31. DMD Exanthems 2025
Exanthems, STIs and Infections in Pregnancy
Learning Objectives
Describe the infectious risks associated with childhood exanthems.
Examples of STIs leading to genital ulceration or mucosal/urethral inflammation.
Pregnancy features increasing susceptibility to infection.
Infectious targets in antenatal infectious disease screening program.
Appropriate specimens/tests for infections.
childhood exanthems - VZV, measles, scarlet fever, rubella, Erythema Infectiosum (fifth disease)
Chickenpox (Varicella Zoster Virus)
Incubation Period: 15 days., shedding for 24 hours before rash starts
may june, droplet infection, very infectious
Symptoms: rash, disseminated infection, pneumonia, encephalitis, congenital varicella.
reactivation as shingles
Diagnosis: PCR test for VZV, serology helpful at later stages (IgM, IgG).
Immunization: Aciclovir for treatment/prevention; immunoglobulin for prevention.
Complications of Varicella
Pneumonia: inflamation in lung, air sac with fluid. Particularly severe in pregnant and immunocompromised individuals.
Congenital Varicella Syndrome: Fetus infected in utero
Encephalitis: inflammation and swelling in brain
vesicular intraoral lesions, chickenpox palatal lesions
Shingles (Zoster)
Occurs due to reactivation of varicella zoster virus.
Measles
Incubation Period: 10 to 14 days.
Symptoms: runny nose, cough, conjunctivitis (pink eye), maculopapular rash, high fever. FERBILE RASH
Koplik's spots - clustered white lesions on buccal mucosa 2 days before rash
Complications: miscarriage, pneumonitis, encephalitis, subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE).
Diagnosis: Direct detection of viral RNA using swab, IgG testing, oral fluid sample , MMR vaccination 2 dose - Measles, mump rubella all droplets
high risk in infants, pregnant woman, immunosuppression
Scarlet Fever - GAS
sore throat, like sand paper rash , characterized by a fine pink-red rash, fever, strawberry tongue
Complications: rheumatic fever, rheumatic heart disease, acute glomerulonephritis.
Diagnosis: throat culture for Streptococcus pyogenes (GAS), ASOT serology test.
Treatment: Penicillin or Erythromycin
Rubella - rubella virus
Incubation Period: 14-21 days.
Symptoms: cold-like symptoms (sore head, runny nose), red-pink rash, swollen glands.
spread through droplets
Diagnosis: Rubella IgM test; prevention via MMR vaccine.
Congenital Rubella Syndrome: Infection <15 weeks gestation孕期 can cause severe fetal damage, including eye problem, deafness, heart abnormalities, brain damage
Erythema Infectiosum (Fifth Disease)
parvovirus B19
Incubation Period: 4-20 days.
Symptoms: mild illness, "slapped cheek" appearance, lace-like rash.
in young children during spring
Diagnosis: B19 IgM, PCR for pregnant women; fetal tissue PCR.
Risks: fetal loss and hydrops fetalis.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Mucosal/Skin Infections:
Urethritis and cervicitis caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis. → oral sex, transmit to the mouth → Cause oropharyngeal infection
warts - human papilloma virus HPV
Complications -
Chlamydia and Gonorrhea: can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, persistent urethrits, septic arthritis, conjunctivitis.
Antimicrobial Resistance: Gonorrhea particularly challenging due to growing resistance.
Skin Ulcers: (genital or the mouth)
caused by HSV-1/HSV-2 and syphilis
HSV1/2 - in the mouth → cold sores. Primary infection → gingivostomatisis (sores in gums) recurrent infection - herpes labialis at the same place
Syphilis (caused by treponema pallidum) - primary chancre - painless ulcer in mouth or genital area
secondary syphilis - mocosal lesions spread to systemic infection, snail track ulcers
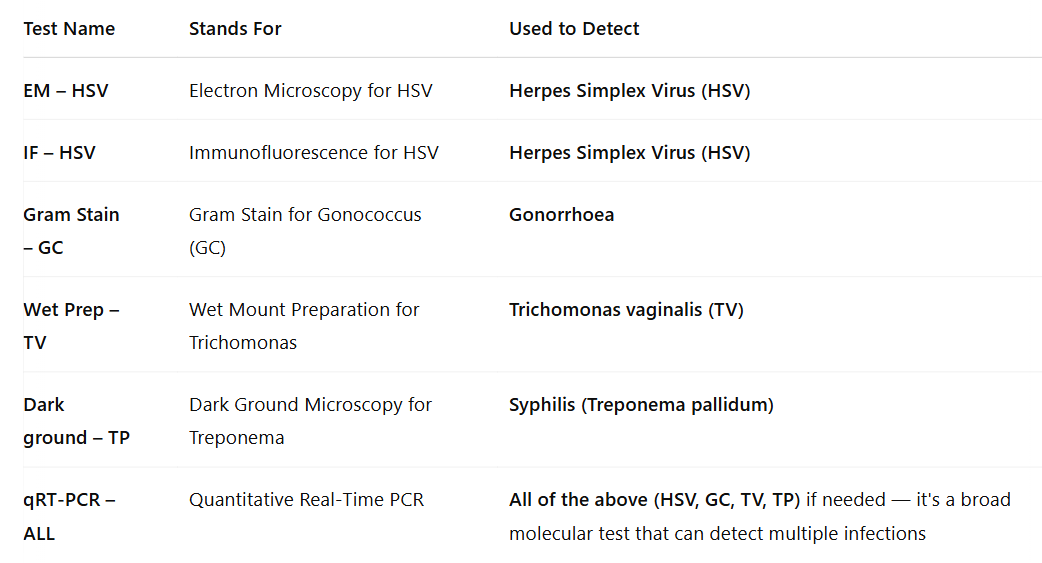
Laboratory Diagnoses for STIs
Serology: blood tests for syphilis, BBV (HIV, HBV, HCV)
PCR: for urethritis and cervicitis (clamydia and gonnorrhoea) swab or urine
Pregnancy and Infection
Increased infection Susceptibility: Immunosuppressed state and physiological/anatomical changes in pregnancy.
criteria for a good screening program BIRS
condition severeness, natural history (symptons, how it spead, what it does to body), detectabel stage, availability resources, risk less than benefit
Key diseases: HIV, HBV, Syphilis, Rubella. - they meet all the criteria
Antenatal Infection Screening Program - related to pregnancy
Screen for: HIV, HBV, Syphilis, Rubella (immunity).
Use serology blood tests.
Antenatal Screening
Tests offered for every pregnancy, results in 10 working days, referred clinic will arrange additional blood test if abnormal is found
if after 24 weeks of pregnancy, results are urgent, test in 24 hrs
if in labour and not screened → urgent test for HIV, HBV, syphilis
test should be offered again before 28 weeks of pregnancy if initial offer was declined by pregnant pers
store aliquot at -20 for 2 years
Common Infections in Pregnancy
Includes: Syphilis, HIV, HBV, Rubella, Toxoplasma gondii, Cytomegalovirus, Parvovirus B19, Varicella, several herpes types, E.coli, group B streptococcus.
Effective Interventions for Antenatal Infections
HIV: HAART therapy, C-section considerations, avoid breastfeeding.
Syphilis: Penicillin treatment.
HBV: Antiviral medications, vaccinations.
Rubella: MMR vaccination 2 dose postnatally.
For all infections: surveillance, monitoring, and treatment options as necessary.