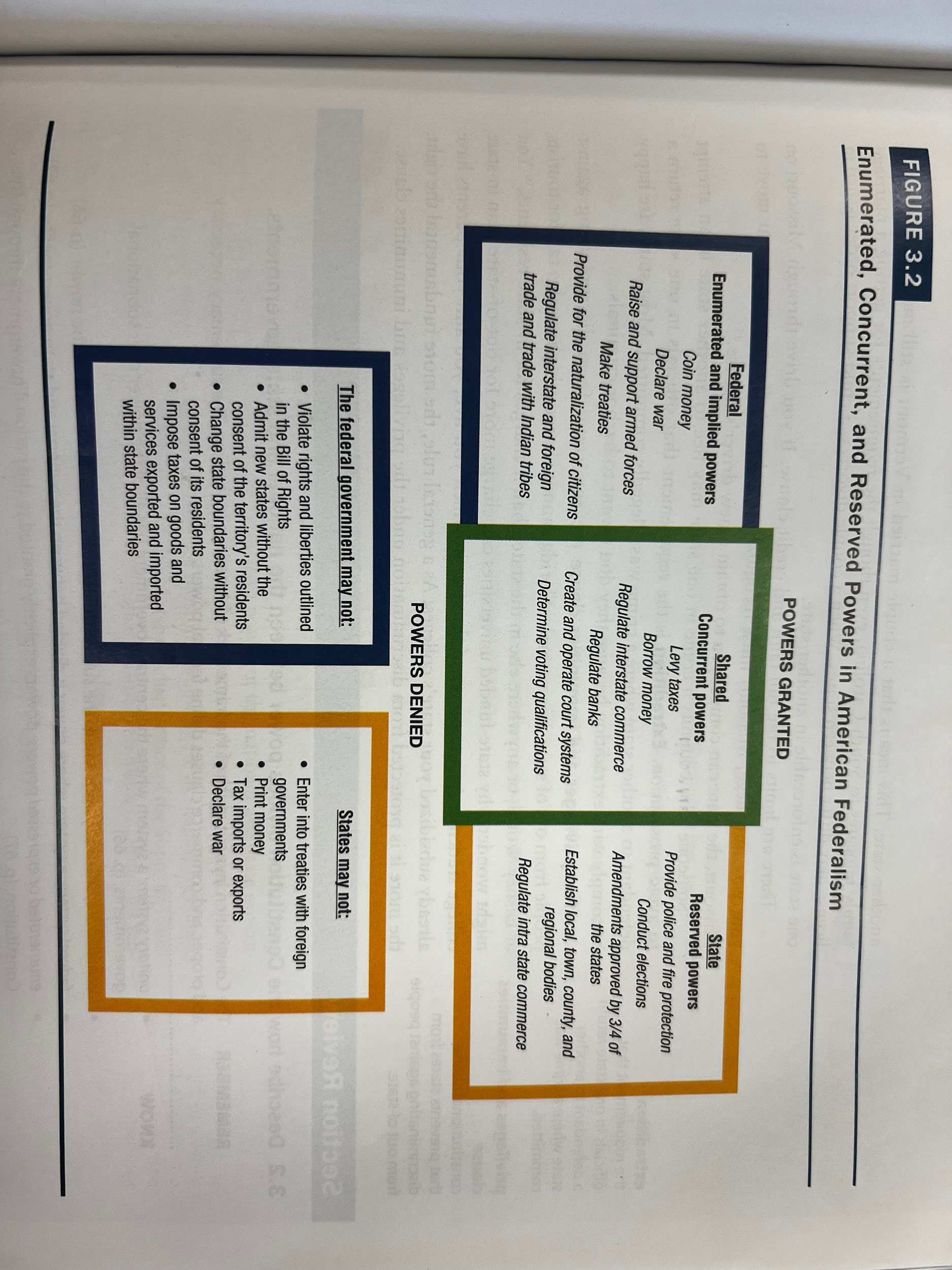
- Powers of national govt. Enumerated in constitution
- Exclusive powers only national can exercise.
- Most in A1S8
- Implied powers not explicitly given
- Necessary and proper clause allows congress to make laws to carry out enumerated powers
- Constitution denies certain powers to national govt.
- Violating some rights
- Bills of attainder
- Ex post de facto
- Not suspend writ of habeas corpus
- Cant make states borders change w/o consent
- Cannot force in other states
- Cannot tax interstate commerce
- What are the Commerce, Necessary and Proper, and Supremacy clauses?
- These and 10th amendment set relative powers
- Commerce clause modern influence, regulate commerce with
- Foreign nations
- Interstate commerce
- Indian Tribes
- With necessary and proper clause, can be defined any productive activity as commerce
- Necessary and proper clause allow Congress to make laws to execute enumerated powers
- Aka elastic clause
- Supremacy clause states federal laws highest law of land, Constitution extreme highest law
- States must follow federal law
- What are the Powers of the State Government
- 10th amendment protects state authority
- States rights advocates say the 10th amendment restricts national govt. To only enumerated powers, states superior on all other things
- US v. Darby decided truism, meaning that state and individual powers don't supersede national govt.
- Congress can decide when to regulate state and local activity
- Reserved powers are powers retained by the states
- Police powers
- Conducting elections
- Establish local governing bodies
- Final say on amendments
- 3/4s of legislatures or ratification convention
- Sometimes both govts given power together, called concurrent powers
- Both can borrow money, but states have more restrictions
- Taxing power
- How do regional and local governments rely on the states?
- Constitution does not describe power of governments below states
- State and local governments unitary in general
- Can disband local govts
- Set rules
- Govern public utilities
- Really only 2 levels of American Federalism
- Article IV outlines interactions between states
- Full Faith and Credit means states have to recognize records, public acts, etc. from other states
- Limits, drivers license for example
- Extradition is required, most states happy
- Privileges and Immunities clause says you cannot discriminate based on state residence
- Exception in-state and out-state, but parents pay through taxes, subsidize in state
- More fundamental, more protected
- The Dynamic Nature of Federalism

- Federalism changes, evolves like politics does
- John Marshall important
- What impact did the Marshall court have on Federalism?
- First McColloch v. Maryland
- Over Second BoUS
- Some questioned power
- Maryland taxed
- Unanimous favor on national govt.
- Cited N&C clause
- Consistent with spirit, did not advocate literal
- Established implied powers
- Other major case Gibbons v. Ogden
- Over commerce clause
- Aaron Ogden had granted by NY to monopoly on steamboats in NY&NJ
- Gibbons had federal license
- Gibbons won, due to power to regulate interstate commerce
- Also cited supremacy clause
- What are the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments
- 13th outlawed slavery
- 14th placed limits on state actions
- All born in US citizens
- Cannot deny equal protection
- Due Process clause prevents limitations of Due Process
- 15th all men allowed to vote
- After Civil war, Supreme court did not strongly support African American rights
- Recognized federalism that help us state authority
- Plessy v. Ferguson restricted rights
- Legalized segregation
- Separate but “equal”
- Only one dissented, argued constitution is color blind
- What was the shift from Dual to Cooperative Federalism?
- For most, dual federalism

- Distinct separation of powers
- Like factory with 2 sets of machinery, wheels interconnected, but doing own work without interfering with other
- Supreme court drew similar image in 19th century
- Division never clear and neat
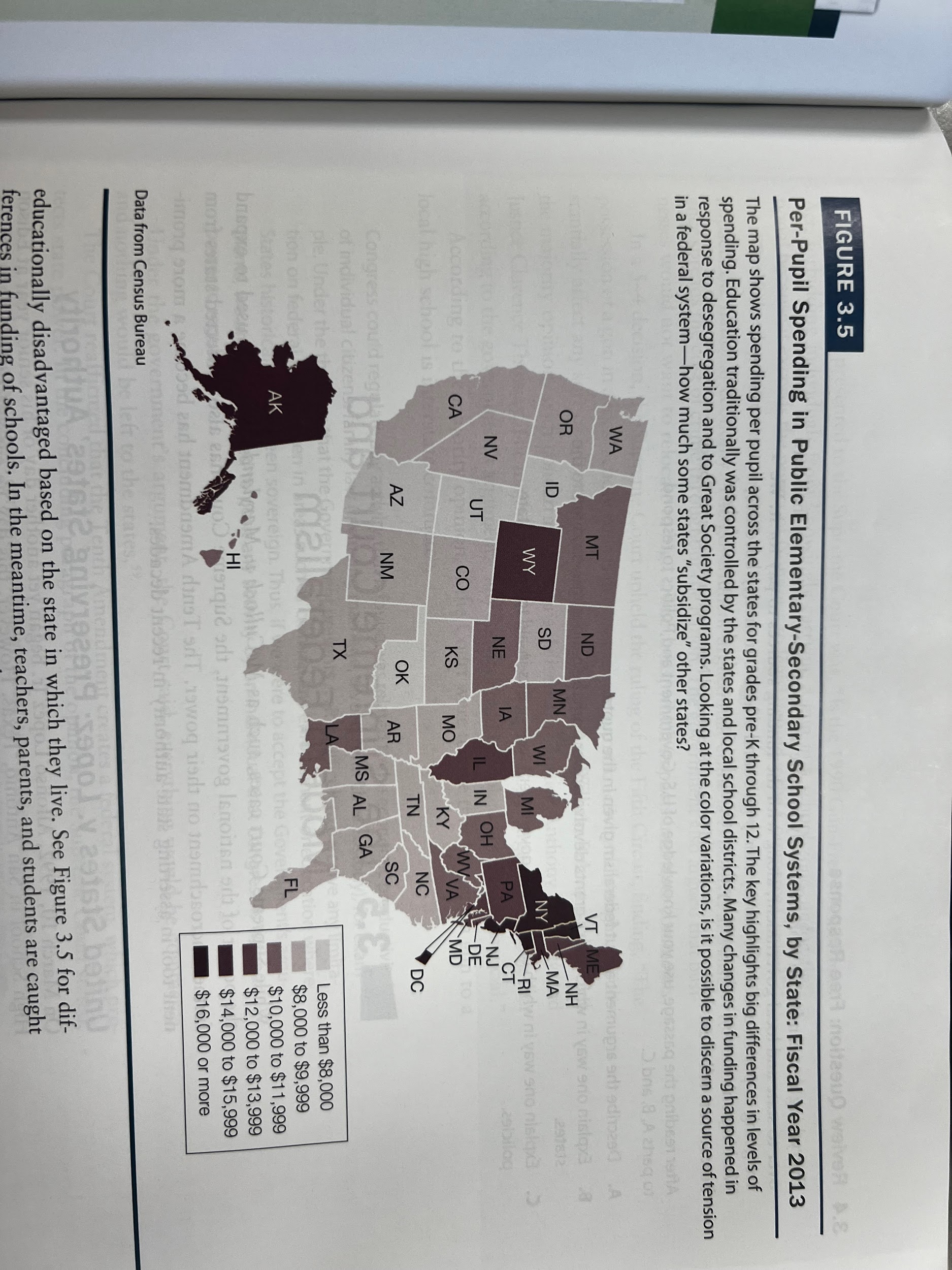
- Example education
- As industrialized, govts tried regulation, but SCOTUS struck it down
- Violated liberty (Lochner v. NY)
- 1925 weight in on rights given by states, selective incorporation
- SCOTUS said 1st amendment rights cannot be violated by states
- Late 18th early 19th, shift toward cooperative federalism

- Don't play same roles though
- States administer, National fundraise
- How did the Great Depression affect Federalism?
- Increase in national power, states could not cope
- GD strained it
- 20s states increased spending, esp. Highways, took out loans, could not repay debt.
- Local govts. Could not care for unemployed
- Appealed to the National govt.
- How did FDR greatly expand the role of the national govt.?
- FDR clear he was going to use full power of executive on GD
- IDC about congress, ill just ask them?
- Savvy politician, powerful influence over short period
- Knew state governments could not handle crisis
- Could not refuse, even if it meant giving up state authority
- Fundamentally changes dynamic, especially national and economy
- Expand regulation of interstate commerce under New Deal
- Cooperative federalism replaced Dual Federalism
- Examples Social Security
- Works Progress Administration
- Provide jobs
- Made possible by economic crisis
- States desperate
- Modern American Federalism
- 2nd half of 20th century, national govt. Expanded economic role, many federal agencies, cooperative federalism still in place
- What are Grants-in-aid and the expansion of Cooperative Federalism?
- One of the primary tools used by the national govt. To get stuff done is grant-in-aid
- Money to states in order to get stuff from the national govt. Decides is important
- AKA Fiscal Federalism
- Categorical grants give states money for specific projects and and certain conditions for receiving and spending
- One may require lower govts. To match spending
- May have instructions
- Some awarded based on population, location, etc.
- Important source of national power
- Not required to accept, once they do, they accept regulation
- Categorical grants like carrot and stick for will of national govt.
- Critics say this is problem
- Wealthy states subsiduze poorer states
- Some mandates unfunded
- Example ADA
- Advocates say it reduces inequality
- Help improve to extend not possible w/o national govt
- Socail welfare under states undil Great Society program under Johnson
- Medicaid concurrently fundes
- ESEA provided federal funding for low income families
- What are devolution and block grants?
- Nixon promised to role back national authority, some back to states
- Main strategy use block grants
- Still grant-in-aid
- Increase in authority o how that money spent to state, local govts.
- Trend continued under Reagan
- Increased block grants for social welfare
- HHS block grants for drug and alcohol addiction
- DoE block grant to wean off oil and gas, improve efficency
- Revenue Sharing is whe fed. Govt. apportions money no strings attached
- Ended 1986
- Not likely in future due to deficit
- Devolution returns federal authority to states
- Increase autonomy, decentralize administration and control
- Example PRWORA, replaced AFDC with TANF, time limits imposed, work requirements
- How does Federalism and Public Policy affect Education?
- ESEA tried to level playing field by providing funding, esp. To low income families
- Federal money to states to improve retention and education
- Reauthorized by No Child Left Behind
- States provided grant money if they standardized tested
- Very criticized
- ESSA gave more flexibility but still testing
- Advocates say that federal govt. Overstepping its bounds
- Others say that students should not be disadvantaged by state they live in
- The Supreme Court and Modern Federalism
- 10th amendment more prominent recently
- What was US v. Lopez
- Kid brought gun into school, charged with state law, dropped, charged with federal law
- Lopez claimed unconstitutional, could not regualte public schools
- Appealed to 5th circut CoA, won, US appealed to SCOTUS
- Required to prove Gun-free school act was allowed under commerce clause
- Increase crime, affects economy our business
- SCOTUS said no
- Then everything would be commerce, 10th amendment issue
- Dissenting said it did affect commerce, look at overarching effect, gun violence problem
- Reversed trend of national power expanding, reaffirmed state powers
- What about Smae Sex Marriage?
- States decide requirements for marriage
- SCOTUS overutnred prohobotion on interracial
- Lesbian Marriage not legal under fed. Law, but under Canada and NY law
- More taxes
- Sued under 5th amendment due process clause
- Challenged DOMA
- Man and woman
- Reaffirmed state power
- SSM did not fall under full faith and credit protections
- 5-4 ruling DOMA unconstitutional
- Interference wth equal protections
- Dissenting said that constitution does not protect right to SSM
- 2 men flew from Ohio to Maryland, reconized SSM
- Medical plane, married while they still could
- Ohio did not recognize one as spouse, sued, 5-4 case affirmed right to SSM, right to privacy
- Obergefell case legalized SSM nationwide
- What was Gonzolaes v. Raich?
- Did federal government have power to ban medical marijuana
- 6-3 sided with federal govt.
- Different from lopez, had rational basis that it affected interstate commerce
- Still illeagal under federal law, but legal in many states
- Obama’s solicitor general said supreme court shouldn’t hear case against colorado
- Boundry between state and federal on drugs still undefined
- Difficult to enforce CSA, have to put millions in jail
- DOJ confirmed this impossiblity
- With Trump, thought that authority would shift to states
- No because Sessions appointed, did not want to relinquish federal authority
- Break federal but obey state law unanswered.
- Federalism always loosely defined
- Still hotly contested.