Tropical Design
%%Tropical Design%%
Is a passively designed, climate- responsive architecture for hot and humid locations. It's all about achieving @@thermal comfort@@. through the use of passive elements.
What will this place require us to do?
Permit us to do?
Help us to do?
“Wendell Berry 1992”
%%Site Considerations%%
Maximize beneficial use of the sun while minimizing it's impact to the environment.
Design Considerations 🏠
- Orientation
- Building design
- Building envelope
- Fenestration
- Building materials
Use of High-pitched roofs so rain gets off fast as hot air rises and escapes to keep you cool. Retractable doors and windows to raise the air flow to the ventilation s and allow you open the house on the great lazy days. Use of outdoor gardens. Simple details and finishes compatible with the environment.
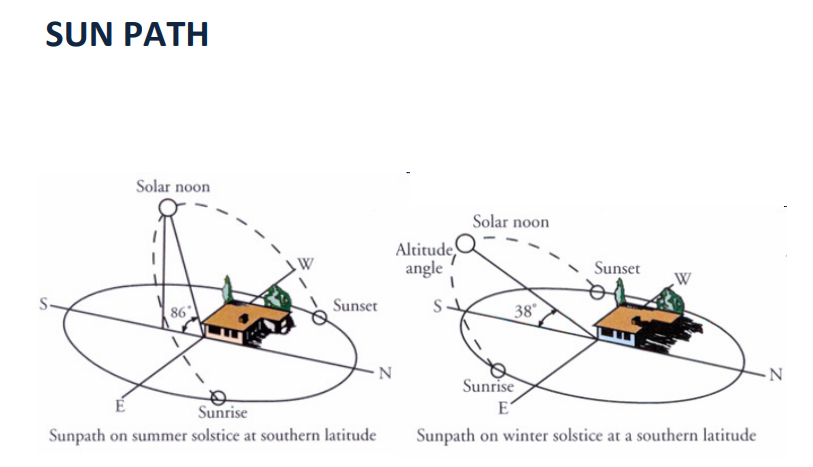
%%Sun Path ☀%%
Refers to the apparent significant seasonal & hourly positional changes of the sun as the earth rotates and orbits around the sun. Relative position of the sun is a major factor in the heat gain of buildings & in the performance of solar energy system. Accurate location and specific knowledge of sun path & climatic condition is essential for economic decisions about solar collector area, orientation, landscaping, summer sharing and the cost-effective use of solar trackers.
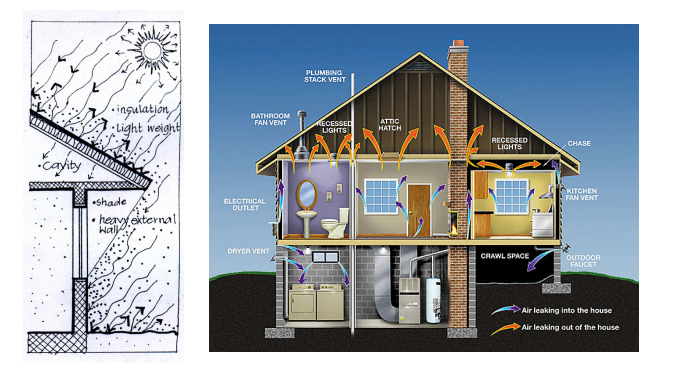
%%Passive Cooling%%
A cooling system using a buildings design and construction to maintain a comfortable temperature within a building. This is essential for low-energy design achieved by the building’s organization rather than electro-mechanical means.
%%Building Orientation%%
In tropical countries such as Philippines, it is best to place service areas in West and East for direct sunlight.
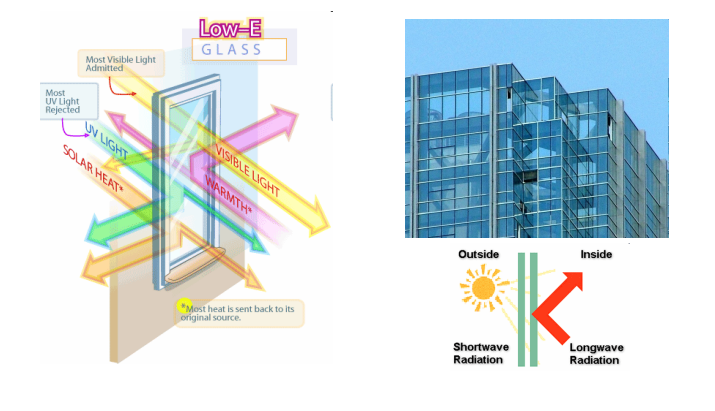
%%Facade Design%%
Use of double layered facade to minimize heat gain.

Use of low-emissivity glass
Use of insulation
%%FENESTRATION%%
Is the arrangement of openings of building envelope. This includes glazing, windows, curtain walls, slope glazing, and exterior doors.