Lecture 11: States & Development: Modernisation Keynesianism & Dependency
Lecture Outline
Modernity & modernisatyion
Keynesianism
Linear Stage models
Dualistic models
Spatial dimensions of modernisation
Structuralist & dependency approaches
Structuralism theories
Dependency theories
World systems theory
Conclusions & preparation for next lecture
Modernity & Modernisation
Multiplier effect that is kickstarted by an investment made by a government or private sector
The Marshall Plan: US invested $15 billion to restore Europe together = A strong European economy is beneficial for Amercia’s economy
Linear Stage models:
Walt Rostow - modernization theory (1960)
5 stages of development/modernisation
Traditional
Pre-conditions for take off
take off
Drive towards maturity
Age of high mass consumption
Dualistic Models:
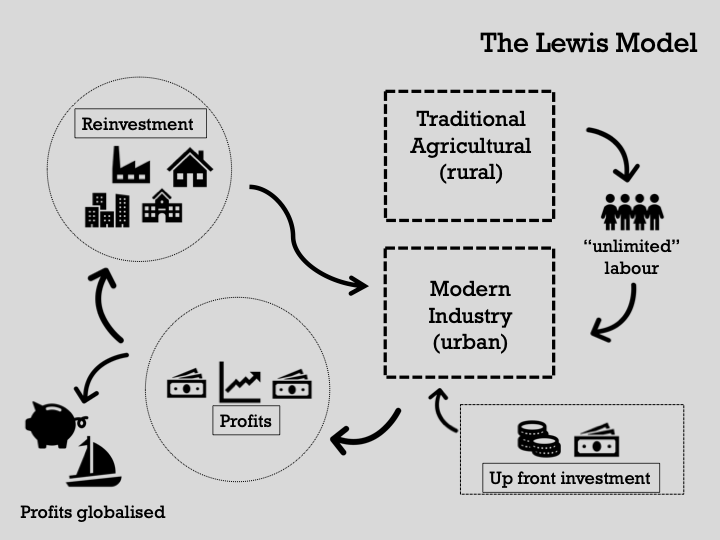
Sir W. Arthur Lewis: (1915-1991)
Believed that economies were ‘dualistic’ - transitioning from ‘traditional to modern’.
External capital - foreign investment - could aid and accelerate this transition
Spatial Dimensions of Modernisation:
Key figures:
Albert O. Hirschman (1915-2012) Argues that inequality is an inherent part of development and the inequality would reduce as a country becomes more developed.
Karl Gunnar Mydral (1898-1987): Argues that you will only get less inequality in terms of development if there is government aid.
Aid: ‘a transfer of resources on concessional terms - on terms that are more generous or ‘softer’ than loans obtainable in the world’s capital markets’ Cassen 1994
Different ‘kinds’ of Aid
Humanitarian aid
Rapid, short term
Aims to saves lives and alleviate suffering
Made available in emergency conditions or the aftermath of a disaster
Development aid
Long term
Addresses prolonged, structural issues
Aims to improve everyday quality of life, strengthen economy and tackle social challenges
3. Structuralist & Dependency approaches:
Structuralist Theories:
Raúl Prebisch (1901-1986)
United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America (ECLA)
Challenged ‘modernisation theories’ - argued that developing nations couldn’t emulate the path of developed nations
Free trade acted as an ‘obstacle’ for Latin American development.
Import-Substitution Industrialisation (ISI):
Brazil, Argentina and India adopted ISI from 1940s
Protected domestic industry and promoted production for export
Tariff Barriers to encourage production for export
Dependency Theories:
‘Dependistas’:
The ‘West’s pathway to modernity was not replicable’
The ‘Wests’ development was built on the world of exploitation of the ‘developing world’ which is maintained by the global economic system
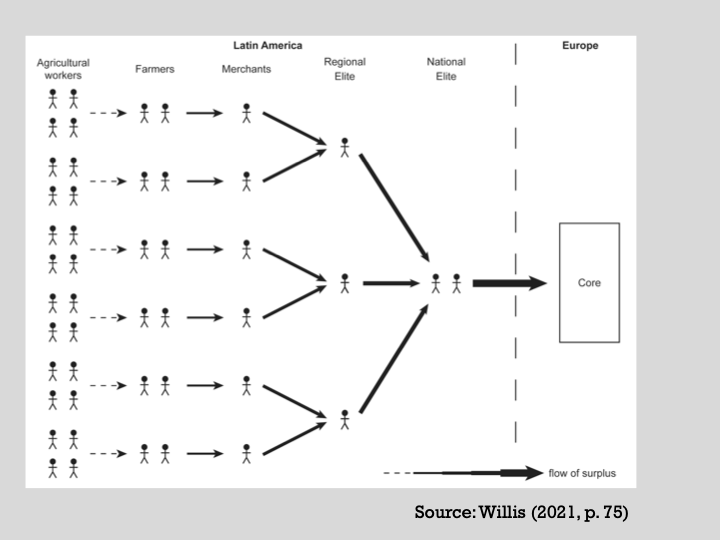
The Global system is too unequal to allow development without exploitation of other countries = Under this theory, exploitation leads to underdevelopment, leaving countries that were exploited to be dependant on more developed countries = countries are unable to develop or at least in the same model of the Global North
HOWEVER:
Countries were able to ‘break out’ of the dependancy relationships, in particular East Asian economies
Very economic focus, no other factors were being considered ie: political social etc.
Exogenous: little consideration of what was going on internally
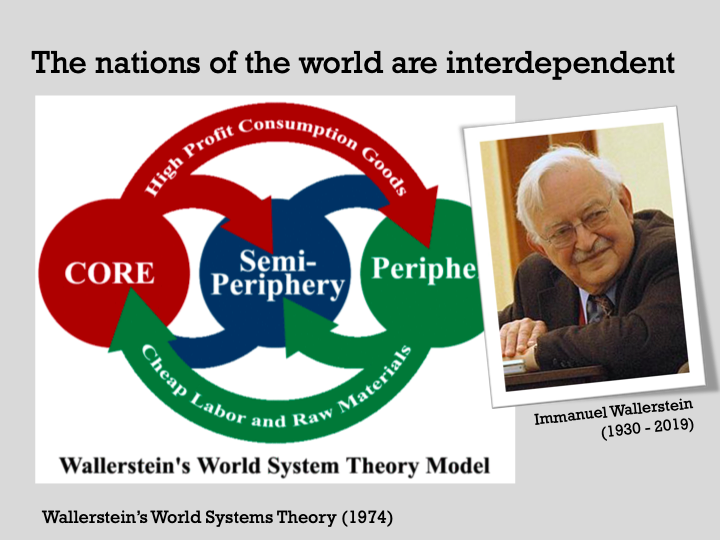
World Systems Theory:
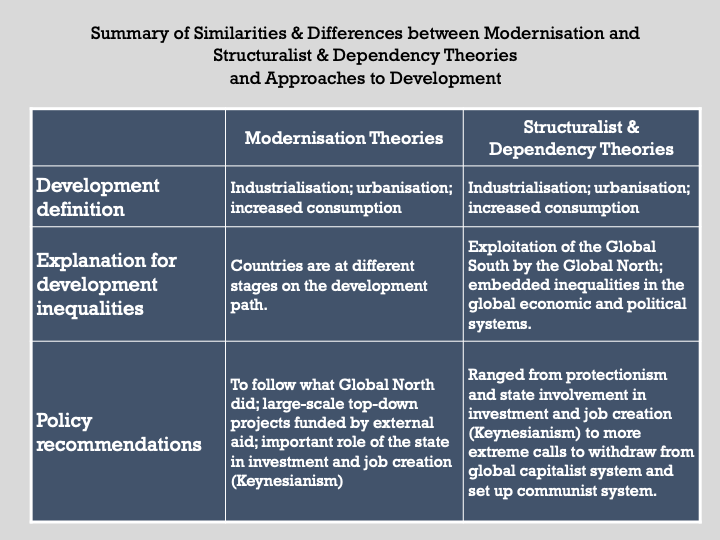
Summary of similarities & Differences between Modernisation and Structuralist & Dependency theories and Approaches to Development: