Blood
Blood is made of many parts
In centrifuge, heavy stuff will sink
Light - Plasma: Liquid component of blood — 55%
Mostly water, also sugar, amino acids
Middle - WBC and platelets (buffy coats) — >1%
Platelets are clotting
Heavy - Erythrocytes/RBCs (Hematocrit): Sinks to the bottom — 45%
Has iron
When sick, WBC and platelets go up, RBCs go down
RBCs carry oxygen → Lack of oxygen in body = Less ATP —> Lethargy
When sick, you are anemic
Red blood cells do NOT have nucleus !! — This causes the middle to collapse
Why no nucleus? Because they needed space for HEMOGLOBIN
Hemoglobin:
Heme - Iron component - Transports oxygen
Transports 98% of our oxygen! SUPER important!
Globin - Protein component - Transports carbon dioxide
DOES NOT TRANSPORT AT THE SAME TIME !!!
They die within 120 days
Without nucleus, how do they reproduce? HEMATOPOESIS in the BONE MARROW!
They used to have a nucleus, but had to “spit” it out before being released from bone marrow.
Blood cell types:
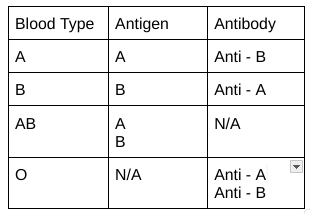
Why specific transfusions?
Immune system looks for an ANTIGEN:
Exterior protein that is used for immune system to DETECT which cell is which —> does NOT affect function
When they detect a protein that does not belong, they create those ANTIBODIES !
There is one one more factor —> the Rh factor or D
Either you have it or you don’t (+/-)
Still only causes a small reaction, EXCEPT when baby and mom have different (baby +, mom -) AND you have a second child —> Erythroblastosis fetalis
You can fix using shot of RhoGAM
Agglutination/coagulation (clumping of cells) - Occurs when blood types which are NOT compatible are mixed
This is what clogs up blood vessels
IF there is nothing to attack, then it is not there
Ex. question: You find a blood spill which reacted with anti-A, but not Anti-B or Ani-Rh
It is A -
Blood color —> More oxygen means the blood is brighter
Arterial blood = SCARLET red
Oxygenated
Venous blood = DARK red
Deoxygenated
Reversible oxygen —> Only with iron
If it was LEAD, the hemoglobin would not let go of the oxygen —> Not give oxygen to the rest of the body
Erythropoeisis
Formation of RBCs
Regulated by erythropoietin (EPO) which is found in kidneys
Occurs in bone marrow
Anemias —> Low oxygen carrying capacity; not a DISEASE, a SYMPTOM
Insufficient RBCs
Hemorrhagic - Bleeding out
Hemolytic - Red blood cells die sooner than expected
Mononucleuosis - Mono/Kissing disease: Blood disease by EBV —> Spreads through saliva
Aplastic - Bone cancer
Making blood cells incorrectly —> They die
Low hemoglobin - Dietary
Iron deficiency - Not eating red meats
Pernicious - No B12 = No mitosis = No new blood cells
Abnormal hemoglobin
Thalassemia - DNA does not have proper components to build RBCs, so they fall apart
Sickle cell - Some cells are sickle-shaped
This is actually helpful in places with malaria, as they help protect against this disease.
Polycythemia: Too many blood cells
Makes blood thicker —> Plasma content goes down
Heart does not like syrup-y
Natural polycythemia
Not able to flow easily
Leukocytes (WBC) - Protect from the body - 5 types, which can be differentiated into two groups based on the CYTOPLASM
When looked at under a microscope, they will be the color of the stain
Granulocytes - Short life (>1 day) - Grainy cytoplasm - React to DIFFERENT stains — Start up inflammitory response
Basophils - Blue
Absorbed base stain, made cell blue
Respond to forein antigens (allergic reactions)
Secretes:
Heparin: Blood thinner; prevent clotting
Histamine: Vasodilation = increases bloodflow; but also increases swelling
Eosinophils - Red
Absorbed acid stain, made cell red
Respond to parasitic infection
Perform apoptosis next to the parasite, and the perforins poke holes through the parasite
Secretes:
Perforins: Rupture cell membrane
Neutrophils - Purple
Absorbed both, made cell purple
Respond to bacterial + ungal infections
They eat bacteria, which have lysosomes in them
Lysosomes have H2O2, which kills everything
Also poison themselves with that as well
Secretes:
H2O2: Damages cell membranes and DNA (found in lysosomes in neutrophils)
Agranulocytes - Long life - THIS is your immunity (allows you to not get same disease again)
Lymphocytes - In the lymph nodes (When lymph nodes = swollen, sign that you are fighting disease)
T-Cells - Destroy foreign substances + cancerous cells
Just kill ALL cells
B-Cells - Antibody factories
Mark foreign cells for T-Cells to kill
If B-Cells mark good cells, then T-Cell kills those also - AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE
Circular nucleus
Monocytes
Inside blood vessels
Outside blood vessels —> Turn into macrophages
“Scavengers” clean up cellular debris
Biggest
U-Shaped nucleus
Break down:
Never - 60% - Neutrophils
Let - 20% - Lymphocytes
Minions - 8% - Monocytes
Eat - 2% - Eosinophils
Bananas - <1% - Basophils
Leukemia: Cancer of the Blood Cells
Occurs most often in adults > 55, but is the most common cancer in children < 15.
Myelogenous
Lymphocytic
Thrombocytes (Blood clot): Clot blood when there is a damaged blood vessel
Thrombus = Clot
Fragments of the megakaryocyte
Too big to be in circulation
Maintain hemostasis —> Maintains blood from leaking out
Need calcium to even BEGIN clotting the blood
Hemophilia = Love of blood; cannot stop bleeding
Steps:
Prothrombin activator comes into contact with prothrombin, turning it into thrombin
Thrombin activates the fibrinogen to turn into fibrin
Fibrin is the mesh which makes your scab/clot
Thrombus vs. Embolus
Thrombus: When your blood forms in your veins, and gets stuck in the valves
Ex. DVT - Deep vein thrombosis in thigh
Embolus: A piece of the thrombus that is flowing free, flowing back to the heart; it is growing bigger
PE - Pulmonary embolism
What dissolves a clot?
Plasminogen (Circulating, inactive protein)
If activated by tPA (Tissue plasminogen activator)
Creates plasmin —> FIBRINOLYTIC
Important information —> You can inject tPA to turn your plasminogen into plasmin and reduce negative permanent effects of stroke.
Anything that ends with -ogen is INACTIVE