biology 1
cell structure
cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently
animal
eukaryotic
cell membrane → control which substances pass in and out of the cell
nucleus → contains DNA
cytoplasm → where chemical reactions take place
mitochondria → provide cells with energy
ribosomes → site of protein synthesis
plant
eukaryotic
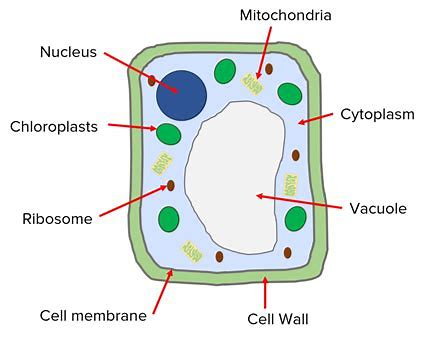
cell wall → support and structure
vacuole (permanent) → contains cell sap
chloroplasts → where photosynthesis happens (contains chlorophyll to absorb light energy for photosynthesis)
bacteria
prokaryotic
single-cellular
don’t have a nucleus instead have strands of DNA (nucleiod)
don’t have chloroplasts or chlorophyll
some have plasmids → extra small loops of DNA
flagella → tails to propel the bacteria forwards
diffusion
DIFFUSION IS A PASSIVE PROCESS
→ diffusion is the net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
diffusion can occur in gases and liquids
diffusion can also take place THROUGH partially permeable membranes (usually only very small molecules can diffuse through)
factors affecting rate of diffusion (increasing these factors increases rate of diffusion)
concentration gradient
temperature
surface area
osmosis
osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules
→ it is defined as the net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration
→ water concentration means the amount of water as compared to other molecules, called ‘solutes’ that are dissolved in the water
IT IS NOT ABOUT VOLUME OF WATER BUT ABOUT THE RATIO OF WATER TO SOLUTES
inside a cell we have lots of water and solute particles
outside we have almost pure water
therefore water particles will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside of the cell
active transport
→ defined as the net movement of molecules from a lower concentration gradient to a higher concentration requiring energy from cellular respiration
→ therefore it requires energy from the cell
active transport always takes place across a cell membrane and it also requires special proteins
IN ROOT HAIR CELLS (which have large surface area due to their shape)
root hair cells need to absorb water (by osmosis) and mineral ions (by active transport because it needs to go against the concentration gradient)
root hair cells need lots of mitochondria
balanced diet
we need:
carbohydrates (bread, pasta) → provide us with energy
lipids (oily fish, avocados, dairy → provide longer term energy to store as fat which also keeps us warm
proteins (legumes, meat and fish) → need them to grow
vitamins (fruit and vegetables, sunlight) → helps us absorb calcium
mineral ions (calcium, iron) → needed for bones and haemoglobin
fibre (whole bread, brown rice) → helps food move through our intestines more easily
water (fruit, water) → chemical reactions, most of our body is made of water
biological molecules
biological molecules are molecules found in living organisms and are produced by cells
nutrients are substances that are needed for growth, repair and metabolism
carbs made of C, H, O
monomers like fructose and glucose can bind together to form polymers like starch
protein is made of amino acids
C, H, O, N
lipids are NOT polymers
fat is a lipid which is solid at room temperature
made of C, H, O
enzymes
enzymes are biological catalysts
→ catalyst is a substance which increases the speed of a reaction without being changed in the process
enzymes have an active site which is complementary to the shape of the substrate (reactant)
it has to fit
LOCK AND KEY MODEL (LESS REALISTIC)
we thought a substrate had to be the exact right shape to fit into the active site
INDUCED FIT
we now know the enzyme changes shape a little bit to fit the substrate
temperature - originally enzyme activity increases with temperature because of energy but once we reach 37 degrees some of the bonds in the enzyme begin to break so it starts to change shape or ‘denature’
at first it will not fit as well and rate of reaction will be slower
eventually it will no longer be able to bind to the substrate at all (the damage is also permanent)
optimum temp - the temp where the rate of reaction is highest
pH - same as temperature, most have an optimum temp of 7
digestive enzymes:
→ proteins carbs and lipids are too big to be digested so they need to be broken down by enzymes
carbs → starch then amylase makes it into maltose then maltase breaks it down into glucose
proteins → protease breaks it down into amino acids
lipids → lipase breaks them down into glycerol and fatty acids
bile also helps in the breakdown of lipids because it emulsifies them which increases their surface area
all of the enzymes are made in the pancreas and small intestine
amylase is made in salivary gland
protease made in stomach
microscopy
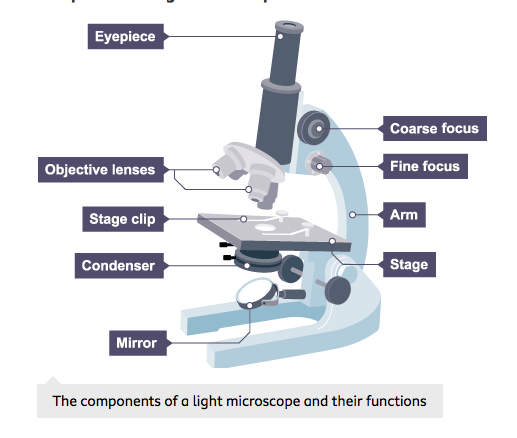
first objective lens - 4x
second - 10x
eye piece lens - 10x
third - 40x
image refers to the image we see when we look down the microscope
real refers to the actual onion cells
magnification means how many times larger the image is than the actual
→ mag = image size/object size
resolution means the shortest distance between two points on an object that can still be distinguished as two separate entities
light | electron |
easy to use | expensive |
cheap | hard to use |
lower resolution (limited to 0.2 micrometres) | higher resolution (0.1 nanometres) which is 2000x more than light |
a cell is 1 - 100 micrometres