Bio: Intro to Evolution
The Origin of The Universe and Earth
One of the greatest mysteries of our world. While we have no first-hand evidence of the universe’s formation, we have substantial secondary data.
These various forms of evidence have led to the development of the Big Bang Theory
1) First was the Big Bang (14 billion years ago)
2) Inflation (Fractions of a second after big bang)
The universe expanded faster than the speed of light, leading to a rapid cooling and the formation of fundamental particles.
Made the universe smooth and uniform.
3) Formation of fundamental Particles (first few seconds)
energy turned into quarks, electrons, and neutrinos
Quarks combine to form protons and neutrons
4) Nucleosynthesis (3-20 minutes after)
Protons and neutrons fused to create hydrogen, helium, and lithium nuclei
The universe was too hot for atoms to form yet
5) Recombination (380,000 years later)- formation of atoms
Electrons joined with nuclei to form neutral atoms
Light was finally able to travel freely, creating the Cosmic Microwave Background
6) The Dark Ages
The universe was mostly dark and filled with gas
No stars or galaxies existed yet
7) Formation of Stars and Galaxies (a few hundred million years later)
Gravity pulled hydrogen and helium together to form the first stars
Stars grouped into galaxies, including the Milky Way
8) Formation of our Solar System
A giant cloud of gas and dust collapsed, forming the Sun
The leftover material formed planets, moons, and asteroids
9) Present-Day Universe
The universe continues to expand
Stars are born and die, forming new elements
Scientists study dark matter and dark energy to understand the future of the universe

The Formation of Chemical Elements
They are any substance that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by ordinary chemical processes
The number of protons in the nucleus changes their identities
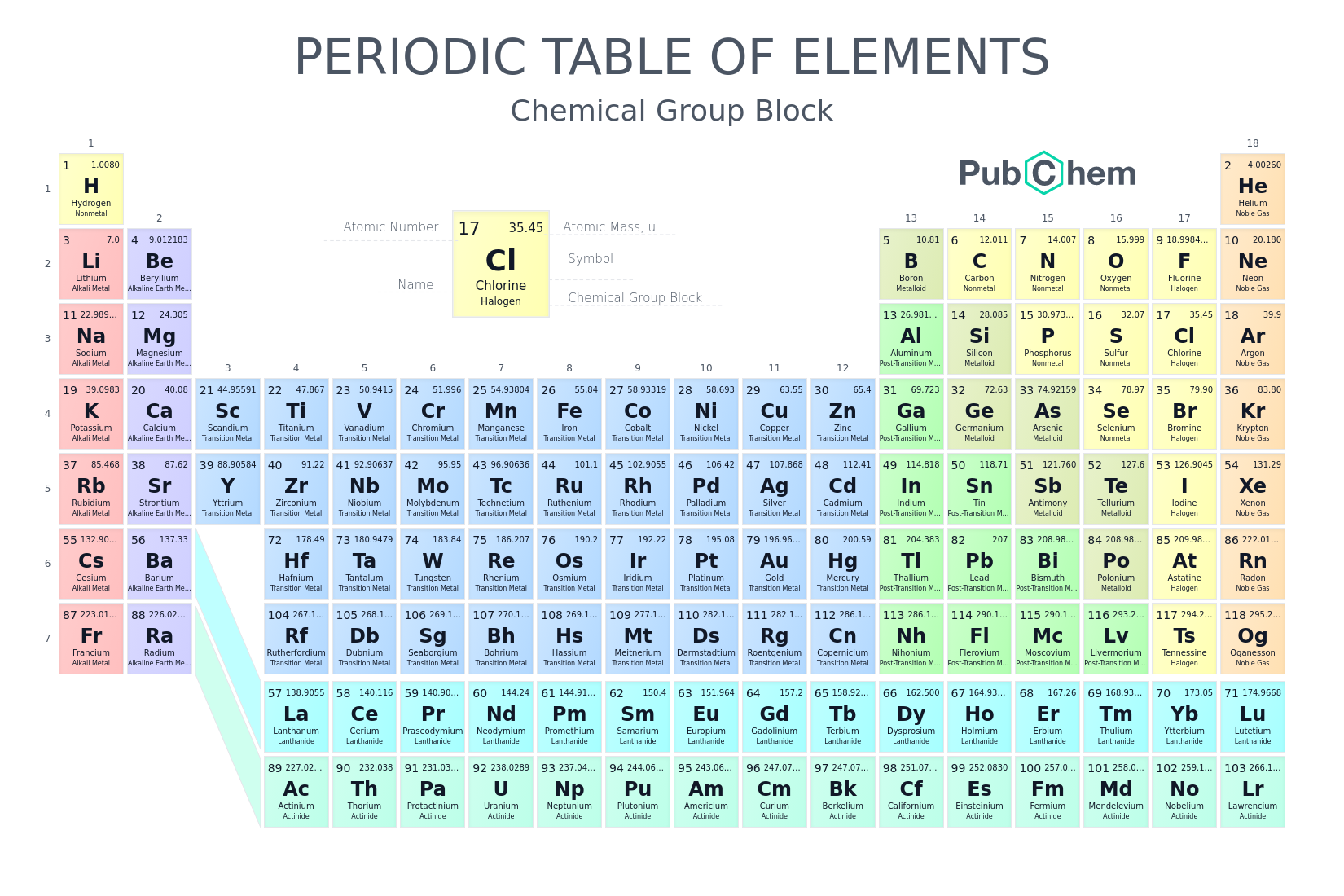
Most common elements for life are: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus
The first elements to form were the simplest; Hydrogen and Helium
One of the main sources of energy in the universe is solar energy (during nuclear fusion in stars of hydrogen isotopes)
The Formation of the Earth
The best theory for the formation of the solar system is the Solar Nebula Theory, that high density, high pressure core became a proto-star and eventually the sun.
The bits of matter that were not part of the Sun became planetesimals and eventually the planets such as Earth
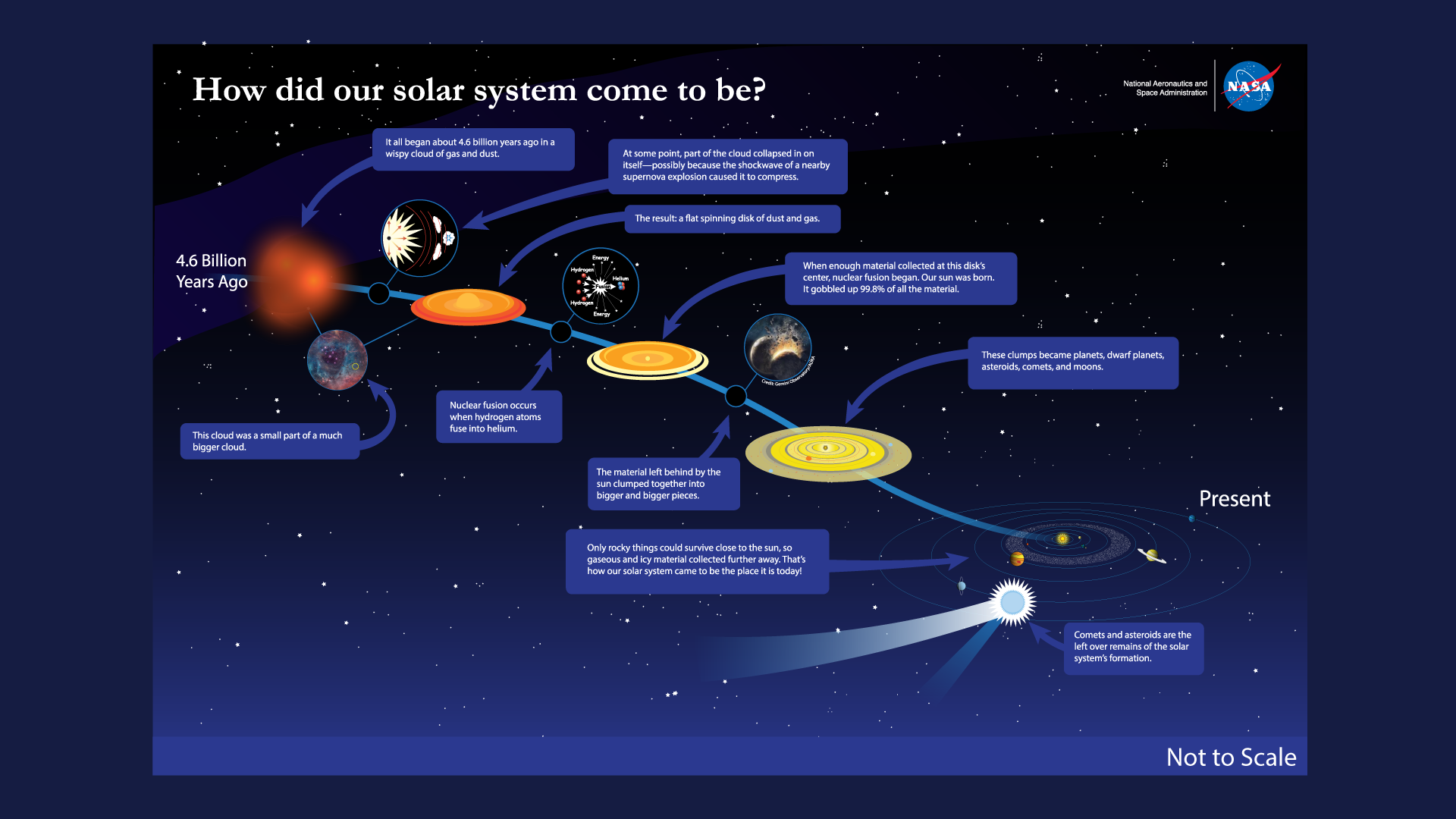
Evidence for Solar Nebula Theory:
The placement of the rocky planets, then the gas giants both with the debris that never became a planet between them
All planets orbit in the same direction
Some meteorites are 4.6 billion years old, the same age as the Sun and planets
Early Earth
The atmosphere was toxic (CH4, H2, H20, N2, and NH3)
There was substantial volcanic activity
Meteorite impacts were a regular occurrence
Temperature changes were extreme (lack of ozone layer and previous factors)
Key events
Formation of Earth (4.6 billion years ago)
First life (prokaryotic bacteria, 3.5 billion years ago)
Photosynthesis evolves (2.5 billion years ago)
Oxygen revolution (2.4 billion years ago)
First multicellular organisms (600 million years ago)
First land plants and animals (500 million years ago)
First mammals and dinosaurs (230 million years ago)
First humans (200,000 years ago)
Evolution of Photosynthesis
Mutation led to photosynthesis
First time that an organism used sunlight to generate its own food and energy source
Waste was oxygen, a toxic element to much of primal life
Surviving creatures evolved to use oxygen as fuel, leading to more rapid evolution, leading to single-cell organisms developing into multicell organisms
Oxygen reacted with the greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere, cooling the planet (snowball Earth) and then mellowed out to a good temperature
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants and other autotrophs are able to convert solar energy into chemical energy
The first organisms to evolve the ability to do photosynthesis were bacteria (cyanobacteria)
One of the waste products is oxygen, changing the composition of Earth’s atmosphere
Organisms that can exist in the presence of oxygen are called aerobes while those that cannot are anaerobes
The Rate of Speciation
Speciation is the process through which new species form through evolution
The rate is very inconsistent over the planet’s history
Gradual vs. Punctuated Equilibrium

The primary influencing factor on changes in speciation rate is environmental conditions
Under some conditions, selection occurs quickly or radically
ie: A species of snails living with the same basic form for thousands of years, their fossils would appear similar for a long time. When a change in the environment occurs, such as a drop in the water level, a small number are separated, creating two populations. Because the gene pool quickly became so small, any variation that helps with survival in new conditions will become predominant.