Week 6 - study manual
Case study
note: it’s basically 2 different case studies



Anamnesis
Note: this case is divided into 2 courses (A & B)
Impairments
heart complaint
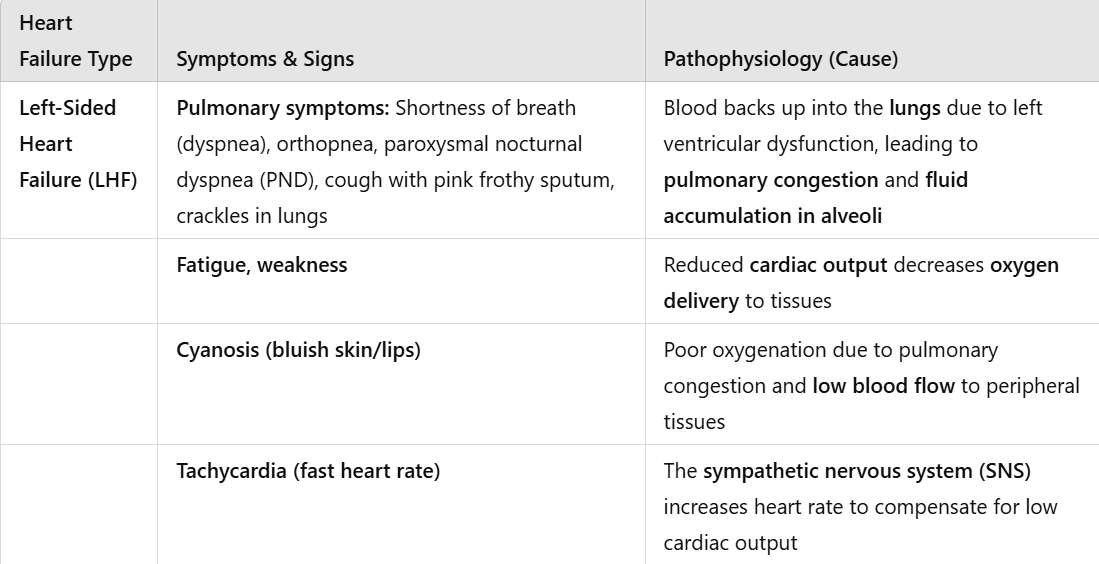
chest pain and shortness of breath
extreme fatigue
Activities -
Partecipation -
Personal factors
male, 68 yo
retired at 67 yo, used to be a taxi driver
he is married
like gardening
walks around the block
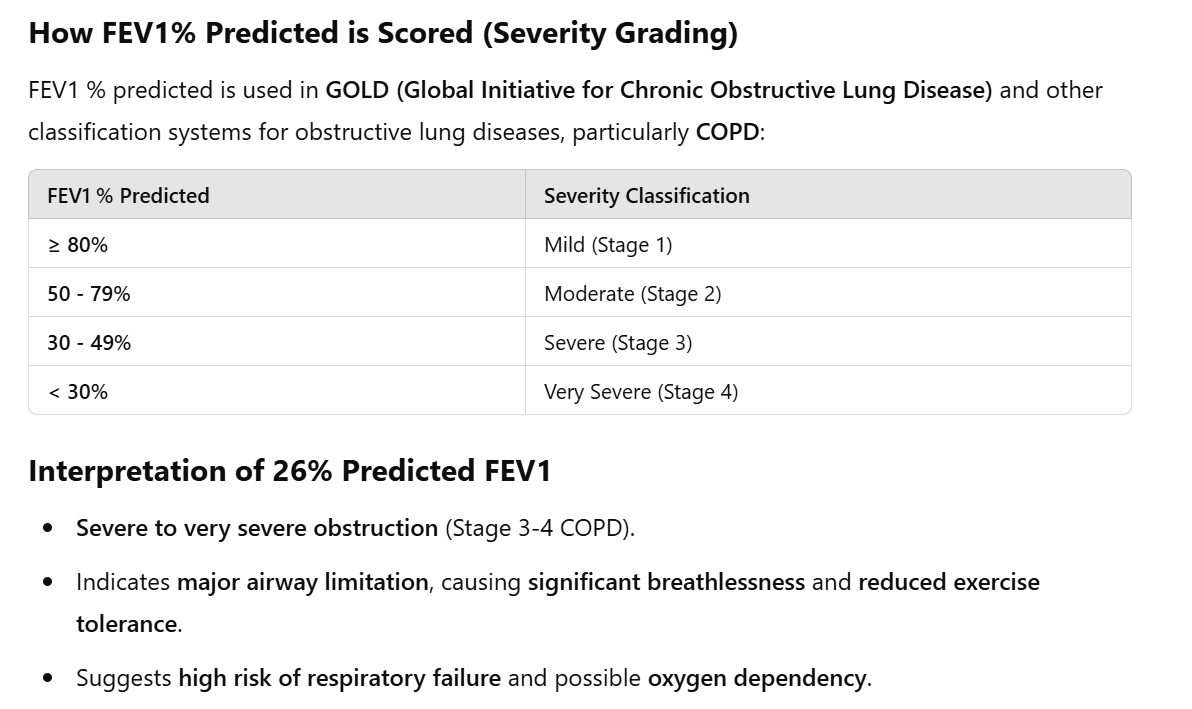
15 years ago - diagnosed with COPD GOLD C (panlobular emphysema → look into this)
he was not “too fussy“ (undertook things)
Environmental factors
lives with his wife in Veendam (has a terrace)
COURSE A
IMPAIRMENTS
chest pain symptoms
extreme fatigue
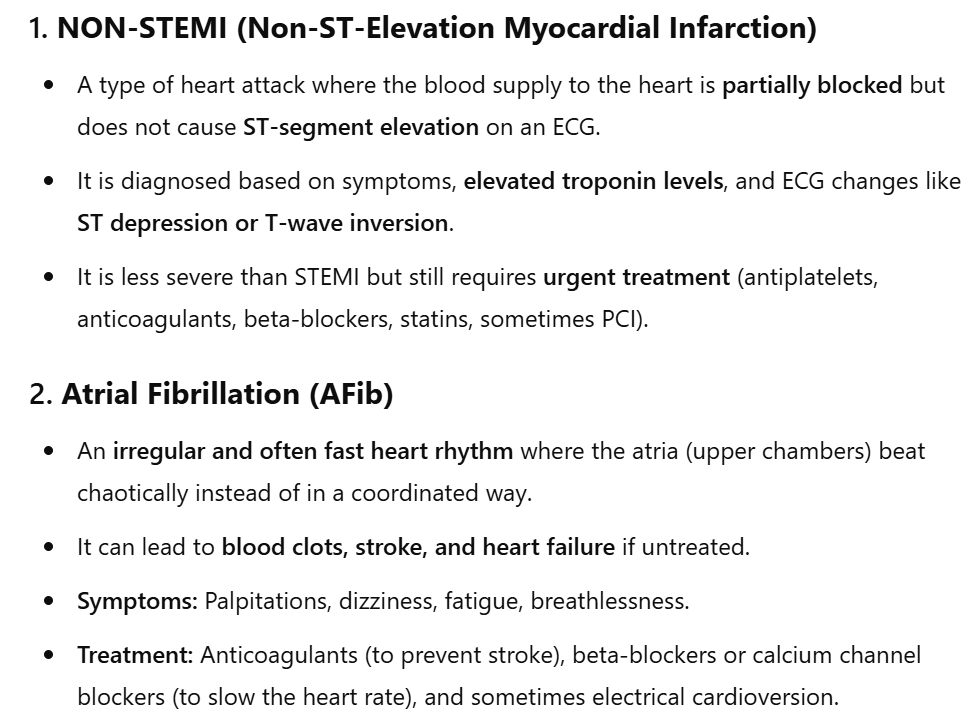
NON - STEMI with atrial fibrillation
Infarct affected the heart
Implantation ICD
fatigue and constipation → GP referral to hospital
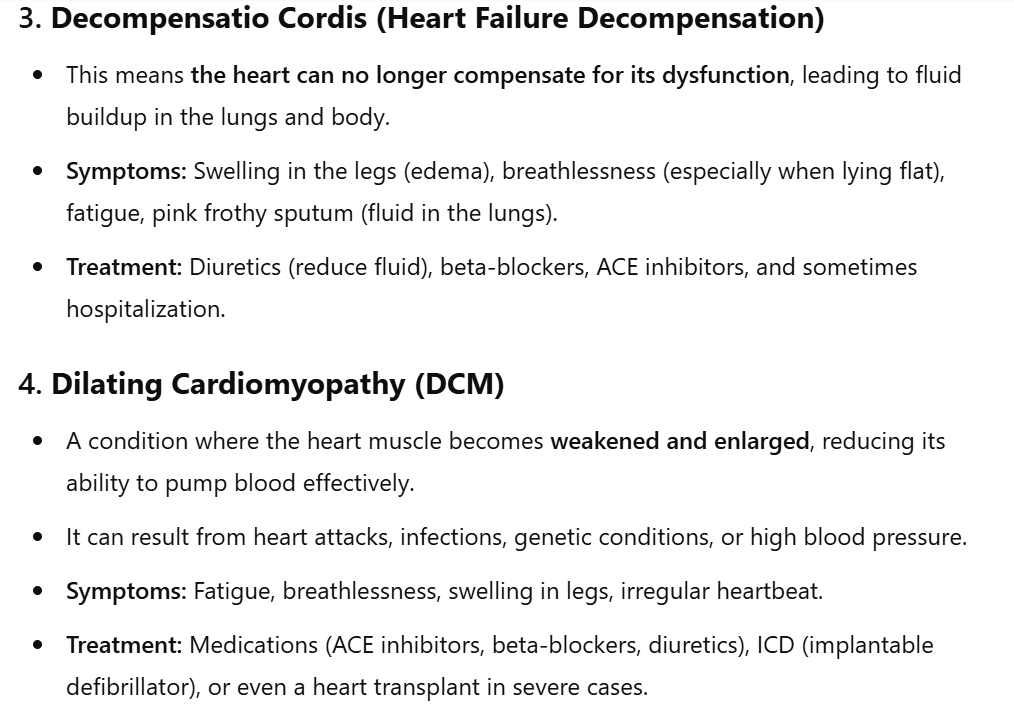
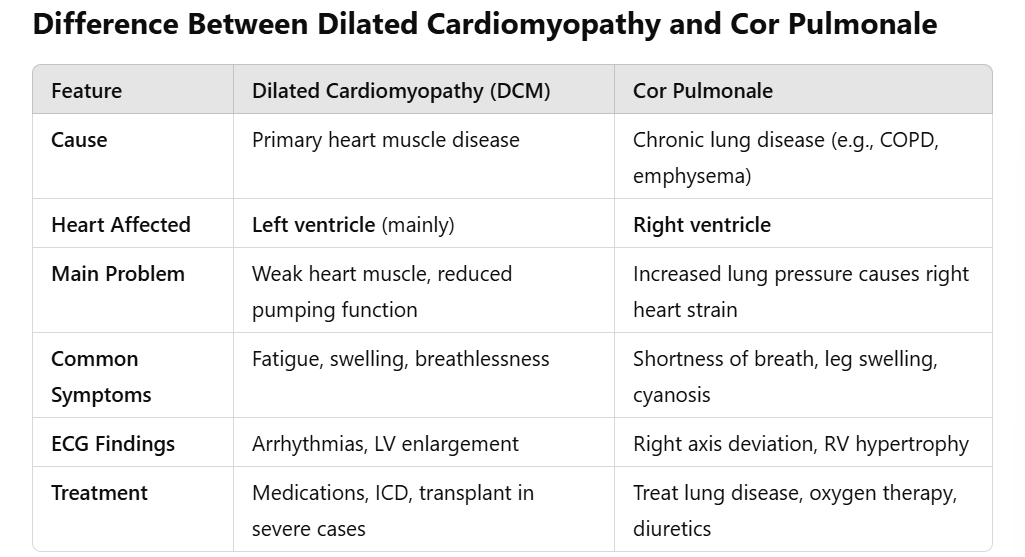
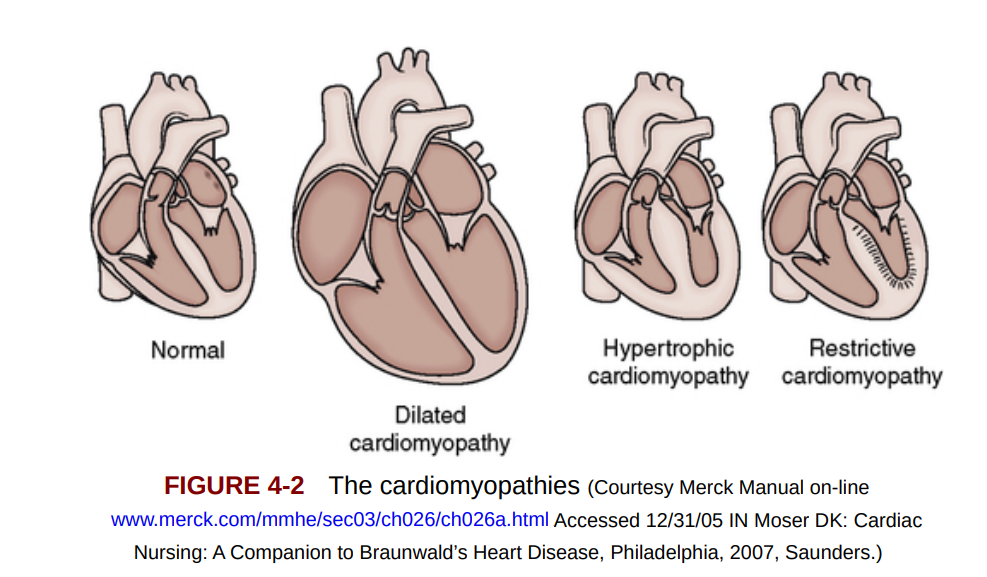
diagnosis → left and right decompensatio cordis with dilating cardiomyopathy (DCM)
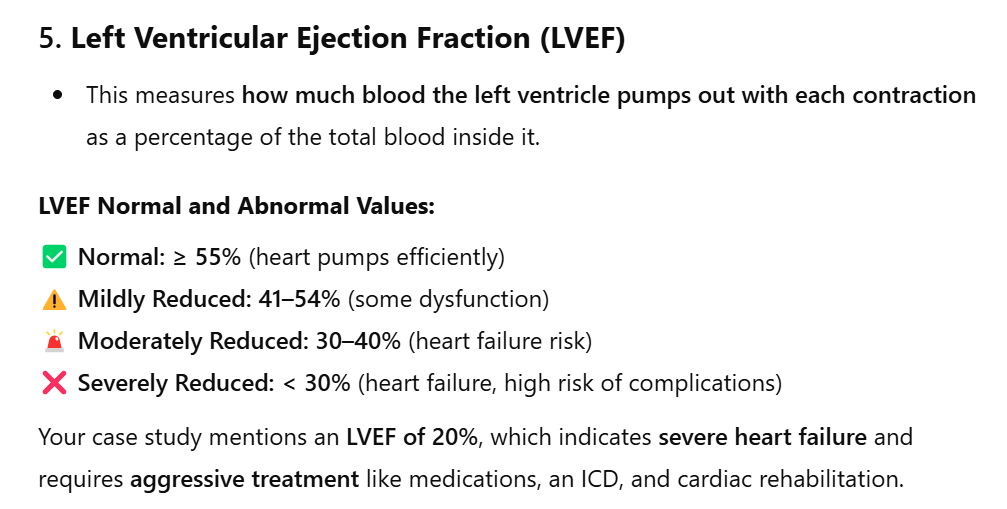
LVEF was 20%.
at night ankles become thicker
he coughs pinkish sputum
ACTIVITIES
gardening
PARTECIPATION
PERSONAL FACTORS
fear of straining strong after the surgery
Hospital gave him diuretics → lost 10kg
his condition deteriorated in the last 6 months
he can no longer lie flat
cannot sleep with a single pillow, he needs more
ENVIRONAMENTAL FACTORS
Notes
he was sent to cardiac rehab for 6 weeks x endurance
Request for help: work in the garden again
COURSE B
Impairments
Emphysema
increased pulmonary circulation
coronary sclerosis
partial respiratory insufficiency
moderate dyspnoea
obstructive, expectoration is still marginal.
During auscultation, bronchial breath sounds are found mainly in the basal lung areas with fine rhonchi here and there.
There is also substantial weight loss (BMI 19) and muscle depletion.
no ischemia
slow blood pressure
PVCs (premature ventricular contractions also called ventricular extrasystole)

Activities
needs help with ADLs
gets into chair 2x day with the help of the nurse
Partecipation -
Personal factors
PT seems reasonable even after severe exacerbation
he lies mostly in bed
it takes a lot of effort to move
medications : cardiotonics, mucolitics, bronchidilatants and analgesics.
Environmental factors
lies on the bed
nurses help him
Physiotherapeutic goal (request for help)

PT classes - practice
1) look into terms that are not clear from COURSE A
non stemi → partial blockage of coronary arteiries ( plaques)
More questions for the anamnesis
how tired do you get when u walk from a scale of 1 to 10
describe your routine
PSC questionnaire
Assessment
1) read chart
2) observation (total, local, functional)
VITALS
3) RR
4) observation respiration pattern
5) saturation
6) auscultation
7) blood pressure
8) heart rate
Specific tests
Endurance → 6MWT, Bruce test
5TSTS, 1 RM (gym) grip strength, TUG
BORG scale 9extersion) NPRS scale
MEP test → look this up
Tampa scale of kinesiophobia
cardiac anxiety questionnaire (CAQ)
SQUASH (for ADLs)
dysponea scale
GOAL: work in the garden again
Treatment
1) endurance: build up of tollerance
HIIT
stationary biking
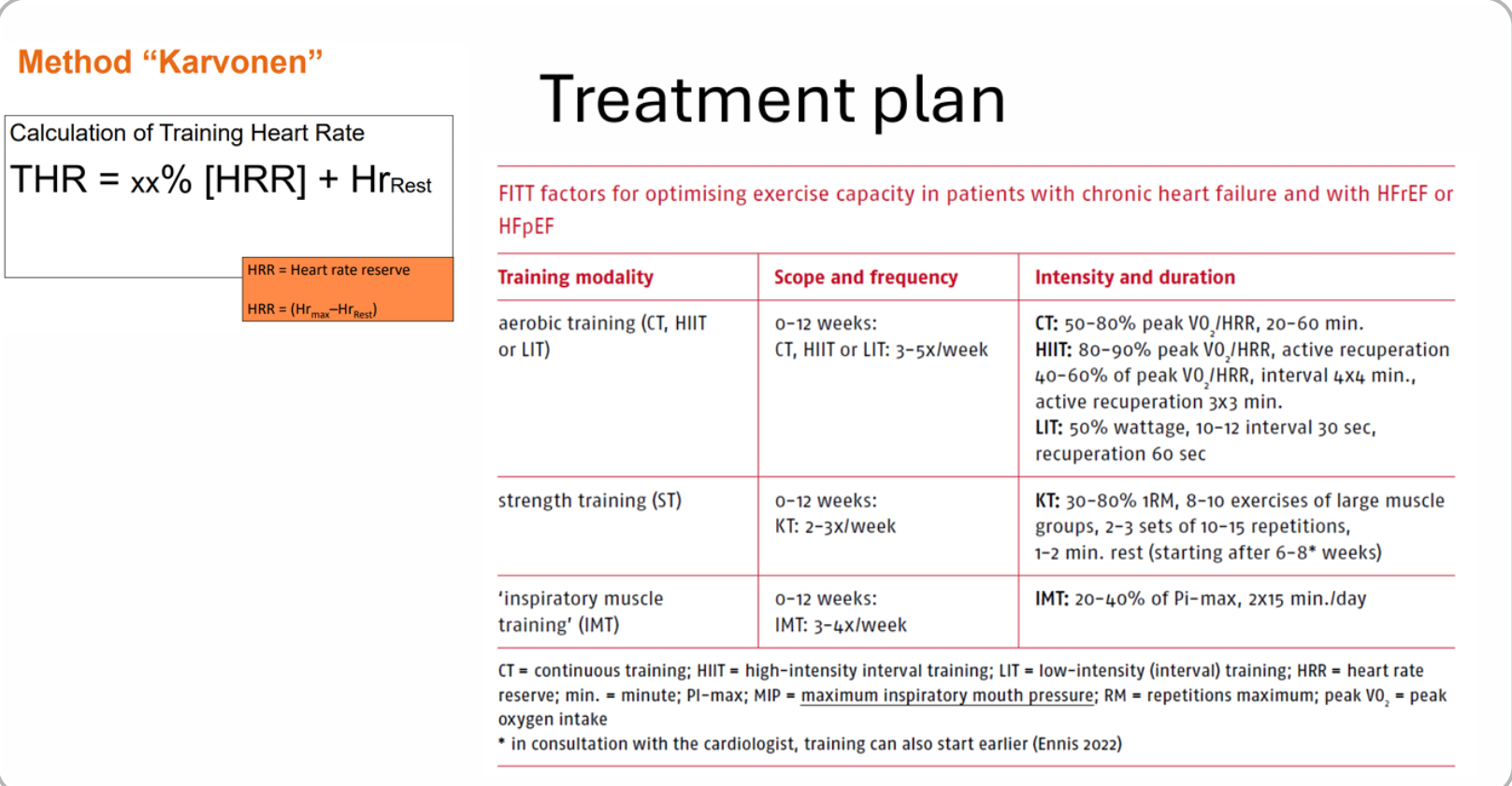
THR:
HIIT + CT = 0.8 (152 - 75) + 75 → 136 BPM (BPM max for PT)
COURSE B




Note: ischemia not present in course B
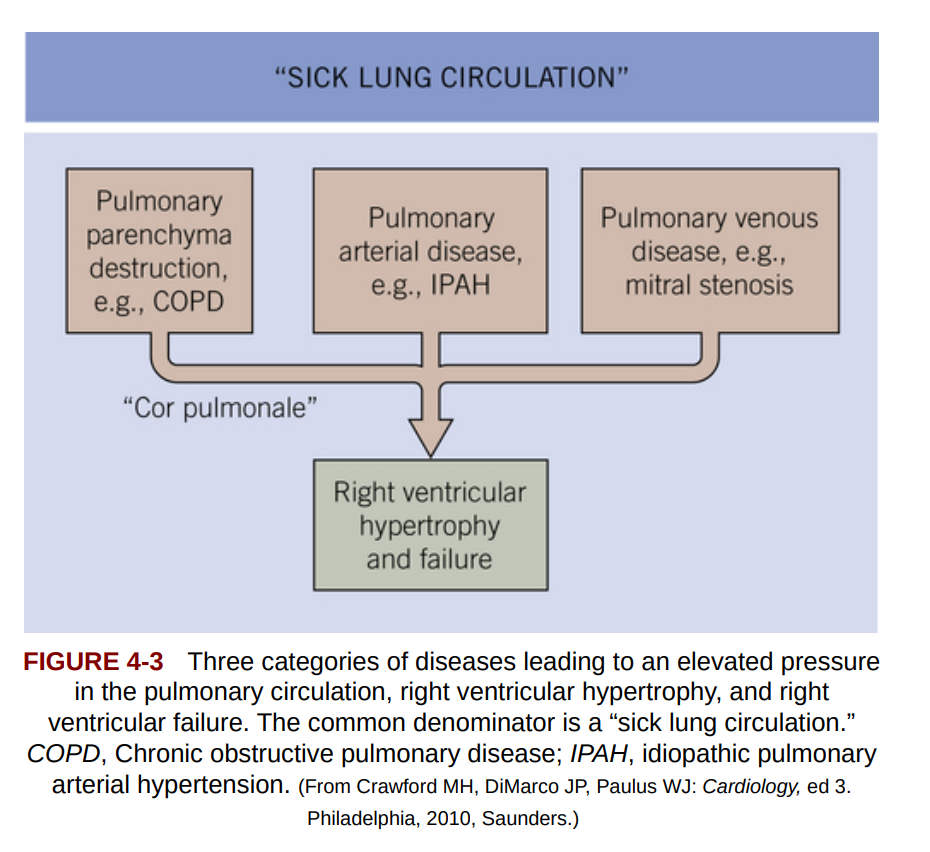
Cor pulmonae:
the alveoli in the lungs are diminished due to the emphysema, because of that the perfusion of arteries in the lungs, this increases the presssure and causes coronary sceloris due to plauqe build up. The higher pressures are not tolerated by the right ventricle and it causes the right ventricle to become hyperthrophic overtime.





Assessment
VITALS
3) RR
4) observation respiration pattern
5) saturation
6) auscultation
7) blood pressure
8) heart rate
Specific tests
Endurance → 6MWT, Bruce test
5TSTS, 1 RM (gym) grip strength, TUG
BORG scale 9extersion) NPRS scale
MEP test → look this up (quello che devi soffiare dentro si chiama cosi)
Tampa scale of kinesiophobia
cardiac anxiety questionnaire (CAQ)
SQUASH (for ADLs)
dysponea scale
HADS (hostital anxiety ditress scale)
MB preparations
watch lecture week 5 → to do lol

PT preparations
1) study task 1
read KNGF guidelines “cardiac rehab“ (Elco sent the translated part, read that) → TO DO
ICF core sets (did it, look into week 4)
look into Hillegass “CHF“ aka congestive heart failure
PT class practice

We talked about how to use spirometry
Instruction:
Inhale as much as possible
Exhale as much fast and hard as you can
Show them where (tube) and how to perform it
Explain them that they have to put the clip to the nose
while PT does it, incitate them (Go go go goooo lol)
Jolanda does it 3 times → learning curve
Protocol: IMT is for PT with reduced inspiratory breathing muscle strength (PI max </= 70 % of what is predicted) or ventilatory limitations in addition to aerobic training
IMT training → inspiratory muscle training
what to use? It’s like some sort of “whistle object“ and they have to blow into it
6 - 12 weeks, IMT: 3 to 4 x week, 2× 15 minutes x day
IMT: 20 - 40 % of PI - max

Heart failure (CHF)
main function → pump blood
Pump has a “pre - load“ (body → heart ) and an “after - load“ (heart → body)
The pump can fail, can be pre- load (back ward) or after - load failure (forward)
Consequences
Pre - load → fluid build up (swelling aka edema)
after - load → blood not getting to body (fatigue, dysonea)
pre load RA → RV after load → lungs → LA pre-load → LV after- load
Systolic → after load (atrias)
Diastolic → pre- load (hypertrophy of the myocardium, chambers are getting thicker, walls become rigid) (ventricles)
the problems begin “upstream” and a
ffect the chain downstream to
Assignment 1
a)
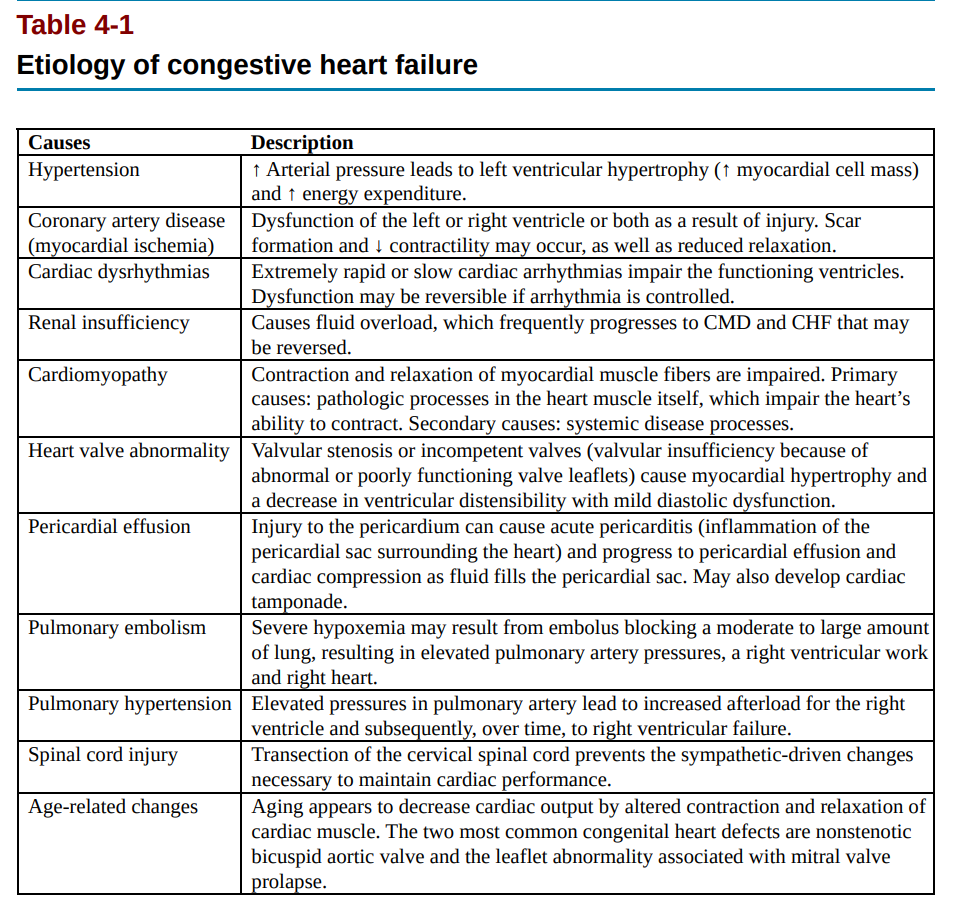
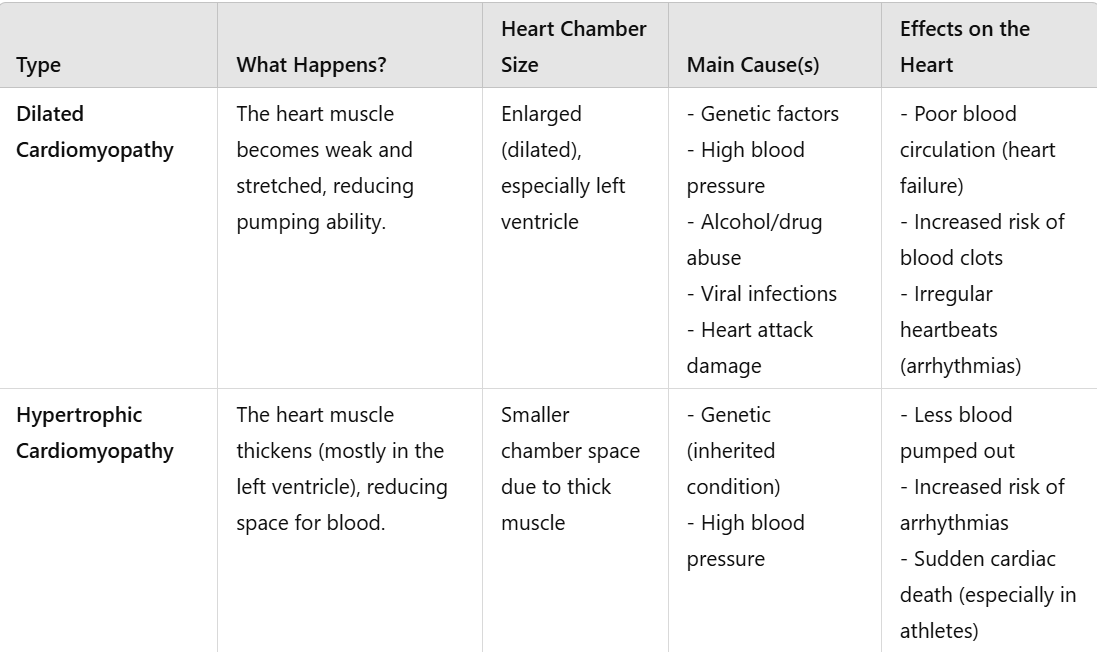
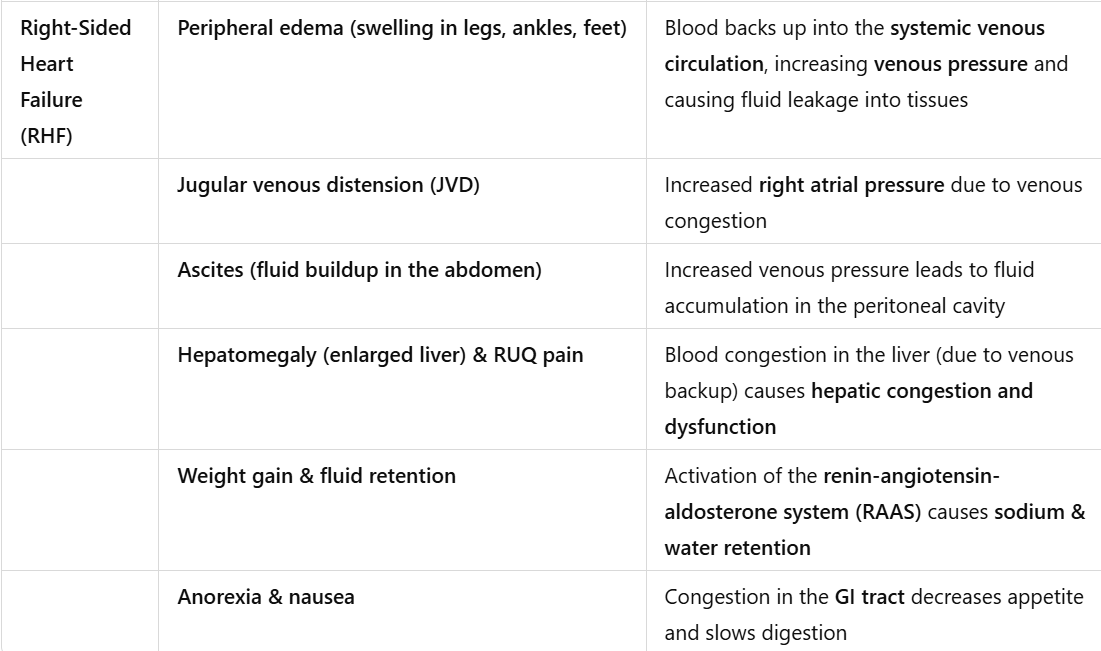
Table explained a bit better
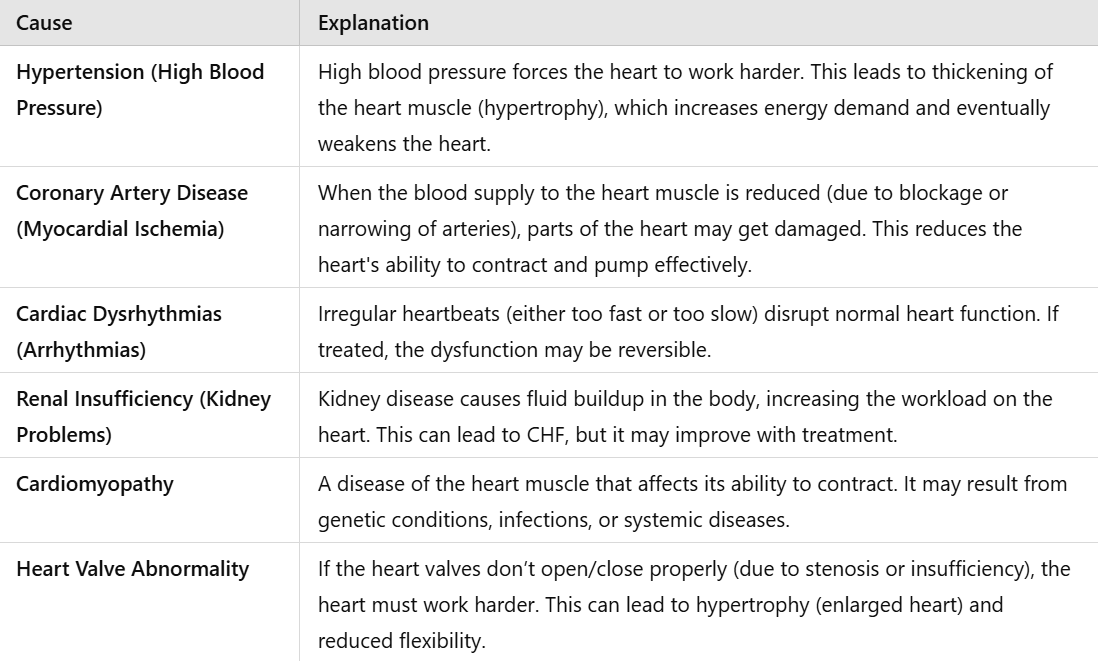

b)
COPD patients and CHF
COPD leads to progressive damage to the alveoli, reducing gas exchange efficiency (number of alveoli decreases) As a result, oxygenation decreases while carbon dioxide accumulates, causing chronic hypoxia (the blood full of CO2 return to the body) The body compensates by vasoconstricting pulmonary arteries, leading to pulmonary hypertension (pressure increase in the arteries of the lungs) Over time, increased resistance in the lungs forces the right ventricle to work harder, leading to right ventricular hypertrophy. This happens because the right ventricle it’s used to work under low-pressure, but because of the increased pressure in arteries of the lungs, the pressure rises in the right ventricle, it cannot handle it. (right ventricle becomes hyperthrophic) This condition, known as cor pulmonale, eventually leads to heart failure due to reduced cardiac output. Wasserman’s model explains how these progressive inefficiencies in ventilation and circulation lead to metabolic strain, worsening systemic hypoxia and increasing the heart’s workload.
c)

D)
Assigment 2
A)
B) “treatments“
1) PT 2) medicines (GP) 3) surgery
1) PT
improve angiogenesis → the more blood vessel, the less the resistance.
By increasing that, we decrease the effort of the heart
How does it work? heart works bad, the muscle need oxygen anyway, body gets scared cauze it needs air, body produces more blood vessels to get more oxygen in there, body happy, heart happy because the increase of vessels reduces the pressure.
HOW? HIIT training, resistance training
lifestyle changes
2) Medicines
diuretics → gets rid of fluid by making u pee more (for pre-load)
digitalis purpurea (it’s a flower) → increase contractility of the heart (for after load aka ventricles)
Dopamine → increase contractility of the heart (for after load aka ventricles)
3) surgery
transplant (u have to be sick asf)
syncronizing the beats (left and right side of the heart are fused together to get them to squeeze together) + pace maker to make it work together (just to make sure)
SIDE NOTE: beta blockers (metoprolol) → they help with hypertension, they reduce heart rate (side effect) U DON’T GIVE IT TO PEOPLE WITH HEART FAILURE, only if u want to end their suffering.