CHEM 4TH SEMESTER
STAGE 1
Chemistry: the study of the structure of atoms and the transformation of matter + chem reactions.
Metabolism: collection of biochemical reactions.
Biochemistry: focuses on reactions and processes within compounds.
Molecules that compose living organisms: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur (CHONPS)
- Structural biochem: structure of molecules as well as functions.
- Metabolic biochem: transformations and chem reactions (regulation)
- Molecular bio or genetics: processes of molecules involved in storage and transmission of genetic info.
Inorganic molecules: water is the most abundant, molecules not consisted of carbon.
Organic molecules: molecules composed of CHONPS, may contain metals and non-metals.
Hydrocarbons: single covalent bonds with hydrogen atoms.
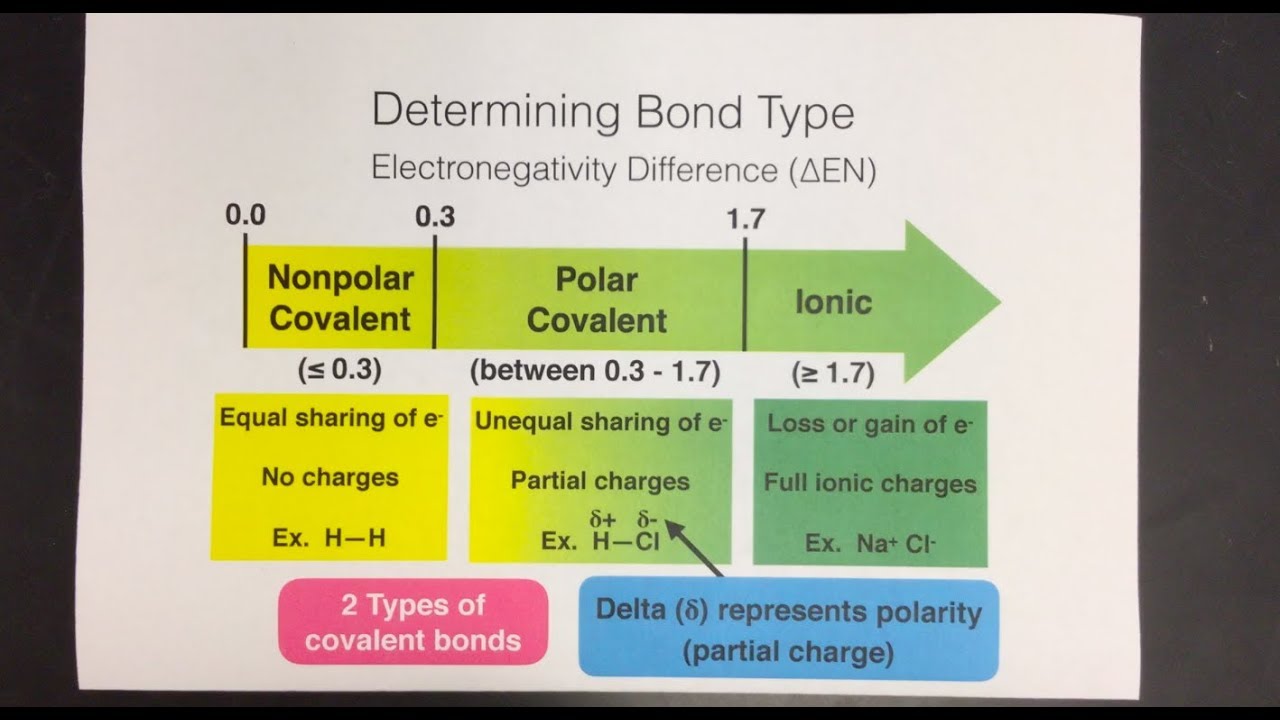
Ionic bond: when atoms either ACCEPT or DONATE electrons in outer orbitals, for stability. IONIC: metal + non-metal.
Covalent bond: when atoms SHARE electrons in outer shell fopr stability, most common bc they are stronger than ionic bonds. COVALENT: non-metals.
Glycosidic bond: when a carbon from a monosaccharide connects to another carbon atom through an OXYGEN atom.
Hydrolysis: chem reaction involving water molecule and another macromolecule.
Oligosaccharide: several monosaccharides linked together.
Polysaccharides: when the number of linked monosaccharides exceeds 11.
Galactose: monosaccharide, sugar, combines with glucose for lactose.
Fructose: monosaccharide, sugar found in fruits and veggies.
Sucrose: disaccharide, main sweetener for humans.
Lactose: disaccharide, secreted by mammals to feed off-springs.
Maltose: disaccharide, from barley fermentation, present in beer production.
Polysaccharides: cellulose and starch.
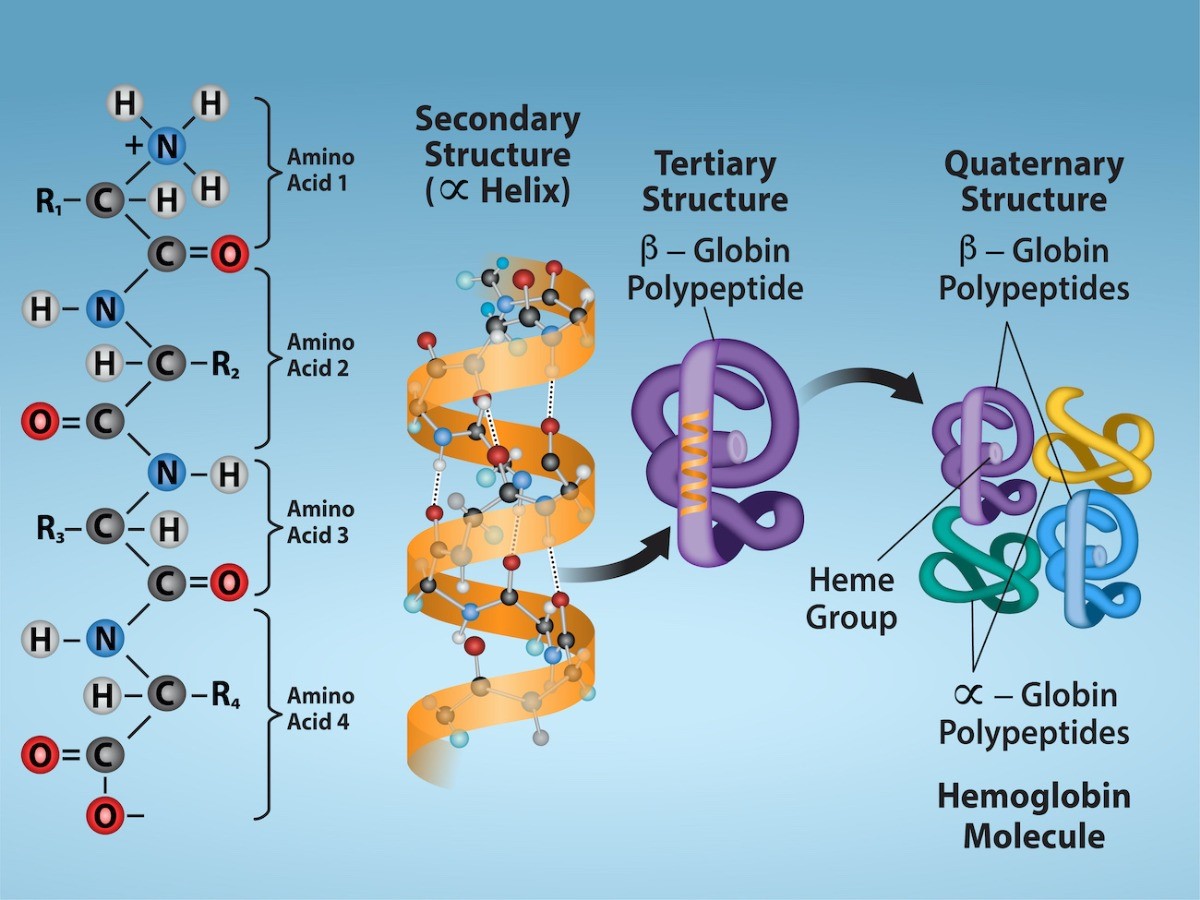
Peptide bond: type of covalent bond formed between an amino acid’s carbon atom and an amino acid’s nitrogen atom.
Enkephalins: polypeptide related to reducing pain sensitivity.
Bradykinin: peptide hormone related to the CAUSE of pain.
Aspartame: synthetic sweetener 200 times sweeter than sugar.
PROTEINS
Type of macromolecule formed by units of amino acids linked bhy peptide bonds.
They are divided into simple and conjugated.
SIMPLE: when hydrolyzed, yield amino acids (fibrous proteins like hair and nails and globular proteins like insulin).
CONJUGATED: when hydrolyzed not only yield amino acids but also organic and inorganic compounds.
Functions of proteins are: structural, bioctalysts, reserve of nutritional materials, transport vehicle, protective and regulatory.
ENZYMES
Enzymes are catalysts used to accelerate metabolic processes, most enzymes are globular proteins, crucial for changing rate of chem reactions.
In catalyzed reactions, enzymes attach to substrates, which facilitate conversion into specific products.
Enzyme catalyzed reactions: when an enzyme and a substrate come together, this complex is essential for facilitating reactions.
Enzyme action models: proposed by Emil Fischer in 1890, suggest active site of enzyme has a rigid shape like a lock and the substrate is like a key that fits into this lock.
Induced adjustment: by Koshland and Neet, suggests that the active site can adapt to the shape of the substrate.
SUGARS (CARBS)
Most abundant biomolecules in nature, produced through photosynthesis, sugars serve as fundamental units of carbohydrates, general formula is Cn(H2O)n. Their roles are the following:
Energetics
Reserve
Support
LIPIDS
From geek word “lipas” (fat), biomolecules soluble in organic solvents but insoluble in water, crucial in cell membranes, fat-soluble vitamins and steroid hormones (include waxes, fats, oils, phospholipids, etc.)
Saturated: when there are only SINGLE bonds between carbon atoms in the chain (chains in this class are straight), they can have an unlimited number of hydrogen atoms.
Unsaturated: when the chains between carbon atoms are DOUBLE, when a fatty acid has 1 double bond it is monounsaturated, when it has multiple double bonds it is called polyunsaturated.
Omega fatty acids - salmon and flaxseed.
Waxes - in animals skin
Phospholipids - essential in plasma membranes, protects cell.
Steroids - hydrophobic and insoluble in water
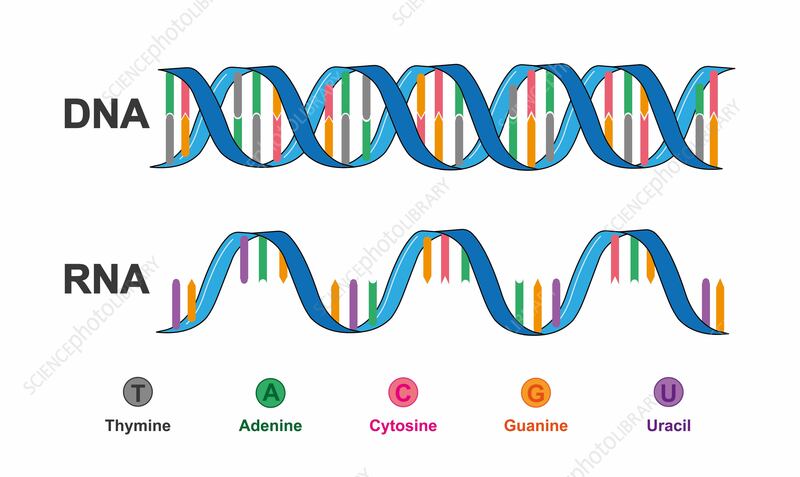
NUCLEIC ACIDS
Nucleotides are chemical units that combine to form nucleic acids, most common nucleic acids are DNA and RNA
Each nucleotide is made up of a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group and a five-carbon sugar.
VITAMINS: essential organic compounds necessary for growth and health obtained through diet.
NON-VITAMINS: essential for chemical processes in enzymes like blood clotting and metabolism.
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS IN INDUSTRY
The production of soap involves a chemical reaction: saponification, it happens between a base and a fatty.
Detergents are composed of linear alkyl sulfates.
The first antibiotic, penicillin, was derived from a fungus called Penicillium Notatum.
Agrochemicals: pesticides and fertilizers.
Polymers are made up of monomers, used in a wide variety in industry.
Plastic is used the most in packaging, the least in agriculture.
 Knowt
Knowt