Energy, Work and Power
- Energy: amount of work and its measured in Joules (J)
- ^^Conservation of energy:^^ energy cannot be created or destroyed, when work is done, energy is changed from one form to another.
- Energy can be stored
- A book on a shelf has g.p.e , if it falls of the shelf it will have k.e
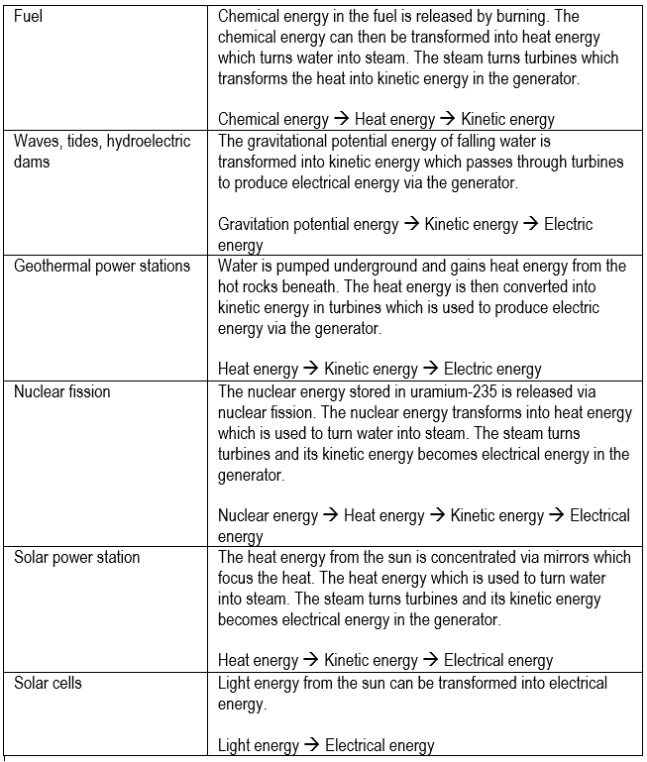
| Energy type | What it is |
|---|---|
| Kinetic | Due to motion |
| Gravitational | From potential to fall |
| Chemical | In chemical bonds |
| Strain | Compress/stretch |
| Nuclear | Atoms rearranged/split |
| Internal | Motion of molecules |
| Electrical | Carried by electrons |
| Light | Carried in light waves |
| Sound | Carried in sound waves |

Due to the processes through which energy transfers take place not being 100% efficient
energy is lost to the surrounding and therefore energy gets more spread out (dissipated)
^^Efficiency:^^ ^^how much useful work is done with energy supplied^^

Energy Resources
^^Renewable sources:^^ Energy sources that are not exhaustible/ Infinite
^^Non-renewable sources:^^ Energy sources that are exhaustible/ finite
Work and Power
^^Work^^: Work is done whenever a force acts on an object that moves (or is moving) in the direction of the force
- The greater the force, the greater the work
- The larger the distance moved, the larger the work

Whenever any work is done, energy gets transferred (mechanically) from one form to another
The amount of energy transferred (in joules) is equal to the work done (also in joules)
- ^^energy transferred (J) = work done (J)^^
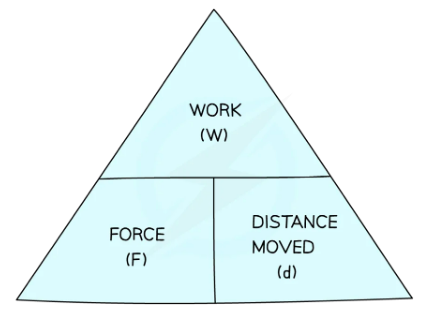
Work done = Force x Distance travelled
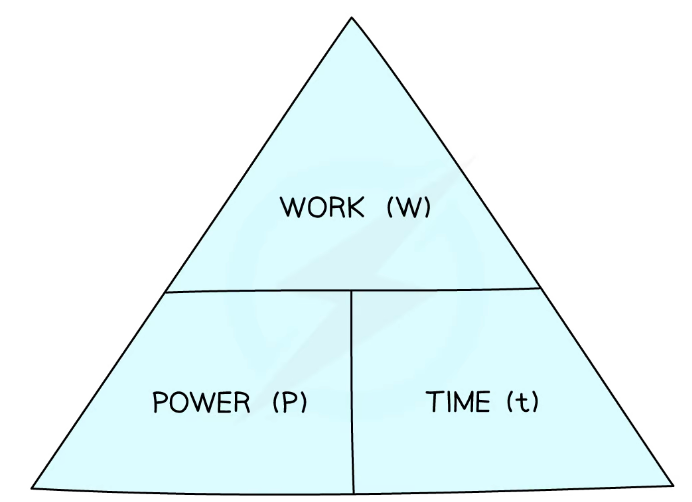
^^Power:^^ is the rate at which a machine transfers energy
The greater the rate at which energy is transferred, the greater the power
- Because work done is equal to energy transferred, the power is also equal to the rate of doing work
Power = Energy/time