AP World History: Unit 4 Notes
Technology
Dar al Islam
medical advances, advances in astronomy, advances in mathematics, preservation of Greco-Roman philosophy and literature
China
gunpowder, magnetic compass, moveable type, paper
Europe
Humanism, Enlightment, guns, The Renaissance, discovery of New World, scientific revolution, printing press
Indian ocean commerce increased as mariners learned monsoon winds
improvements in sails
new ships (chinese junks, Indian/arab [middle east] dhows)
calculating latitude using astrolabes
used Polaris/north star to measure the distance of things
evolving versions of magnetic needle or compass
Chinese used bigger sails to survive storms
Middle East used sails made for rivers
increased jobs for cartographers (got their info from explorers)
lateen (triangle sails) from middle east
compass from china
astronomical charts from china and arabs
caravel sails (europe)
used all of China & Middle East’s inventions
North Atlantic currents are fixed year round, unlike monsoon winds
Gulf of Mexico stream pushes currents back out into the sea
Europeans were motivated by 3G’s: God, gold, glory
increased competition & rivalries between Ottoman Empire and European States
growing merchant class in Europe wanted to increase trade and wealth
desire for easy access to Indian Ocean
wanted to bypass Muslim intermediaries
Missionaries
Henry the Navigator (prince of Portugal) led ventures, didn’t actually travel
taught people how to find their way in the sea
astrolabes, magnetic compass, Jewish cartographers, caravel, cannons for enemy ships
used for measuring the positions of celestial bodies to determine time, location, and other astronomical data
can’t know latitude and longitude at same time, memory was important
Travel
Portuguese very early explorers (Africa & India), didn’t want to go out of sight of land, superstitious thought it led to death
ended up in Calicut, India, founded and made it trade capital
Atlantic ocean unpredictable weather, dangerous
Cape of good hope had many sharks
Vespucci one of the first to realize the Americas weren’t familiar
Named Continents after him (Amerigo)
Cortes important for conquering the Aztec Empire
Pizarro conquered the Incan Empire
Ponce de Leon looking for Fountain of Youth
Magellan first person to travel the world (his expedition)
died in the Philippines before reaching Africa, pickled his body for the rest of the expedition
Reconquista, re-conquering Spain
King Ferdinand & Queen Isabella overthrew the Moors
the Muslim inhabitants of the Iberian Peninsula (modern Spain and Portugal) from North African and Arab descent who ruled much of the area from 711 to 1492 CE.
Columbus convinced Queen Isabella to sell her crown jewels to fund the expeditions
Ships: Nina, Pinta, Santa Maria (flagship, Columbus rode Santa Maria)
Cartographers were important but inaccurate
overestimated Antarctica, added Northwest Passage
sea route connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago.
Trade
Columbian Exchange
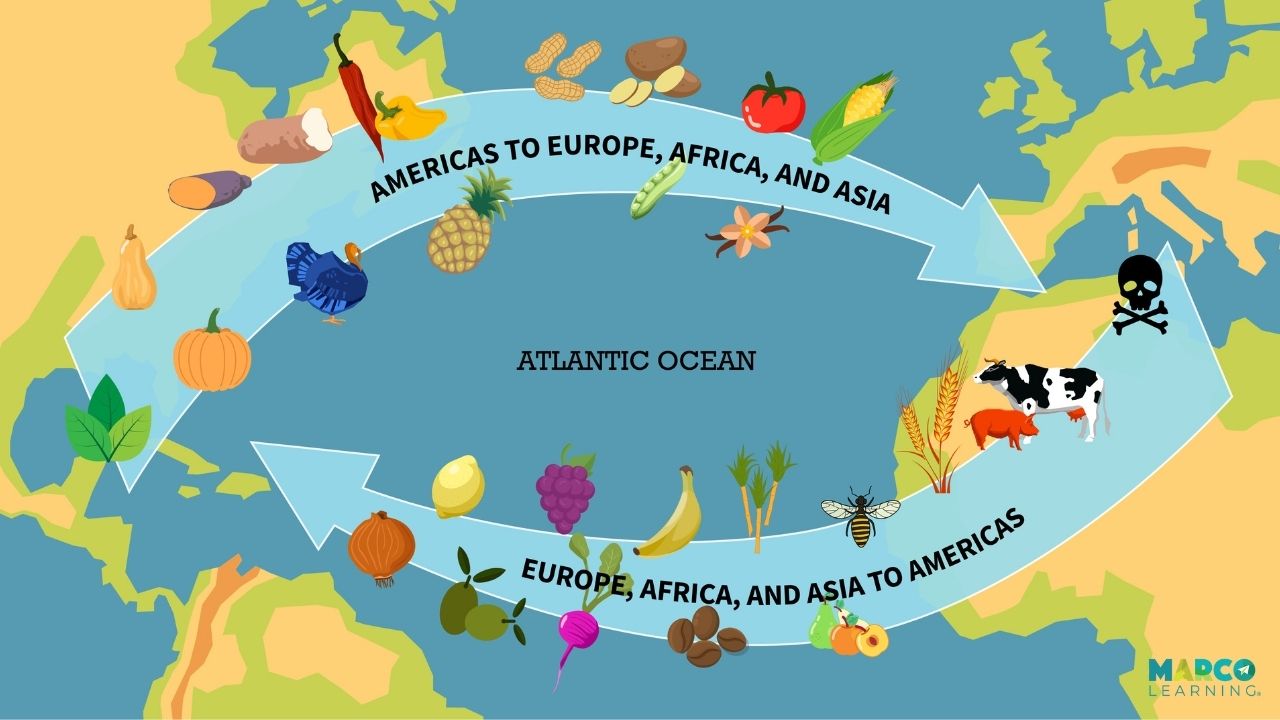
Exchange also involved plants & animals which transformed the landscape and made a European diet possible
Long-term benefits of this Atlantic network were unequally distributed
Western Europeans were the dominant players and reaped the greatest rewards
New information entered Europe contributing to a revolutionary new way of thinking known as the Scientific Revolution.
Wealth of the colonies (precious metals, natural resources, new food crops, slave labor, financial profits, colonial markets) provided foundations (political and economic) for Europe’s Industrial Revolution
Colonies provided an outlet for rapidly growing population of European societies
Changing global balance of power trust the previously marginal Western Europeans into central and commanding roles on the world stage
animals played a big role, horses, cows, sheep, goats, pigs
changed worldwide food supply
horses were most important
used land to grow wanted crops, destroyed natural and native vegetation
Strait of Magellan was smaller, but safer than the Drake Passage
Europeans in Africa
Portuguese explored West African coast; trading guns, textiles, manufactured goods for African gold and slaves
set up trading posts along Africa’s coasts
Had interactions with the Kongo and Benin kingdoms
Vasco de Gama invaded the Swahili states in 1498 (located on the east coast of Africa)
took over with heavily armed ships
Portuguese dominated for 150+ years, as demand grew, other Europeans joined slave trade
European demand for slaves drove African supply
African sellers wanted textiles, metal goods, firearms, gunpowder, tobacco, and alcohol
Part of a worldwide exchange network
1700-1850 peak of the slave trade due to the American plantation economies
Drew slaves from the West and South-Central Africa
Moved into the interior as the slave demand increased
Portuguese Maritime Empire
Promoted maritime developments
Seized Moroccan city of Ceuta (this boosted their confidence)
Conquered uninhabited islands of Madeira and Azores Islands which they colonized
Cultivated sugarcane on their conquered islands
Also explored the West African coast trading guns, textiles, and manufactured goods for African gold and slaves
Caused increase demand for slaves, transporting them to Atlantic islands to work as laborers, but some were household slaves in Europe
Portuguese merchants and sailors dominated the Indian Ocean
Attempted to control all shipping, enforced with superior ships and canons
Overpowered Arabs, Persians, Indians, and southeast Asians
Beginning of European imperialism in Asia
European Empires
Spain focused on Caribbean and then the mainland in the 16th century
Conquered the Mexica (Aztecs) and the Inca
Portugal established colonies along the coast of Brazil
British, French, and Dutch settled eastern coast of North America in the 17th century
Natural resources from these colonies would fund additional expansion and the growth of European colonies
Spanish attacked the English with the Spanish Armada (1588, Elizabeth I)
lost, resulted in bankruptcy
Encomienda (replaced by Hacienda) Systems & social standing
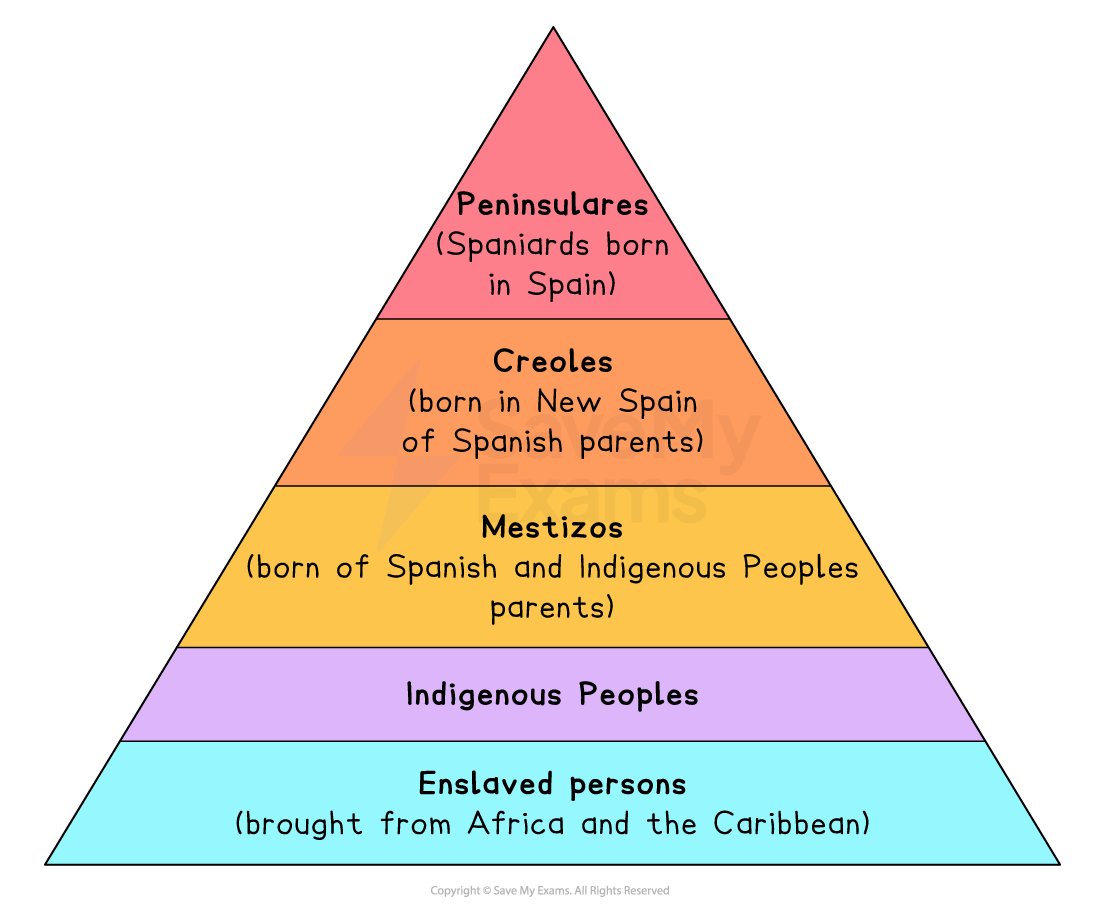
*Mulattos were below mestizos in the social hierarchy, having limited rights and facing discrimination based on their mixed heritage.
British began to rise
Treaty of Tordesillas (1494)
After Columbus’ discovery, political rivalries heated up
Portugal and Spain disagree over control of Americas
Looked to the Church for guidance
Agreed on an imaginary line to divide the lands: Treaty of Tordesillas
Eventually argue about lands around the Pacific
Sugar became a cash crop, desired
must be grown in the tropics
Primary destination for enslaved Africans (80%)
The Great Dying
the arrival of European/Old World diseases into the New World
lack of domesticated animals meant indigenous populations did not have exposure to disease
smallpox, measles, typhus, influenza, malaria, yellow fever
Some areas lost 90% of their population
60-80 million deaths
Indigenous people on Caribbean islands were gone in 50 years, the same was occurring in Dutch and British colonies in North America
Created labor shortage, led to African slave trade
changed slaves, first time in history where slavers targeted specific groups and not prisoners of war
called chattel slavery, dehumanized slaves (cattle)
based largely on plantation agriculture
The Middle Passage
over packed ships with slaves to maximize profits
Male slaves chained together to keep from jumping overboard
special nets to catch any that decided to jump together
cruel punishments, death from disease, bad food, dysentery, refusal to eat, whippings, occasional executions
disrupted African societies
added a substantial African presence to the mix of European and Native American peoples
African diaspora changed race in American societies
loss of millions of young men creating sex ratio imbalance
labor demands on women increased
slave trade brought political unrest
escalated violence
Slowed Africa’s growth
economic stagnation and social disruption
Manioc/cassava and maise from the New World raised calories
European colonization based on Mercantilism*
goal of economic gain to benefit mother country
colonies = raw materials —> mother country
mother country = manufactured goods —> colonies
colonies didn’t profit much, began trading with foreign markets to maximize profit (Black Market)
accomplished by imperialism*
policy of extending a country's power and influence through colonization, use of military force, or other means
goal was to boost exports and minimize imports
New World colonies expanded the mother country’s economy, tilting balance of power towards Europe
Triangular Trade vs Trans-Atlantic Trade
Triangular: Europe, Africa, Americas