Reactions of alkenes and alcohols (chemistry only)
Structure and formulae of alkenes
Alkenes are hydrocarbons with a double carbon-carbon bond. The general formula for the homologous series of alkenes is Cn H2n.
The first four members of the homologous series of alkenes are ethene, propene, butene and pentene.
They are formed during cracking. They are used during the formation of polymers and in chemical feedstock.
During complete combustion carbon dioxide and water are produced.
During incomplete combustion results in a smokey yellow flame.
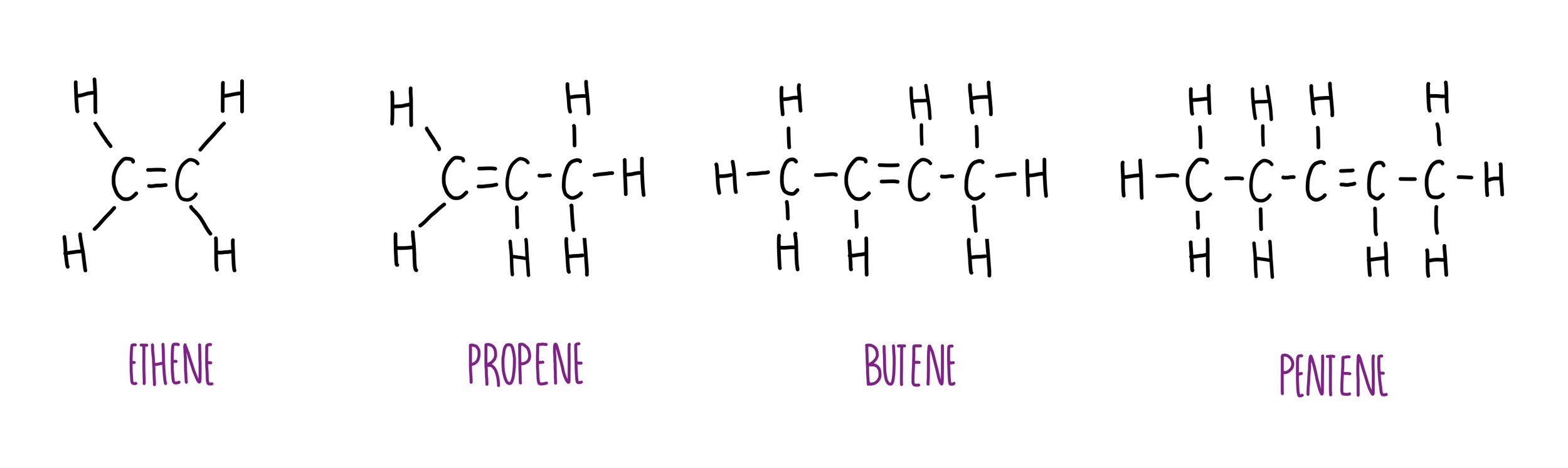
Ethene - C2H4
Propene - C3H6
Butene - C4H8
Pentene - C5H10
Alkenes react with oxygen in combustion reactions in the same way as other hydrocarbons, but they tend to burn in air with smoky flames because of incomplete combustion
Addition with halogens- The two atoms from the halogen molecule are added across the carbon carbon double bond.
Eg:
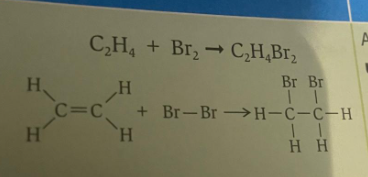
Addition with hydrogen- The two atoms from the hydrogen molecule are added across the carbon carbon double bond to form an alkene
Additon with steam - They react with steam at high temperature and pressure in the presence of a catalyst to form alcohols.
Alcohols
Functional group is OH
First four is Methanol, ethanol, propanol,Butanol
They are formed from the fermentation of sugar which is a warm sealed mixture of yeast and a sugar solution
Ethanol is used to alcohol, The first four alcohols are mixed easily with water so are used as solvents for substances that dont dissolve in water.
Used in perfumes,aftershaves and watches
Short alcohols are very effective fuels and combust easily, burning with a blue flame producing CO2 and water
Reaction with sodium - They react with sodium to release hydrogen. The proudct from this is called a Alcoxide, which if added to water forms a strong alkaline solution
Oxidation - They react with oxidising agents to form carboxylic acids
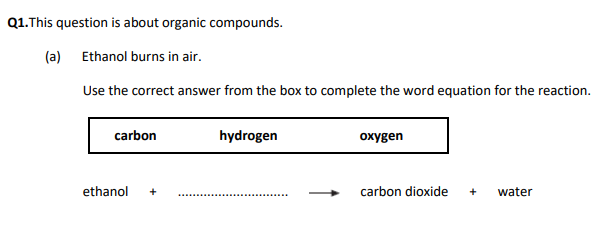
Ethanol + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
Conditions for fermentation:
sugars dissolved in water, and mixed with yeast
an air lock to allow carbon dioxide out, while stopping air getting in
warm temperature, 25-35°C
Carboxylic acids
Functional group is cooh
First four are methanoic acid, ethanoic acid,Propanoic acid and butanoic acid
They are formed from the oxidation of alcohols
Ethanoic acid is used in vinegar
During the reaction with sodium carbonate they react with bases to form salts
They react with alcohols to make water an esters.This requires sulfuric acid as a catalyst
When placed in water they are partially ionised to form Weakly acidic solutions called weak acids.