Photosynthesis + Respiration - 91%
Photosynthesis Process
Photosynthesis is the process in which a plants converts carbon dioxide and water, with the help of light energy, to create glucose and oxygen. Plants don’t have a way of intaking energy, therefore the process of photosynthesis is used to create glucose, practically as a ‘food source’ for the plant. Photosynthesis is also helpful for the environment, due to the fact it releases oxygen. Rather than requiring oxygen like many other living organisms, plant cells have it as a waste product.
The chemical formula for photosynthesis is as follows:
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Or in word form,
Carbon Dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen
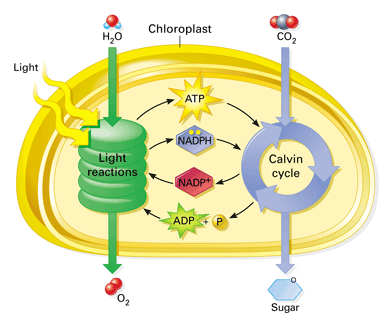
Water and Oxygen are the reactants and products used in light reactions, where the Carbon Dioxide and Water are used in Calvin Cycle
The Chloroplast
Photosynthesis takes place in the plant cell, but typically the chloroplast. The chloroplast is the part of the cell. This is ‘the site’ of photosynthesis, and where the process occurs.
The chloroplast contains compartments known as thylakoids, and a stack of them as seen in the picture is known as granum. This is where the first stage of photosynthesis occurs - Light-Dependent Reactions. The green pigment know as chlorophyll is situated within the ‘pancake-shaped’ structure, which allows for light to be absorbed. The beige colored liquid within the chloroplast is called the stroma, a solution similar to the cytoplasm. In the stroma, the second stage of photosynthesis occurs, the Calvin Cycle.
Stages of Photosynthesis
As mentioned there are two stages of photosynthesis, Light Dependent Reaction and the Calvin Cycle. Both of these process work together and harmoniously to complete photosynthesis.
Light Dependent Reaction
The Light Dependent reaction is the first step of the photosynthesis process and occurs in the thylakoid membrane. The use of this is simple to convert light energy from the sun, into chemical energy within the cell. Water and Sunlight are absorbed by the thylakoid membrane. The water is split into two separate things, an O2 Molecule, and H+ ion. The oxygen molecule, as seen in the equation, is a product, and in fact a ‘waste product’ of the light reactions. Sunlight energy is converted to electrons to carry into the next stage The produce of these reaction also includes two key things - ATP and NADPH. These two are known as energy carriers, which help to carriers the electrons through the chloroplast. ATP and NADPH are charged (fueled) by the positive hydrogen ions from the water splitting. These electrons enter the Calvin Cycle.
Calvin Cycle
The Calvin cycle is the final process in the food-making process (to provide energy to the plant cells) The Calvin cycle involves the conversion of ATP, NADPH, and Carbon Dioxide, into Glucose. Carbon dioxide is input into the chloroplast through the stomata, a small pore on the outside of leaves. Carbon dioxide comes in a relation inorganic, unusable form, but before the reactions occur it is transformed into a more usable, natural form of CO2. Then the energy and the carbon is used to transform into glucose. They use the charge of the ATP given by the hydrogen ions in the first stage, meaning that the ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate) must return back to the first stage to recharge itself and repeat the process.
Cellular Respiration Process
Cellular Respiration is the process in which a cell respire. Respiration occurs in most eukaryotic cells. In the respiration process, glucose and oxygen, is converted into water, carbon dioxide and energy, in the form of ATP.
ATP
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) is like a battery, and is the basic unit of energy on a cellular level. ATP is a charged molecule, and has strong phosphate bonds. When these strong bonds break, lots of energy is produced and used. One ATP is used, ADP is formed, with only two phosphate bonds. In the ATP synthase, an enzyme in the ETC, recharges it, adding another phosphate to the ‘flat battery’.
Chemical Formula for Cellular Respiration
The chemical formula for photosynthesis is as follows:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ~36ATP
Or in word form,
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP
Three stages of Cellular Respiration
The three stages in photosynthesis work together harmoniously together. They include Glycolysis, the Krebs Cycle, and the Electron Transport chain. Each of this have a specific function which helps to create to products.
Where does cellular respiration occur?
The cellular respiration works in the cell. The first stage, glycolysis, occurs in the cytoplasm, whereas the other two process happen in the mitochondria. The mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell, and is where the ATP making process takes place.
Aerobic Respiration vs Anaerobic Respiration
Aerobic Respiration is the processes in the cellular level which require oxygen. These include the Krebs cycle, and ETC.
Anaerobic Respiration is when oxygen is not required. This happens in glycolysis. Glycolysis does not need oxygen to undertaker is processes. In plant cells, anaerobic respiration creates lactic acid, whereas in plants it crates alcohol.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the process where glucose is split into two pyruvate molecules. Carbon is 6 carbons, and is split into the two pyruvate molecule with 3 carbons each. This occurs in the cytoplasm, and also offsets ATP and NADH, the carrier co-enzyme. Glycolysis is anaerobic, meaning that no oxygen is required. It produces two ATP, which the body could last on, but would be highly weak.
Krebs Cycle
In the Krebs Cycle, an aerobic process in the cristae within the mitochondria, pyruvate enzymes attach with Acetyl COA, which helps to break it down into 2 ATP offset, NADH and FADH, and Carbon Dioxide as a waste product. The NADH and FADH are transported into the ETC
ETC
In the Electron Transport Chain within the Mitochondrial Matrix is where O2, and the Hydrogen molecules from FADH and NADH, create H2O, and release a lot of ATP (around 34). The ATP synthase is also found in the process, so the ADP can be changed into ATP.