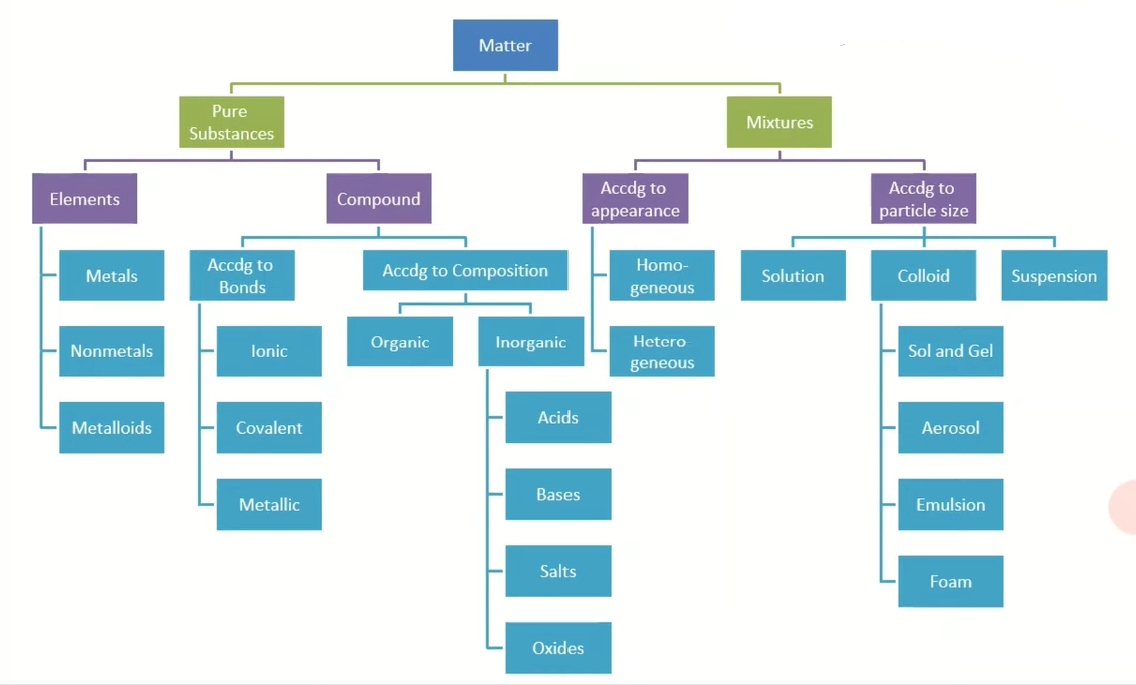
Classification of Matter
Pure Substance
Elements - composed of one type or similar type of atoms (118 elements).
Metals - tend to lose electrons. Good electric conductibility, malleable, shiny and lustrous.
Nonmetals - tend to gain electrons. Lack electric conductibility, malleable, shine and lustrous.
Metalloid - they can behave as metals or non metals.
Noble gases - stable because of full outer electron shell and do not chemically readily react with other elements.
Compound - combination of two or more atoms .
Ionic compound - transferring of an electrons between metals and nonmetals that create charges them.
Covalent compound - sharing of electrons between non metals. Due to electronegativity difference of nonmetals, the strength of attraction can be equal or non-equal.
Polar compound - unequal sharing of electrons. One element has higher EN than the other pulling it to its direction.
Non-polar compound - equal sharing of electron. Both element has equal EN.
“Likes dissolves Likes”
Mixture
Homogenous - uniform and consistent. Composed of solute (higher concentration) and solvent (lower concentration).
Solutions - composed of two or more substance. In the solution, solute (substance dissolved) is evenly distributed in the solvent (substance dissolving).
Heterogenous - non-uniform and inconsistent
Colloid - Particles that floats in a solution because it is too small to dissolve.
Suspension - Particles that settles at the bottom of a solution because it is too big to dissolve.