Properties and mechanisms of carbonyl compounds
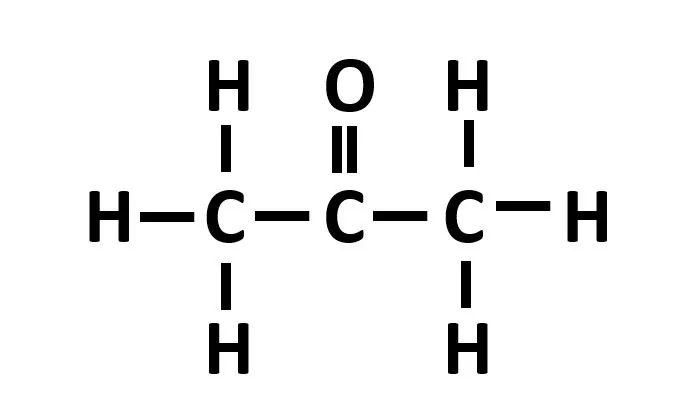
All carbonyls contain a polar C = O (O is deltanegative, C is deltapositive)
Resulting in polar molecules, dipole-dipole interaction
No hydrogen bonds
Lower boiling points than their alcohol counterparts
Higher boiling points than there alkane counterparts
Small carbonyls are water soluble as they can form hydrogen bonds with water
As chain length increases, solubility decreases, as the chain is non-polar and won’t be able to interact with the water and the longer it gets, the more of an effect it has on solubility
Chemical reactions
As the C = O is unsaturated, reactions tend to be additions
Nucleophiles are attracted to the deltapositive carbon of C = O
Reaction with HCN:

The C≡N in the final product (hydroxynitrile) is the nitrile group - useful in synthesis, extends carbon chain by 1
Most hydroxynitriles are optically active
HCN is made in situ. Start with NaCN/KCN plus dilute hydrochloric acid. As soon as HCN is formed, it reactions with the carbonyl
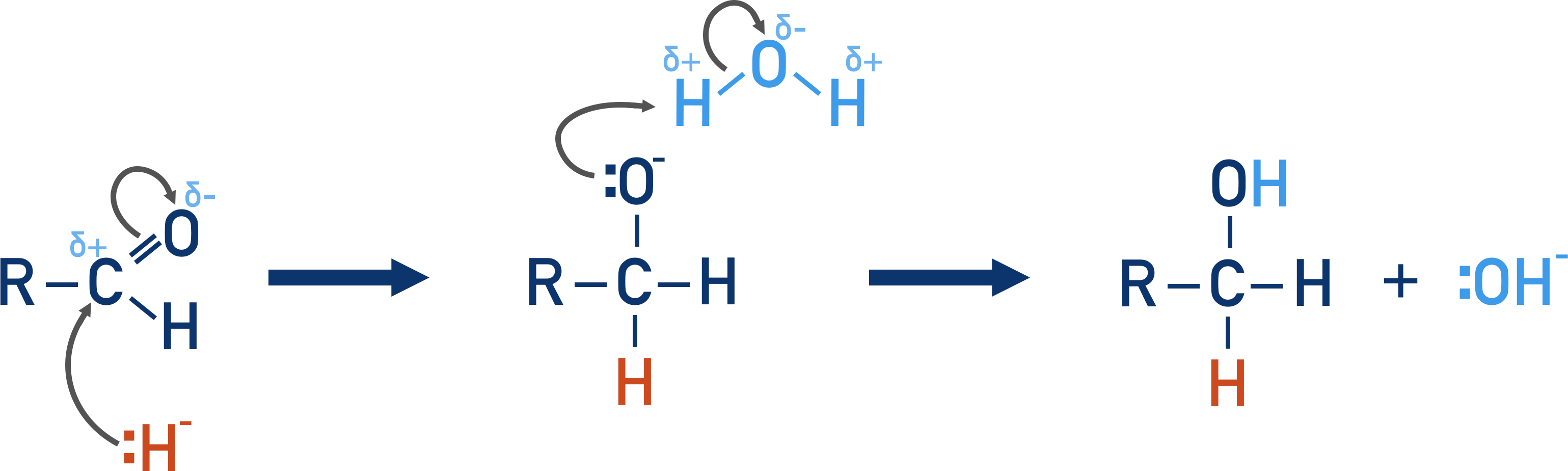
Reduction:
Reagents: NaBH4 (sodium tetrahydridoborate). Provides the H:- nucleophile
Mild reducing agent, only reduces carbonyls
Conditions: Warm, in water