UNIT 5- Fiscal & Monetary Combinations
Review of Fiscal & Monetary Policy
Long Run Effects of Policies:
have to take a look at interest rates
high interest rates aren’t good for investment
low interest rates promote investment
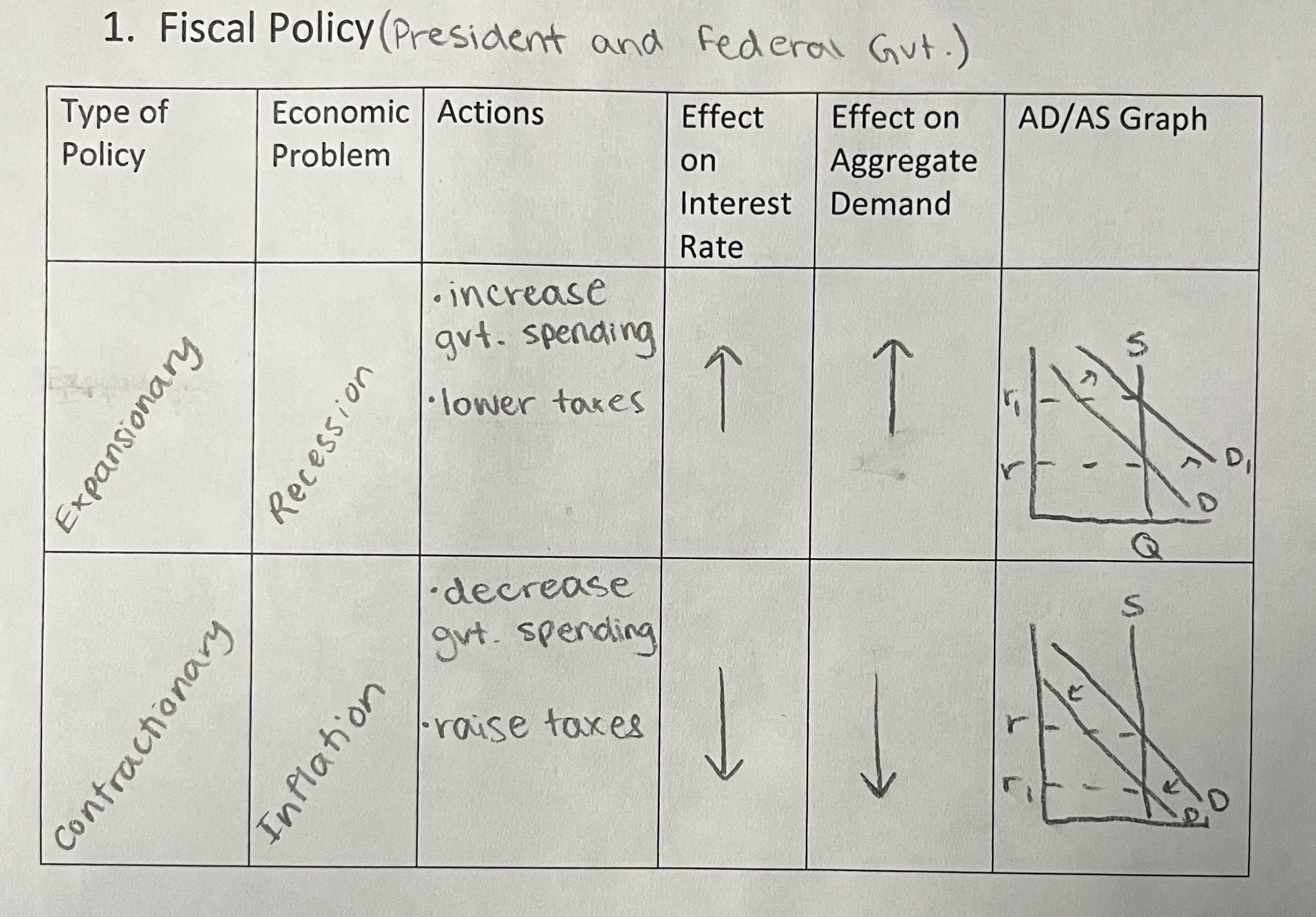
Effects of Expansionary Fiscal Policy
Deficit Spending
government spending is greater than tax revenue
government must borrow money to finance the deficit
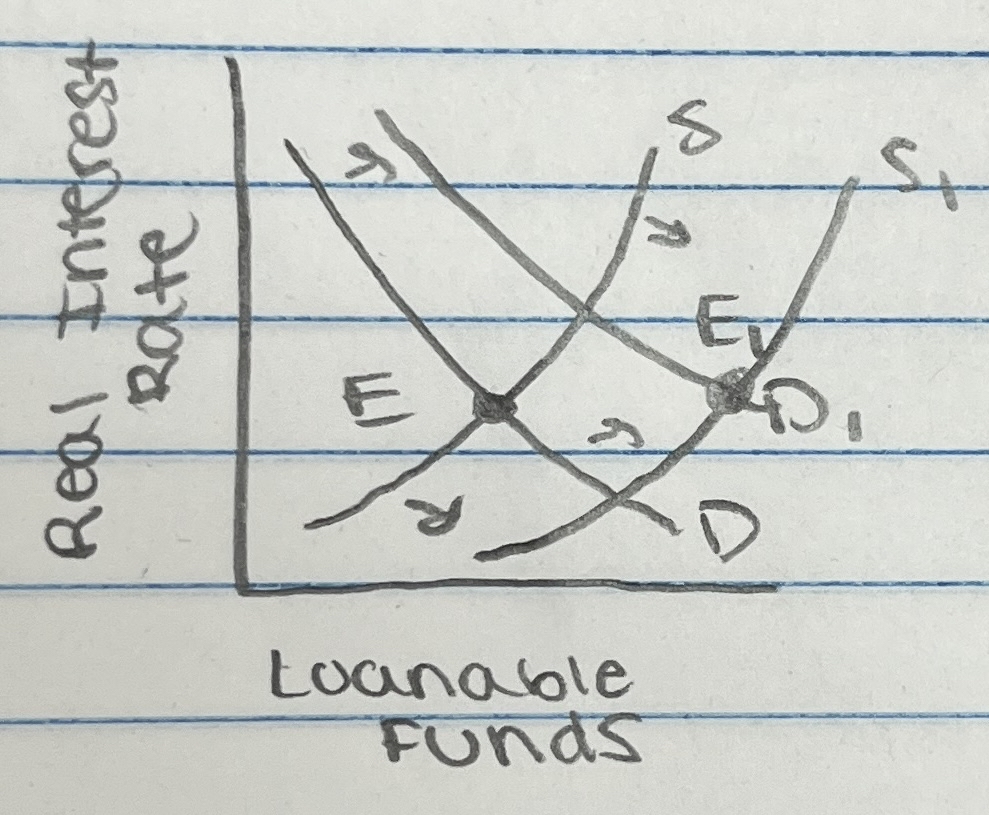
government issues bonds → supply of bonds increases which decreases the price of bonds and increases interest rates
Crowding Out
the budget deficit causes interest rates to rise, which hurts private investment
private investment gets crowded out by government borrowing
hurts the economy in the long run
reduces effectiveness of an expansionary fiscal policy
aggregate demand will increase, but not by as much as you would want it due to high interest rates
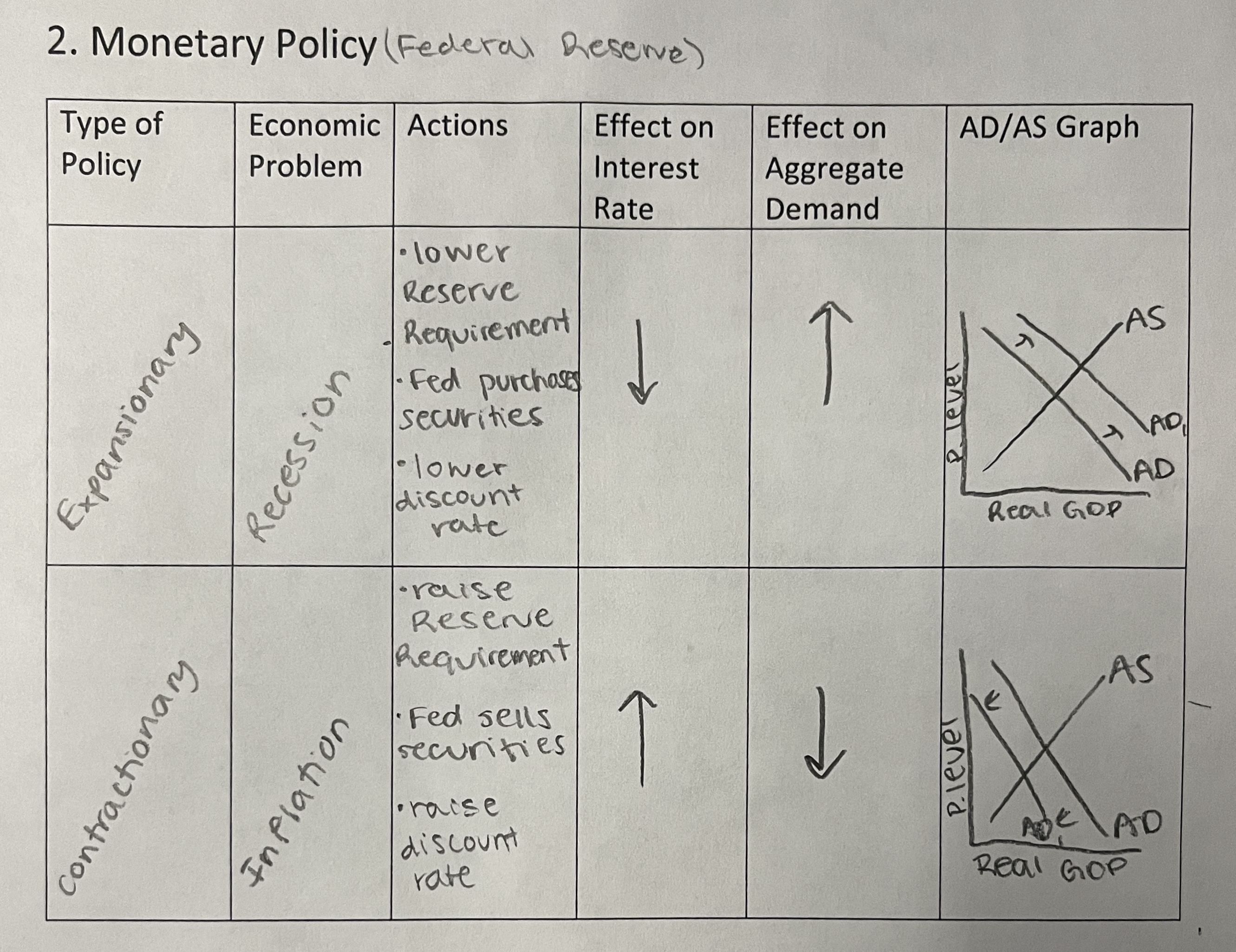
Monetizing the Deficit
Fed will increase money supply to keep interest rates from rising
Trade Off Between Inflation and Unemployment
Philips Curve - a graph relating to the rate of inflation to the unemployment rate
Short Run
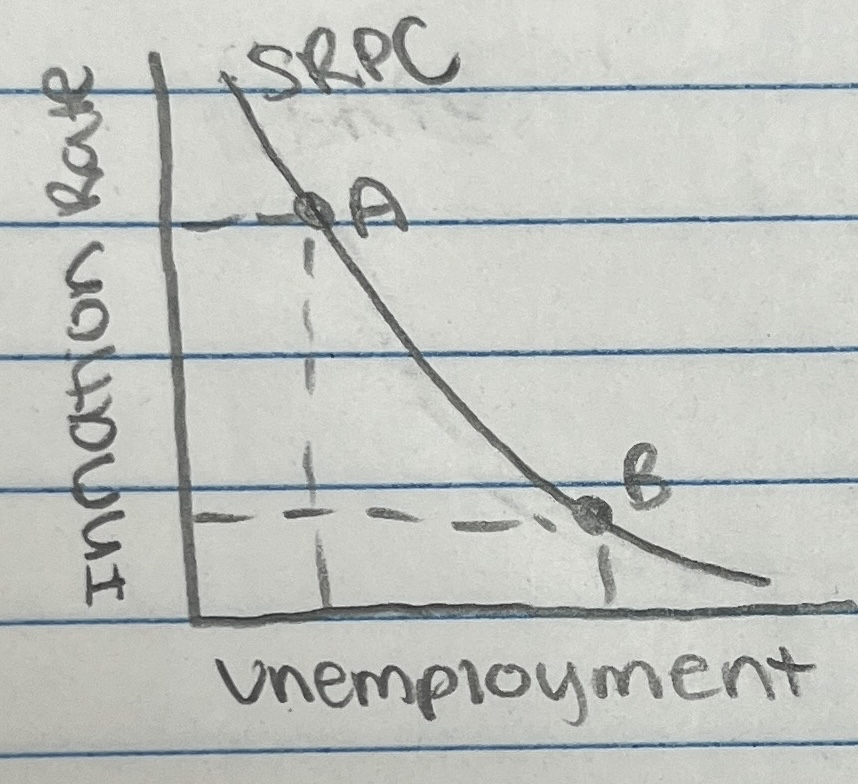
A = high inflation, low unemployment
B = high unemployment, low inflation
short run Philips Curve works mostly when changes come from the demand side
demand-pull inflation
when changes come from the demand side you move along an existing short-run Philips Curve
Shifts in short-run Philips Curve:
cost-push inflation → shifts SRPC to the right
inflationary expectations → if we expect higher prices, we increase our demand today, which shifts SRPC to right
when AS decreases → SRPC shifts right
when AS increases → SRPC shifts left
Long Run Philips Curve

vertical at full employment level
Economic Growth
An increase in the productive capacity of the economy
Measured as a percentage change in Real GDP or per capita Real GDP
per capita = per person
Growth is important to improving our state of living
Evolving technology is part of growth
Rule of 70/72 = divide the rate of growth into 70 or 72 → gives you the number of years it will take the economy to double its capacity
shifts to right → economic growth
Factors to Economic Growth:
Productivity - key to economic growth
amount of output per unit of input
Increase in real capital
interest rates go up → less real capital
interest rates go down → more real capital
Improvement in worker skills (human capital)
education, training, etc.
Improvement in technology
Natural resources
abundance of natural resources increases growth
Economic system to provide incentives to work, save, and invest
Differences between Potential GDP and Actual GDP
Potential GDP is real GDP that the economy would produce if all of its resources were fully employed
Actual GDP is real GDP, that doesn’t necessarily mean you’re at full employment